

Data is now traveling at a faster rate than anticipated. A picture’s file size, measured in KB when the digital revolution first began, has since been upgraded to either MB or GB. When smartphones first emerged, most people only had 1 or 2 gigabytes of storage space. These days, however, users need more than 128 gigabytes. As a result of a rise in consumption, the requirements for data storage space have also increased.
Because modern mobile phones come equipped with a fixed amount of storage that cannot be increased in size. As a result, consumers need a lot of storage space for their pictures, movies, and other types of data. The cloud is now the solution to eliminate all of these problems. It is equipped with some of the most recent architecture, security settings, encryption, and what have you.
It is simple to increase its storage capacity; all that is required is an additional payment, and you can purchase as much storage as you require. When you have cloud storage, there is no need to transfer data from one mobile phone to another. Instead, all you need to do is install the app that the cloud service provider offers, and then you can synchronize all of the data from the cloud to your phone. It is as simple as that.
Since you are storing a lot of data in the cloud, cloud data security is also necessary. Users need to take a few simple steps to ensure their account is secure from unauthorized access.
Ways to Ensure Security for Cloud Data
We have a couple of different ways by which we can ensure that the data in the cloud, as well as the account holding that data, is secure. While strong passwords are important, strong encryption is equally important. Let’s discuss a few methods in detail.
Use of Strong Encryption to Encrypt Sensitive File
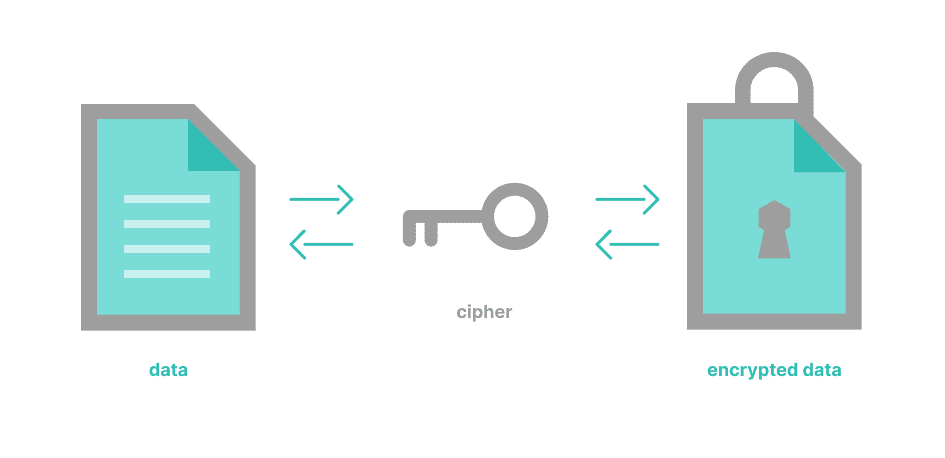
If data transmitted to and from the cloud is not sufficiently encrypted, it can cause security issues if intercepted by a malicious third-party. Therefore, cloud security measures should include the implementation of encryption protocols that protect data while in transit. Encryption, in this context, refers to the process of encoding data using a cryptographic algorithm to render it unreadable and unalterable. Encryption protocols can be used for both inbound and outbound traffic, ensuring that any transmitted data remains secure throughout the cloud journey.
If you are storing particularly sensitive data in the cloud, then it is strongly suggested that you encrypt that data before you upload it to the cloud. This way, even if the data is exposed or stolen, it cannot be read without a key. Protocols like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), RSA, and Diffie-Hellman are all popular methods for encrypting data.
Finally, a comprehensive approach to cloud security should include access control protocols that specify who can access different areas of the system and what they can do with it. These protocols define what activities certain users are permitted to carry out on the system and which resources they have permission to use. This can be managed through authentication measures such as passwords and access tokens and authorization mechanisms such as role-based access control (RBAC).
Use of Strong Password
Strong passwords may seem like a pretty basic way to ensure the security of any kind of infrastructure, whether it’s cloud-based or on-premises, but they are actually very effective.
The key is to make sure that any passwords used are strong, complex, and not easily guessed. To do this, organizations should implement a password policy which dictates the criteria for setting up and managing passwords. This policy should include things like using a combination of upper-case characters, lower-case characters, symbols and numbers when creating new passwords.
It should also include minimum and maximum password length, expiration periods and regular password changes. Along with this policy, organizations should also employ a solution that helps to enforce the policy by ensuring passwords are generated correctly and stored securely.
Use of Two or Multi-Factor Authentication
Two-factor authentication, also known as 2FA, is an additional security measure that can be implemented on top of the traditional login credentials of a username and password. This type of authentication is also referred to as “multi-factor authentication,” because it uses two different steps in order to verify the user’s identity.
