Source

Cloud security refers to the measures taken to protect data and applications stored in the cloud from unauthorized access, use, modification, or destruction. It is a broad term that encompasses a variety of security controls, technologies, and processes implemented to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud-based resources.
Cloud Security: What Is the Need?
With the frequency and scale of cyber attacks increasing worldwide, having an added security layer in any cloud infrastructure is the need of the hour. It is essential for many reasons, from protecting sensitive data to ensuring compliance. Cloud security measures can also help ensure the stability and availability of systems by monitoring access control and giving control to authorized users only. Thus, it is crucial for organizations to carefully assess their cloud security needs and work with a trusted cloud provider to ensure the security of their systems.
Key Concepts for a Solid Security

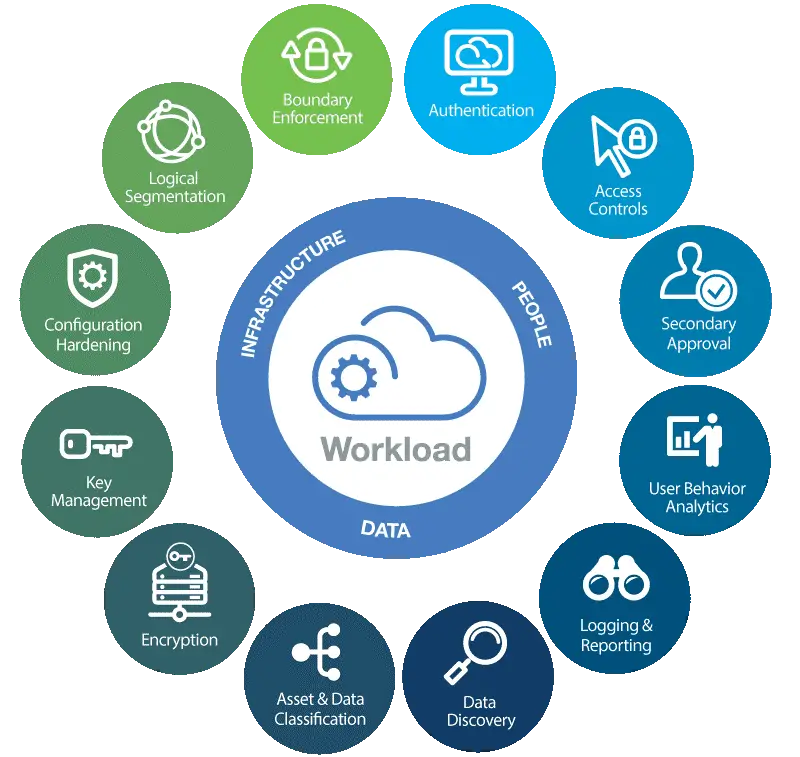
A few must-implement strategies will help you employ better cloud security for your application. Let us brush through some of them.
The foremost implementation to consider is network security. This involves protecting your application’s network infrastructure from external threats, such as through the use of firewalls and other security measures like performing network audits, using private IP addresses, and keeping antivirus and other anti-malware software up to date.
The next important concept is data security, which deals with securing anything related to data. Protecting data stored in the cloud from unauthorized access is of utmost importance, regardless of whether it is at rest or in transit. CI/CD security is usually the best option for protecting code changes in the application. This is because the integration pipeline is wrapped with a layer of security, ensuring the code changes are effected from staging to deployment without any interruption from a middleman trying to change or break the application code.
In the same level of application security, the access control should be clearly defined that identify different users and their authorization levels.
Identity and access management (IAM) is the foundation of cloud security and involves establishing secure identities for users and devices and controlling access to resources based on those identities. However, there’s a minor difference between ACL and IAM: the former can be defined on an individual object, whereas the latter can be implemented to bucket level or higher.
Moving forward, one should also implement application security. This involves protecting your application from vulnerabilities and attacks, such as through the use of secure coding practices and regular security testing.
And last but not least, compliance requirements should be monitored and met. You need to make sure that your cloud security procedures adhere to compliance standards depending on your industry and the laws relevant to your business. This may entail putting in place particular security measures as well as routinely assessing and testing your security posture.
Challenges and Threats
There are several challenges that organizations may face when it comes to securing their applications in the cloud. Practicing the above-mentioned principles in your cloud security will help you overcome the following challenges.
Conflict in Responsibility: In a cloud computing environment, the customer and the cloud provider often share responsibility for security. This may necessitate tight cooperation between the two parties and can result in uncertainty about who is in charge of particular security tasks.
Data Breaches: Cloud environments can be vulnerable to data breaches, particularly if security controls are not correctly implemented or maintained.
Complexity: Cloud infrastructures can be complex at times, consisting of several infrastructure levels and a wide range of tools and services. This can make it difficult to safeguard your application and data.
Insider Dangers: Employees or contractors with access to sensitive data and systems might pose a threat to cloud settings.
Future Scope and Evolution
The global technology landscape has evolved due to the cloud, and cloud security is moving along with it. This has been witnessed most recently in the emergence of zero trust and security service edge (SSE). As a developing market trend, SSE offers secure access to the internet, SaaS, and cloud apps, as well as your company’s proprietary apps, resolving basic issues with remote work, the cloud, secure edge computing, and digital transformation.
A zero-trust approach enables access to data and apps based on specific context—identity, content, location, device, and more—while offering improved user experiences. It is built on the premise that no person or entity should be inherently trusted.
The future of cloud security will likely involve a continued focus on improving and evolving security measures to protect against a wide range of threats. The key areas will probably use AI and ML to improve cloud security by automating the identification of and response to security threats. For instance, machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze large amounts of data to detect an attempted attack.
Cloud security methods will probably continue to develop in order to better defend against online threats. This might include implementing new technologies, such as quantum encryption, which can withstand hacking thanks to quantum physics’ foundational principles.
Conclusion
Any firm using cloud services must be concerned with cloud security since it helps safeguard sensitive information and systems from online dangers like malware, ransomware, and data breaches. Defending against unwanted access to cloud resources is particularly crucial since it might jeopardize the stability and security of an organization’s systems. Overall, it is vital to approach cloud security in a holistic and risk-based manner, considering the specific needs and risks of your application and organization.