Cacti Network Monitoring Tool Patches Security Flaws, Including RCE Vulnerability
Popular open-source network monitoring tool, Cacti, has released an urgent security update addressing multiple vulnerabilities, including a critical Remote Code Execution (RCE) flaw.
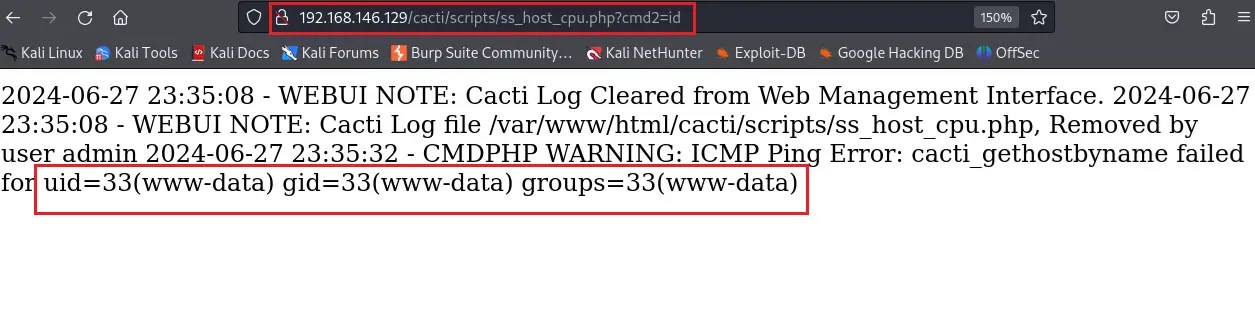
The update, version 1.2.28, patches four vulnerabilities that could allow attackers to compromise systems running vulnerable versions of Cacti. The most severe of these, CVE-2024-43363, allows an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the server by manipulating log files. This vulnerability, with a CVSS score of 7.2, is exploitable through a technique known as “log poisoning.” By creating a malicious device hostname containing PHP code and manipulating the installation process, attackers can inject this code into Cacti’s log files. Accessing the log file URL then triggers the execution of the malicious code, granting the attacker control of the server.
In addition to the RCE flaw, three Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities were also addressed. These flaws, CVE-2024-43365, CVE-2024-43364, and CVE-2024-43362, allow attackers to inject malicious scripts into web pages viewed by other users. By exploiting these vulnerabilities, attackers can steal user credentials, hijack user sessions, or redirect users to malicious websites. The CVSS scores for these XSS vulnerabilities range from 5.7 to 7.3, indicating a significant risk to affected systems.
These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of sanitizing user inputs and validating data before displaying it or using it in critical processes.
Cacti users are strongly urged to update to version 1.2.28 immediately to mitigate these security risks. Administrators should also review their Cacti installations for any signs of compromise and take appropriate action to secure their systems.





