GOOTLOADER Malware Continues to Evolve: Google Researchers Uncover Advanced Tactics
Google researchers recently released an in-depth analysis of GOOTLOADER, also known as SLOWPOUR or Gootkit Loader, an obfuscated JavaScript downloader, revealing new tactics employed by financially-motivated threat actors to deploy ransomware, exfiltrate data, and conduct other malicious activities.
Active since at least 2021, GOOTLOADER is delivered through compromised websites, often targeting victims through SEO poisoning. “Victims are lured into visiting compromised WordPress websites via SEO poisoning. Victims perform a search, often for business-related documents such as legal requirements, agreements, or contracts, and navigate to a compromised site with information purportedly related to their search,” the report noted. This approach capitalizes on users searching for legitimate resources, tricking them into downloading an archive that contains the malicious JavaScript file.
Screenshot of a compromised web page distributing GOOTLOADER malware | Image: Google
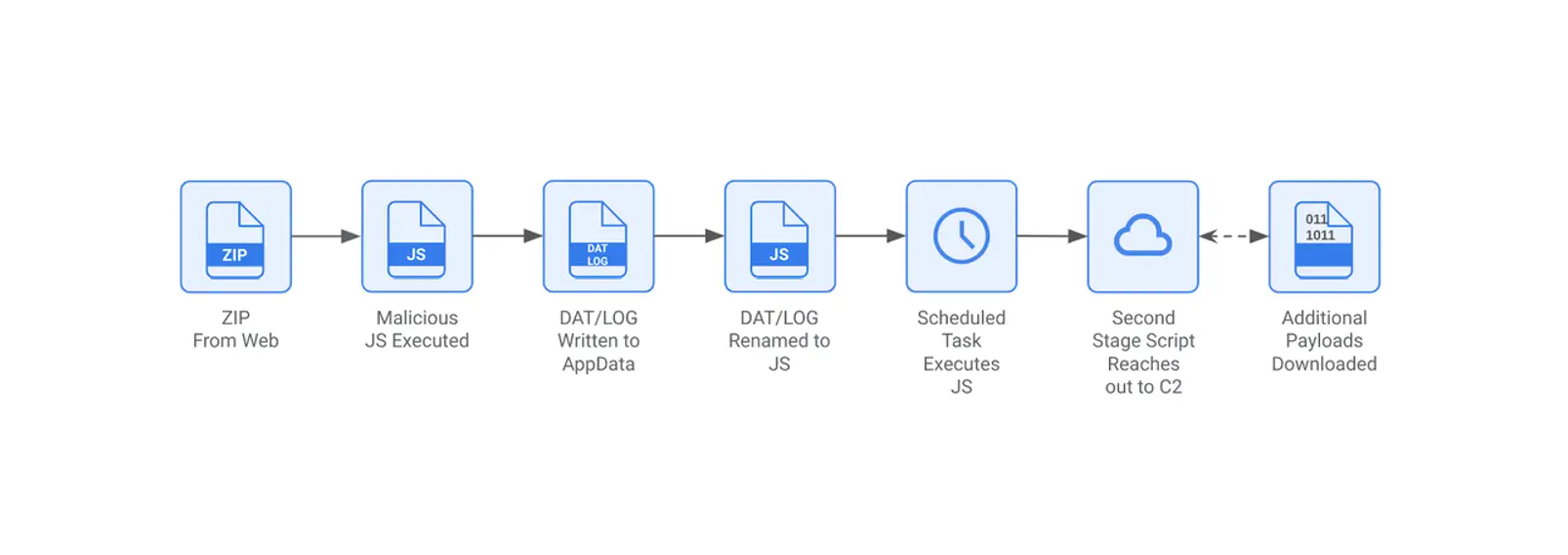
The infection chain of GOOTLOADER is multi-staged, designed to evade detection at each phase. Once the initial JavaScript file from the downloaded archive is executed, it deploys a second-stage payload to the victim’s system. This payload, saved with a deceptive file extension like .dat or .log, is then renamed to .js and launched via a scheduled task for persistence. This sophisticated setup, which includes padded file sizes to avoid detection.
The analysis highlighted, “The scheduled task is created to launch the second stage .js file. The task serves as a form of persistence and a way to execute the second stage file for the first time,” illustrating the malware’s ability to embed itself within the system’s normal operations.
A notable component of GOOTLOADER is the embedded PowerShell script, tracked as GOOTLOADER.POWERSHELL. This script initiates a sophisticated data exfiltration process by collecting system information, which is then compressed, encoded, and transmitted to a command-and-control (C2) server. The script’s obfuscation, using hard-coded bytes and padding techniques, makes it difficult to analyze without prior knowledge. According to the report, “The script Base64 encodes the collected information and compresses it using gzip before sending it to the C2 server,” effectively masking its activity from monitoring tools.
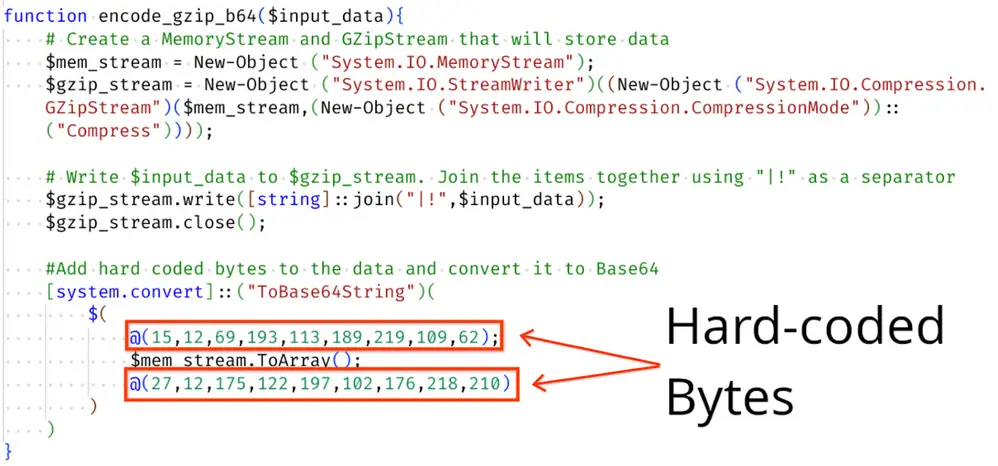
Data encoding function | Image: Google
The encoded data is sent via an HTTP GET request, with unique identifiers corresponding to different types of system information, including environment variables, running processes, and disk space. These identifiers allow attackers to tailor their data collection efforts, gathering only what they need from each compromised system.
GOOTLOADER’s developers are not standing still. Mandiant Managed Defense observed an update to GOOTLOADER.POWERSHELL in mid-2024, shifting from deploying a .NET-based launcher called FONELAUNCH to using a malicious DLL file associated with the CLEANBOOST backdoor.





