In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats, having access to reliable and up-to-date threat intelligence is paramount. One tool that has gained recognition in the cybersecurity community is C2 Tracker, a free and open-source Indicator of Compromise (IOC) feed that leverages Shodan and Censys searches to gather IP addresses associated with known malware, botnets, and command-and-control (C2) infrastructure.
What is C2 Tracker?
C2 Tracker is a community-driven initiative that aims to provide cybersecurity professionals, researchers, and enthusiasts with a valuable resource for identifying and tracking malicious activities on the internet. By utilizing Shodan and Censys, two powerful search engines for internet-connected devices, C2 Tracker aggregates IP addresses linked to a wide range of cyber threats.
What Does C2 Tracker Track?
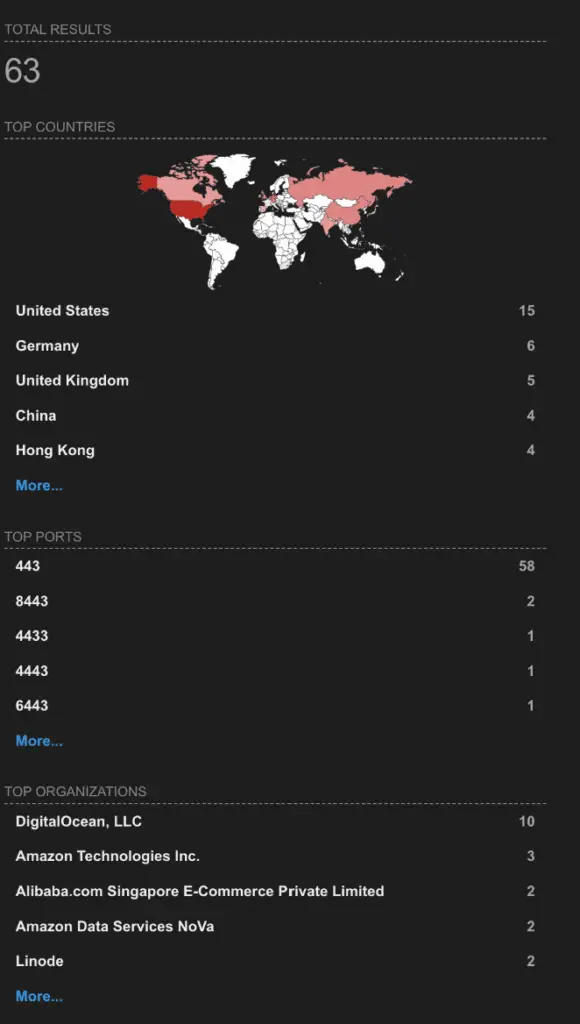
The scope of C2 Tracker’s tracking is extensive, encompassing various categories of cyber threats:
-
C2 Frameworks: C2 Tracker focuses on identifying IP addresses associated with popular C2 frameworks like Cobalt Strike, Metasploit Framework, Covenant, Mythic, Brute Ratel C4, and many others. These frameworks are commonly used by threat actors to control compromised systems remotely.
-
Malware: The tool also tracks IP addresses linked to various malware families, including stealers (e.g., AcidRain Stealer, Misha Stealer), remote access trojans (RATs) (e.g., Quasar RAT, AsyncRAT), and other malicious software.
-
Tools: C2 Tracker doesn’t limit itself to malware and C2 frameworks; it also tracks IP addresses associated with tools frequently used by both security professionals and malicious actors, such as XMRig Monero Cryptominer, GoPhish, BurpSuite, and Hashcat.
-
Botnets: The tool monitors IP addresses related to botnets like 7777, BlackNET, and Doxerina, which are networks of compromised devices used for various malicious purposes.
How Does C2 Tracker Work?
C2 Tracker operates by utilizing the capabilities of Shodan and Censys to scan the internet for specific patterns, signatures, and characteristics associated with known C2 infrastructure, malware, and tools. When a match is found, the corresponding IP address is added to the C2 Tracker feed. This feed is then made available to the community, allowing users to integrate it into their security tools and workflows.
The Community-Driven Aspect
One of the unique aspects of C2 Tracker is its community-driven nature. The project actively encourages contributions from cybersecurity researchers and enthusiasts. Many of the queries used by C2 Tracker to identify threats have been sourced from other CTI researchers, fostering a collaborative environment for threat intelligence sharing.
Why C2 Tracker Matters
C2 Tracker plays a crucial role in the fight against cyber threats for several reasons:
-
Early Warning: By identifying C2 infrastructure and malware early on, C2 Tracker provides an early warning system for potential attacks, allowing defenders to take proactive measures.
-
Threat Hunting: The IOC feed generated by C2 Tracker can be used for threat hunting, enabling security teams to search their networks and logs for signs of compromise.
-
Research: C2 Tracker serves as a valuable resource for cybersecurity researchers, helping them understand the latest trends in malware and C2 infrastructure.
Getting Started with C2 Tracker
C2 Tracker is free and open-source, making it accessible to everyone. The project is hosted on GitHub, where you can find the source code, documentation, and instructions on how to use the IOC feed.
In conclusion, C2 Tracker is a powerful tool that exemplifies the strength of community-driven cybersecurity efforts. By harnessing the capabilities of Shodan and Censys and encouraging collaboration among researchers, C2 Tracker provides a valuable resource for identifying and mitigating cyber threats. Whether you’re a security professional, researcher, or simply interested in cybersecurity, C2 Tracker is worth exploring.
Related Posts:
- Malcolm: A Comprehensive Network Traffic Analysis Tool
- BunkerWeb: The Next-Generation Open-Source Web Application Firewall
- OpenCTI: Empowering Cyber Threat Intelligence Management