Information Stealer Malware on the Rise: ACSC Issues Urgent Cybersecurity Warning
The Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) has issued a warning about the escalating threat of information stealer malware. This insidious type of malware is designed to siphon sensitive data from victims’ devices, including login credentials, financial information, and personal files. Cybercriminals are increasingly leveraging information stealers to gain unauthorized access to corporate networks, leading to devastating consequences such as ransomware attacks, data breaches, and financial losses.
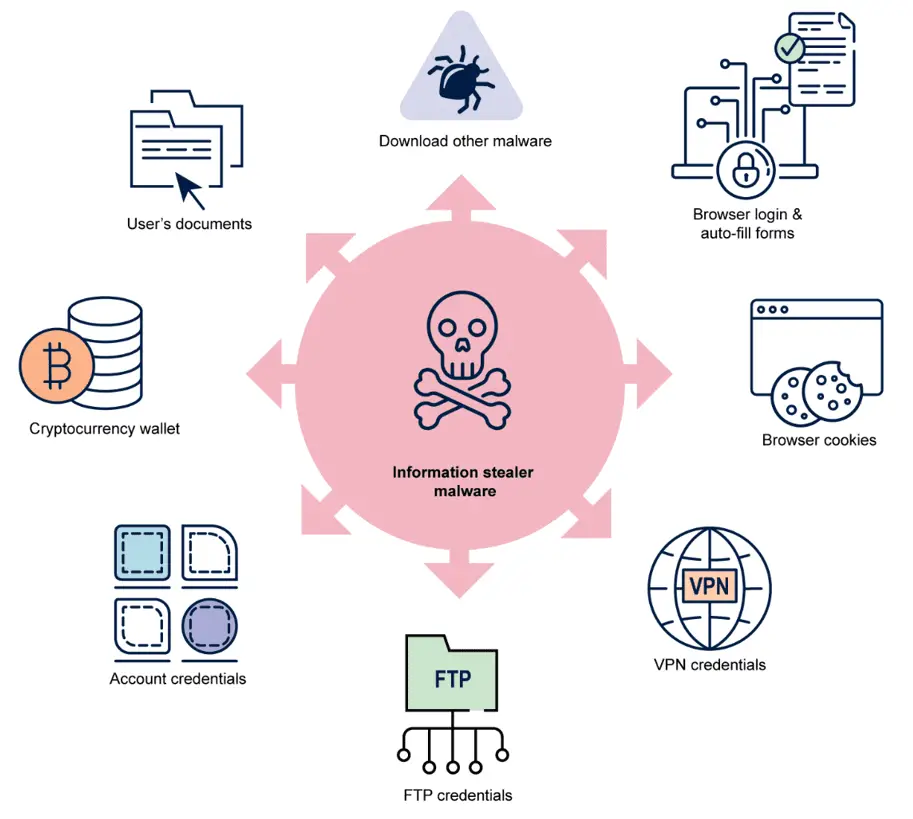
Information Stealer Malware is a type of malicious software designed to harvest sensitive data from victims’ devices, including usernames, passwords, credit card details, and more. Once this data is exfiltrated, it becomes a valuable commodity on dark web marketplaces, where cybercriminals auction it off to the highest bidder. These stolen credentials often serve as the gateway for more severe attacks, such as ransomware, business email compromise, and theft of intellectual property.
The lifecycle of an information stealer attack typically unfolds in four stages:
- Acquisition: Cybercriminals acquire info stealers through various channels, including Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms, which have lowered the barrier to entry for less technically proficient criminals.
- Distribution: Once obtained, the malware is distributed via phishing emails, malicious ads, cracked software, and other deceptive methods, often targeting personal devices used for both work and leisure—a practice that is especially common in remote work environments.
- Data Harvesting: After successful infection, the malware collects sensitive information from the victim’s device, focusing on credentials stored in web browsers, authentication cookies, and other critical data.
- Monetization: The stolen data is aggregated and sold on dark web marketplaces, where it is often purchased by initial access brokers. These brokers specialize in gaining entry into corporate networks and reselling that access to other cybercriminals, who then execute more destructive attacks.
A recent incident involving an Australian business illustrates the severe impact of information stealers. An employee working remotely from a personal device unknowingly downloaded an info stealer disguised as legitimate software. The malware swiftly captured the employee’s corporate credentials, which were later sold on the dark web. The buyer, a cybercriminal, used these credentials to infiltrate the company’s network, leading to a major data breach and subsequent ransomware attack.
ASD’s ACSC emphasizes the importance of proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate the risks posed by info stealers. Key recommendations include:
- Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA across all critical services, particularly for privileged user accounts.
- Security Awareness Training: Regularly educate employees about the dangers of phishing, malicious downloads, and the importance of secure password management.
- Device Management: Ensure that all devices accessing corporate networks, including personal devices, adhere to strict security policies.
- Network Monitoring: Continuously monitor for unusual activity, particularly on remote connections and privileged accounts.