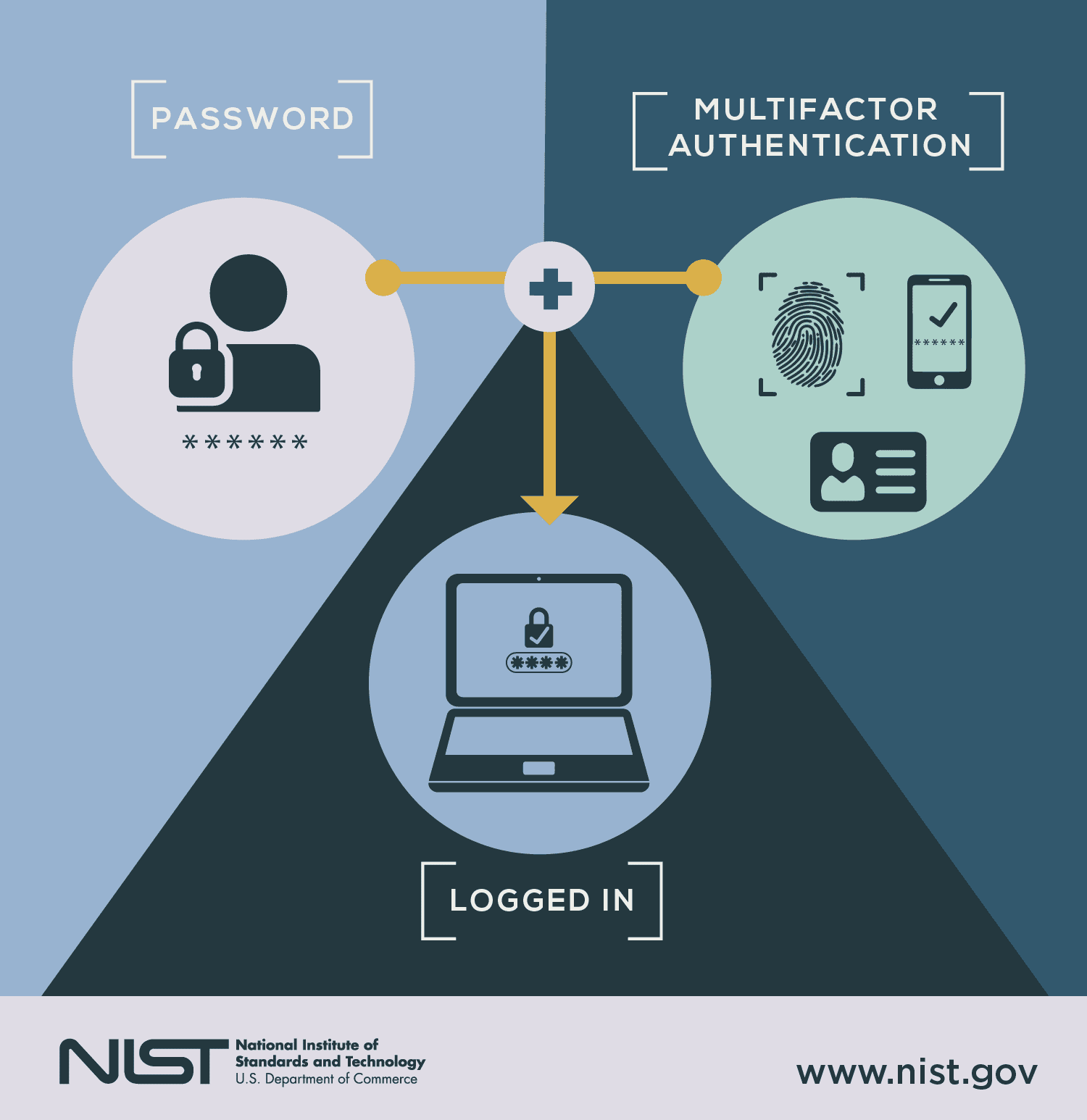
The first step is typically a username and password combination, while the second step could be a code sent via text message or email, a fingerprint scan on a mobile device, or a security key. This second step is designed to prevent unauthorized access, even if an attacker has acquired the user’s login credentials. By using two steps to verify a user’s identity, 2FA adds an extra layer of protection that keeps malicious actors from gaining access to sensitive data and systems.
The main benefit of 2FA is that it adds an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access. Even if someone has your username and password, they would still need the second factor in order to log in. This can help prevent malicious actors from gaining access to your data and systems. Additionally, 2FA can help to protect against phishing attacks, which often involve hackers sending fake emails in an attempt to acquire someone’s credentials.
Conclusion
Two-factor authentication and strong passwords are two essential measures that can be taken to improve the security of cloud-based systems. By using these measures, organizations can help protect their data from unauthorized access and prevent phishing attacks. Additionally, organizations should also implement encryption protocols to ensure that any data stored in the cloud is secure and confidential. By taking these steps, organizations can help keep their data safe from malicious actors. By following these best practices for cloud security, organizations can help protect their data and systems from unauthorized access or other malicious activities.