Beware of MacStealer: The Mac Malware Posing as a Play-to-Earn Game
As the world of play-to-earn (P2E) games continues to grow, cybercriminals are taking advantage of the trend to entice unsuspecting users into downloading malicious applications. One such malware, known as MacStealer (detected by Trend Micro as TrojanSpy.MacOS.CpypwdStealer.A), is wreaking havoc by disguising itself as a plagiarized version of a legitimate P2E game app.
The threat actors behind MacStealer have crafted an elaborate scheme to trick users into downloading their malware. They pose as a legitimate game company looking for testers, promoting their fake app on social media and messaging platforms like Twitter, Discord, and Telegram. The cybercriminals have even created a convincing, albeit fake, game app’s page and Twitter account by copying graphics, text, and images from a real P2E application.

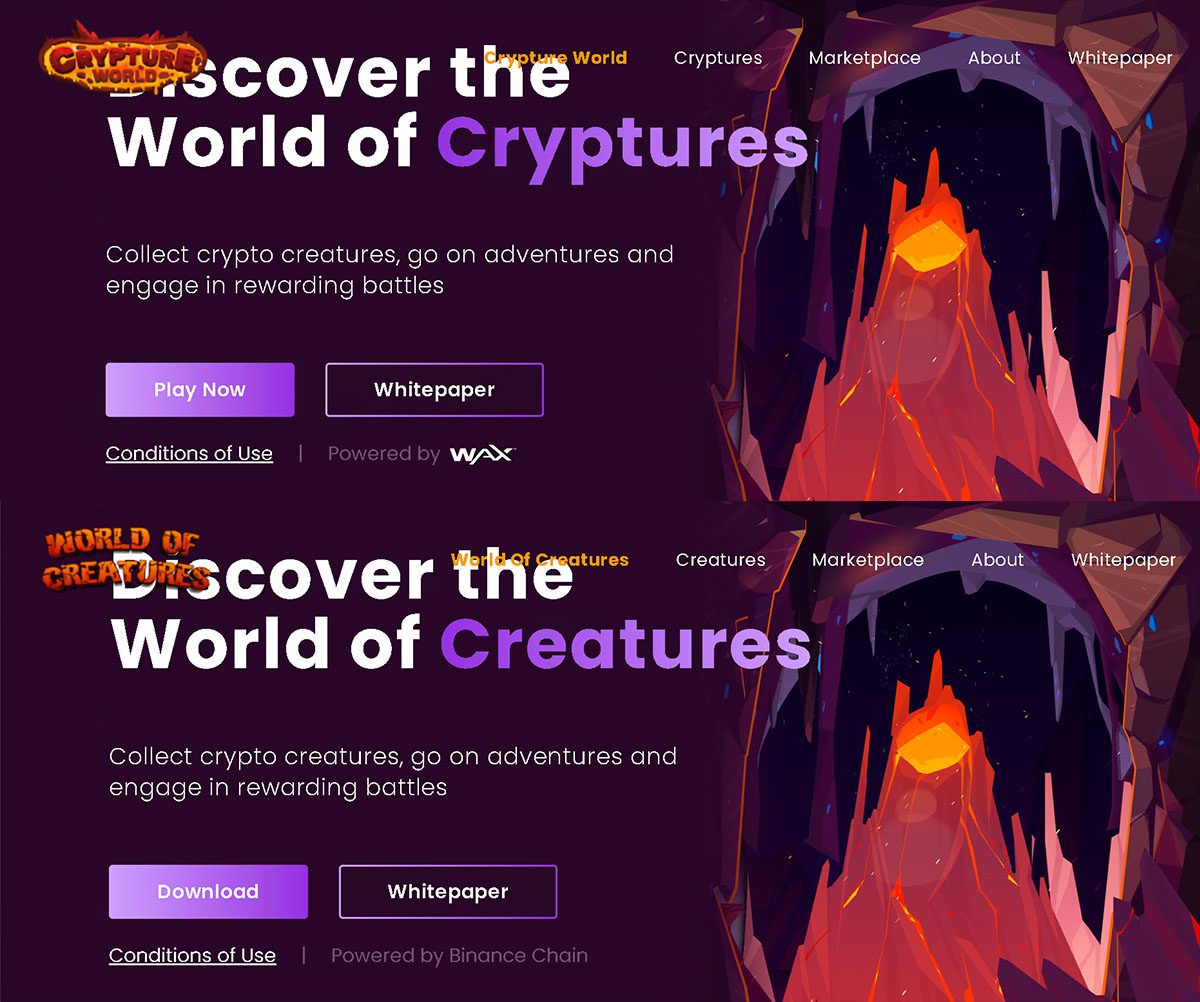
The web page of the real game (top) and the fake one (bottom)
Image: Trendmicro
Despite the similarities, vigilant users can still discern the fake app from the legitimate one by examining details such as the graphics, name, and company. The malware is spreading through third-party websites and social media promotions that offer freebies for new players who join the threat actor’s Discord channel and download the game. Once a user takes the bait, the threat actor convinces them to click on a malicious link or download a malware file.
MacStealer initiates its attack in two stages. The first stage involves executing a Nuitka bootstrap, which drops the malicious payload to a target path. The second stage executes the malicious payload, which is a program based on a CPython implementation compiled by Nuitka from Python.
Upon execution, MacStealer seeks to steal data from various cryptocurrency wallets, including Binance, Exodus, Keplr, Metamask, Phantom, and Trust Wallet. It also attempts to steal browser data and keychain, using chainbreaker to dump the keychain. To deceive users into providing their password, the malware pops up a dialog box titled “System Preferences.” Once it has collected the necessary information, MacStealer sends it to a command and control (C&C) server in a Zip file.
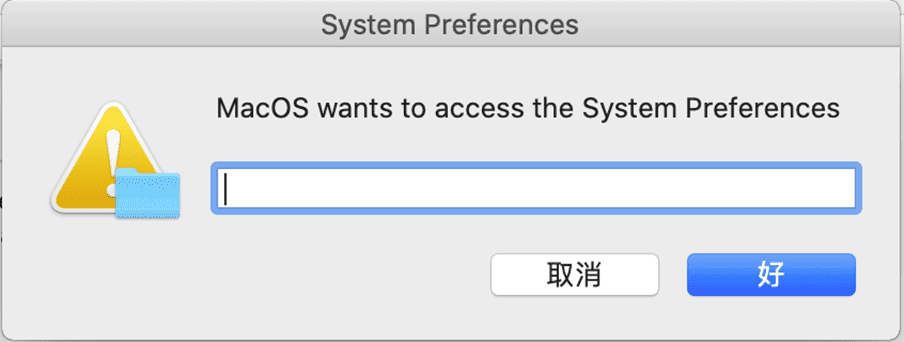
A dialog box to get the victim’s password
Image: Trendmicro
MacStealer’s end goal is to empty the victim’s cryptocurrency wallets. If a wallet is not found, the malware steals user information and the keychain. Victims of this campaign have taken to Twitter to warn others about the threat.
The cybercriminals behind MacStealer create Twitter accounts and related websites to advertise their fake game app, often using plagiarized images and videos from legitimate games like Ember Sword. They attract potential victims through various methods:
- Offering rewards for beta testing and requiring users to join their Discord or Telegram channels to access the malware binary or link.
- Direct messaging content creators to promote their game, likely as a social engineering tactic.
- Posting fake job vacancies to entice job seekers into downloading the malware binary.
As Mac malware like MacStealer becomes increasingly sophisticated, users must remain vigilant and cautious when downloading and engaging with P2E game apps. Always verify the legitimacy of an app, its website, and social media presence before downloading or providing any personal information.





