CyberVolk Ransomware: A New and Evolving Threat to Global Cybersecurity
A relatively new player in the cybercrime world, the Indian hacker group CyberVolk, has been making waves with its sophisticated ransomware. CyberVolk Ransomware, first detected in July 2024, has quickly gained notoriety for its advanced features and rapid evolution. Recently analyzed by ThreatMon, the group’s most concerning weapon, CyberVolk Ransomware, is drawing attention from cybersecurity experts for its advanced capabilities and growing impact.
CyberVolk made its debut in the shadows of the dark web, where it quickly gained a reputation through a series of successful attacks. Specializing in a wide array of cybercrimes—including DDoS attacks, data breaches, and website defacements—the group is known for its bold presence, even maintaining official accounts on platforms like Telegram and X.
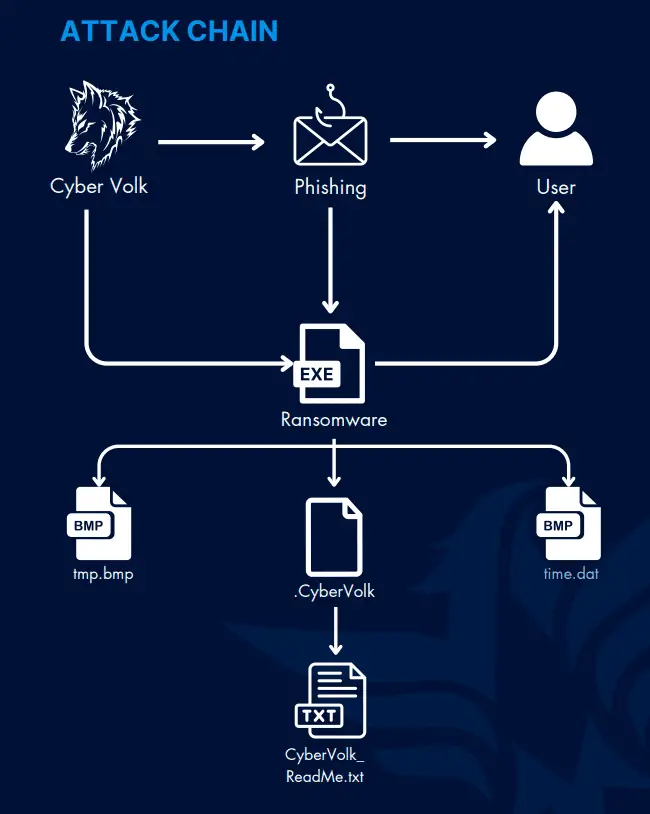
However, it is their ransomware that has alarmed the cybersecurity community. First detected in July 2024, CyberVolk Ransomware quickly appeared on underground forums as a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS). This means anyone with the right connections can rent the tool to launch their own attacks, making CyberVolk’s ransomware a widely available and dangerous commodity in the cyber underworld.
Initially, CyberVolk Ransomware used the AES encryption algorithm to lock down victims’ files. However, a leak on VirusTotal exposed the ransomware’s internal workings, prompting the hackers to release an updated, far more advanced version. This new variant incorporated stronger cryptographic algorithms, including ChaCha20-Poly1305, AES, and even quantum-resistant technologies. These enhancements make it nearly impossible to decrypt without paying the ransom, even for those equipped with quantum computing resources.
One of the most striking features of CyberVolk Ransomware is its ability to operate without connecting to a command-and-control (C2) server. This autonomous encryption process makes the malware harder to detect and block, and the attackers have added a severe penalty for failed recovery attempts. If the wrong decryption key is entered, the ransomware automatically deletes the encrypted data, leaving victims with little recourse but to comply with ransom demands.
ThreatMon’s technical analysis of CyberVolk Ransomware reveals several unique and concerning capabilities. For example, upon execution, the ransomware blocks access to critical system tools like Task Manager, preventing users from terminating the encryption process. The ransomware completes encryption of all files within minutes and then presents the victim with a ransom demand of $1,000. Victims are also given a stark deadline: failure to pay within five hours results in the permanent destruction of their data.
The malware employs advanced tactics to evade detection, including debugger detection and runtime environment checks. It is also capable of spreading like a worm across connected devices and network shares, meaning that a single infected machine can quickly compromise an entire network.
Interestingly, despite its sophistication, ThreatMon identified several vulnerabilities. For example, while the ransomware blocks Task Manager, it does not block PowerShell, which allows skilled users to stop the encryption process using specific commands. Additionally, the ransomware’s five-hour countdown timer can be altered by editing the “time.dat” file located in the user’s system, potentially giving cybersecurity teams more time to mitigate the attack.
While early reports indicated that CyberVolk Ransomware only generated $2,632, their revenues have surged in recent months. ThreatMon estimates that the group has earned over $20,000 from ransomware attacks, signaling a troubling rise in the financial impact of their operations.
CyberVolk Ransomware is a serious threat to businesses and individuals alike. Its ability to spread like a worm, combined with its sophisticated encryption and evasion techniques, makes it a formidable adversary. However, the presence of vulnerabilities in its structure offers hope for effective countermeasures.
Cybersecurity experts recommend regular software updates, robust backup strategies, and employee education on cybersecurity hygiene to minimize the risk of ransomware attacks.





