Bug Bounty Reconnaissance Framework: help you coordinate your reconnaissance workflows across multiple devices
Bug Bounty Reconnaissance Framework
The Bug Bounty Reconnaissance Framework (BBRF) can be used to coordinate your reconnaissance workflows across multiple devices. For more background, read the original blog post.
If you are new to BBRF, you will need to deploy a BBRF server before you can make use of the client.
Dashboard
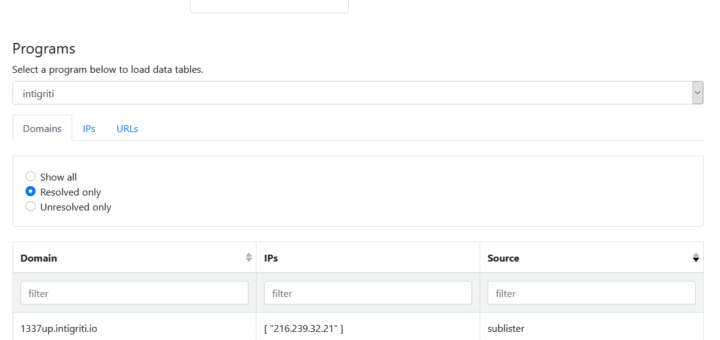
If you like browsing through your recon data with a GUI, you can make use of the BBRF dashboard at https://bbrf.me. Just plug in your server URL, username, and password, and the dashboard will pull your data and make it searchable. Note that all communication to the server happens via your browser, so your data remains safe!
Advanced
Domains
BBRF will accept and store domains in any of the following input formats:
<domain>
<domain>:<ip>
<domain>:<ip>,<ip>,…
Note that adding the DNS resolutions of a domain in this way does not automatically store the IP in the IPs table, but that domains and ips are logically seperated in the client, which requires you to write your scripts so that they handle this distinction appropriately.
bbrf domain add www.example.com:1.1.1.1
bbrf domain update www.example.com:2.2.2.2,3.3.3.3
bbrf show www.example.com | jq
IPs
Similarly, you can store hostnames of an IP address by appending one or more domains with a colon:
<ip>
<ip>:<domain>
<ip>:<domain>,<domain>,…
Again, BBRF will make sure the provided hostnames are valid domain names before storing them, but will not add them to your list of domains for the program, nor does it validate these domains against the defined program scope. Instead, these domains are stored in a domains property on the IP document:
URLs
BBRF will help you manage your URLs, and store their hostname, port, status code and content length for you:
bbrf url add ‘https://www.example.com:8443/a‘ ‘http://www.example.com/b‘ ‘http://www.example.com/c 200 1234‘
Two formats are accepted: <url> or <url> <statuscode> <contentlength> delimited by spaces.
The <url> can be absolute or relative. A relative URL will require the -d <hostname> flag to be specified or will be skipped. Whenever the -d flag is set, it will compare that with the hostname parsed from the URL, and skip the URL if they do not match.
Relative URLs and URLs that do not specify a scheme (http:// or https://) will always be interpreted with scheme http://. If no port is found, ports 80 and 443 will be used as a default depending on the scheme.
The flag --show-new will print a list of new and updated URLs if they were added, or if their status code and/or content length were updated respectively:
To view a list of stored URLs of your active program, simply use:
bbrf urls
Or, to return URLs belonging to a specific host:
bbrf urls -d www.example.com
To list URLs across all programs, run:
bbrf urls –all
To print full URLs with the saved query strings:
bbrf urls –all –with-query
Services
To store services (i.e. open ports) in BBRF, provide the input formatted as ip:port or ip:port:service, and manually specify other properties by means of the tagging system (see below for more info about tags), e.g.:
Note that services can only be stored for an IP address, and not as domain:port for example. This avoids the complexity of mapping domains to IPs (especially when an IP address maps to more than one domain), while still allowing search operations supported by a mix of default properties and tags:
Tagging and querying
By setting custom properties for the different document types (programs, domains, ips, urls and services), you can specify e.g. the platform a program belongs to or the name of a team member that added a bunch of new domains.
To add tags to documents, specify a -t key:value when creating a new domain, ip, url or service, or leave empty to remove the tag:
Note that you can specify the same tag multiple times to store the tags as arrays. BBRF will follow the following rules to determine how to store tags:
- if a single
-t tag:valueis found, treat as a normal value; - if the same tag name is provided more than once, default to an array:
-t cname:one -t cname:two - by default, overwrite existing values for the tags when updating, unless
--append-tagsis specified, in which case append new values to existing values:
To facilitate basic data querying, the BBRF server provides an indexed search based on all custom tags, as well as some default properties of all document types:
This works on domains, ips, urls and services and will search based on text-based comparisons as is defined in the Unicode Collation Algorithm as implemented by Couchdb.
Since all values are stored as text, this allows date comparison if you store dates as unix timestamps or in a ISO-8601 format e.g. 2021-01-15T09:02:40.628Z.
That also means, however, that for example "20" comes after "1000", which makes this less suitable for integer comparison. So if you want to store integers, you may want to use padded zeros at the front to ensure that 0020 comes before 1000.
Dynamic program inference
Use the dynamic program name -p @INFER to infer the program name based on other properties if you’re unable to specify the program flag yourself for some reason; this is currently supported for the following operations:
bbrf ip add 1.1.1.1:example.tld -p @INFERwill set the IP’s program name to the same as the domain example.tld if it already exists;bbrf domain add some.example.tld:1.2.3.4 -p @INFERwill set the domain’s program name to the same as 1.2.3.4 if it already exists – note that this will bypass the scope validation of the program, because the program name is inferred just before writing to the database.bbrf domain add some.example.tld some.other.tld -p @INFERwill add the domains to whatever program scope matches the input;bbrf url add http://this.example.tld https://that.some.tld/robots.txt -p @INFERwill add the URLs to whatever program has the domain in scope;
BBRF Listener
To process changes and alerts as they are pushed to the data store, you need to have an active listener running somewhere:
bbrf listen
This will start listening for changes on the BBRF server and push notifications to your configured Slack instance. Note that this will fail e.g. when the BBRF server is temporarily unavailable or in case of certificate errors, so you may want to loop this to auto-start in case of issues.
Custom execution hooks
The BBRF listener will also execute custom local scripts when it sees new or updated ips, domains, urls, and/or services. It will automatically look for executable .sh files in the following locations:
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/ip/new/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/ip/update/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/domain/new/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/domain/update/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/url/new/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/url/update/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/service/new/,
- ~/.bbrf/hooks/service/update/,
For example, here is a custom execution hook that will resolve newly added domains and store the results back in BBRF. Find more examples in docs/hooks.
Proxy configuration
Since version 1.2, BBRF allows you to store and retrieve proxy configurations per program. This feature was designed to integrate with my OpenVPN via SOCKS5 proxy setup, but can be used with other proxy setups independently.
For example, configure your proxy settings in BBRF as follows:
# add a proxy with name ‘hackerone’ and a valid proxy URL
bbrf proxy set hackerone socks5://user:pass@yourserver.com:1080
Update a program’s proxy settings with the custom tag proxy as follows:
# use the same name as the name of the configured proxy
bbrf program update my_hackerone_program -t proxy:hackerone
Get the proxy settings of a program with bbrf proxy -p my_hackerone_program. For example, you can update your automation scripts to always send traffic through the right proxy as follows:
# note that the use of double quotes will allow this to work even if no proxy is configured for the current program
curl -x “$(bbrf proxy)“ ifconfig.co
Install
Copyright 2021 @honoki




