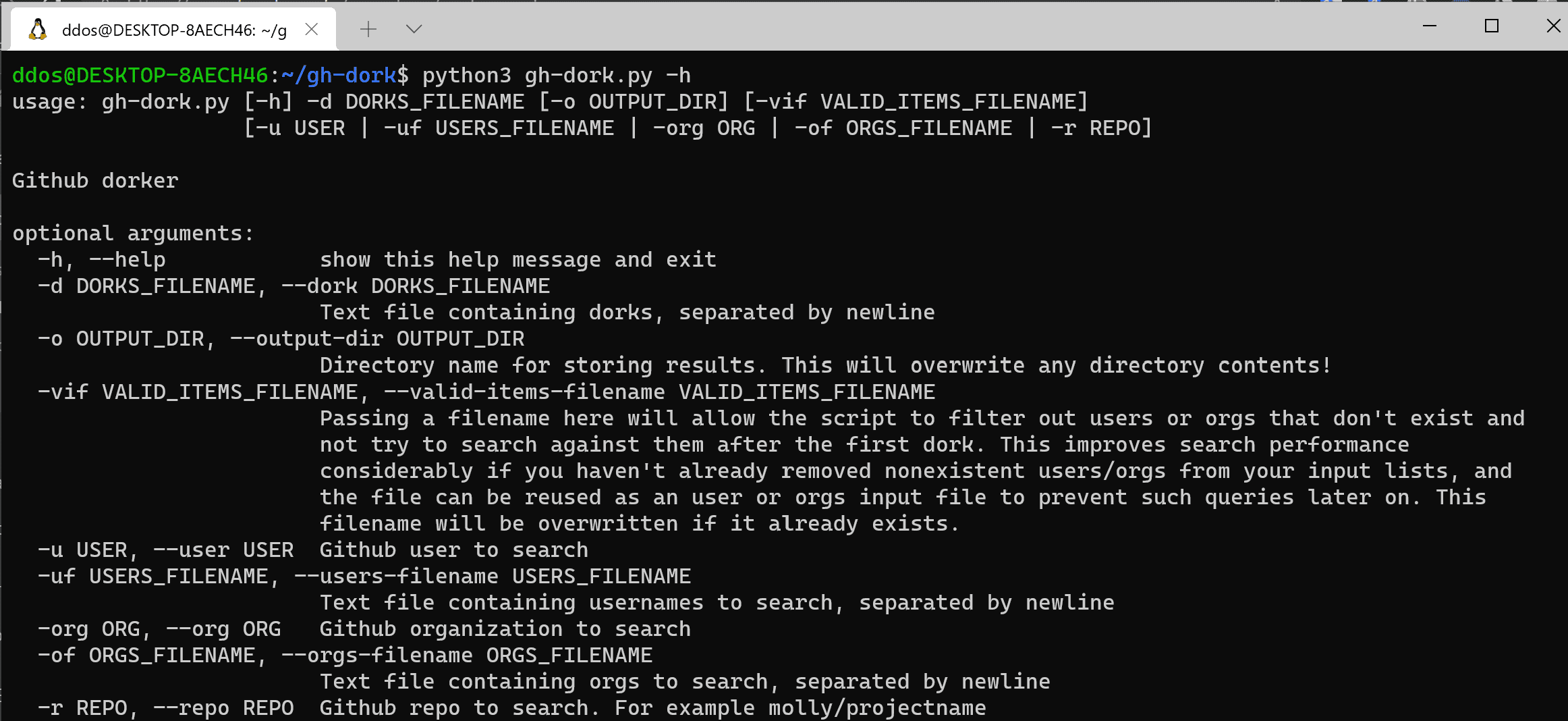
gh-dork: Github dorking tool
gh-dork – Github dorking tool
Supply a list of dorks and, optionally, one of the following:
- a user (
-u) - a file with a list of users (
-uf) - an organization (
-org) - a file with a list of organizations (
-of) - a repo (
-r)
You can also pass:
- an output directory to store results (
-o) - a filename to store valid items, if your users or the org file may contain nonexistent users/orgs (
-vif)
All input files (dorks, users, or orgs) should be newline-separated.
Install
git clone https://github.com/molly/gh-dork.git
pip install -r requirements.txt
Authentication
Authentication is done with environment variables. You can authenticate with a Github private access token (GH_TOKEN), or username and password (GH_USER and GH_PASS). If you have two-factor authentication enabled, you will be prompted for a two-factor code.
You can also pass a Github Enterprise base URL (GH_URL) to search against that Github instance; if omitted, this will run against github.com.
If no credentials are provided or if credentials are invalid, the script will still run but will be limited by the much lower rate limits for unauthenticated users.
Use

The only required parameter is the dorks file (-d). See techguan’s github-dorks.txt for ideas.
If an output directory is specified, a file will be created for each dork in the dorks list, and results will be saved there as well as printed. Only use an empty/nonexistent directory or it will be cleared and its contents replaced.
If your users or orgs files haven’t already been filtered to remove non-existent users/orgs or those without any public code, it’s highly recommended that you pass in a –valid-items-filename (-vif). This will filter out any invalid users/orgs when searching for the first dork, and avoid searching against them for subsequent dorks. The output file can also then be used as the input users/orgs file to speed up later script runs.
Copyright (C) 2021 molly
Source: https://github.com/molly/





