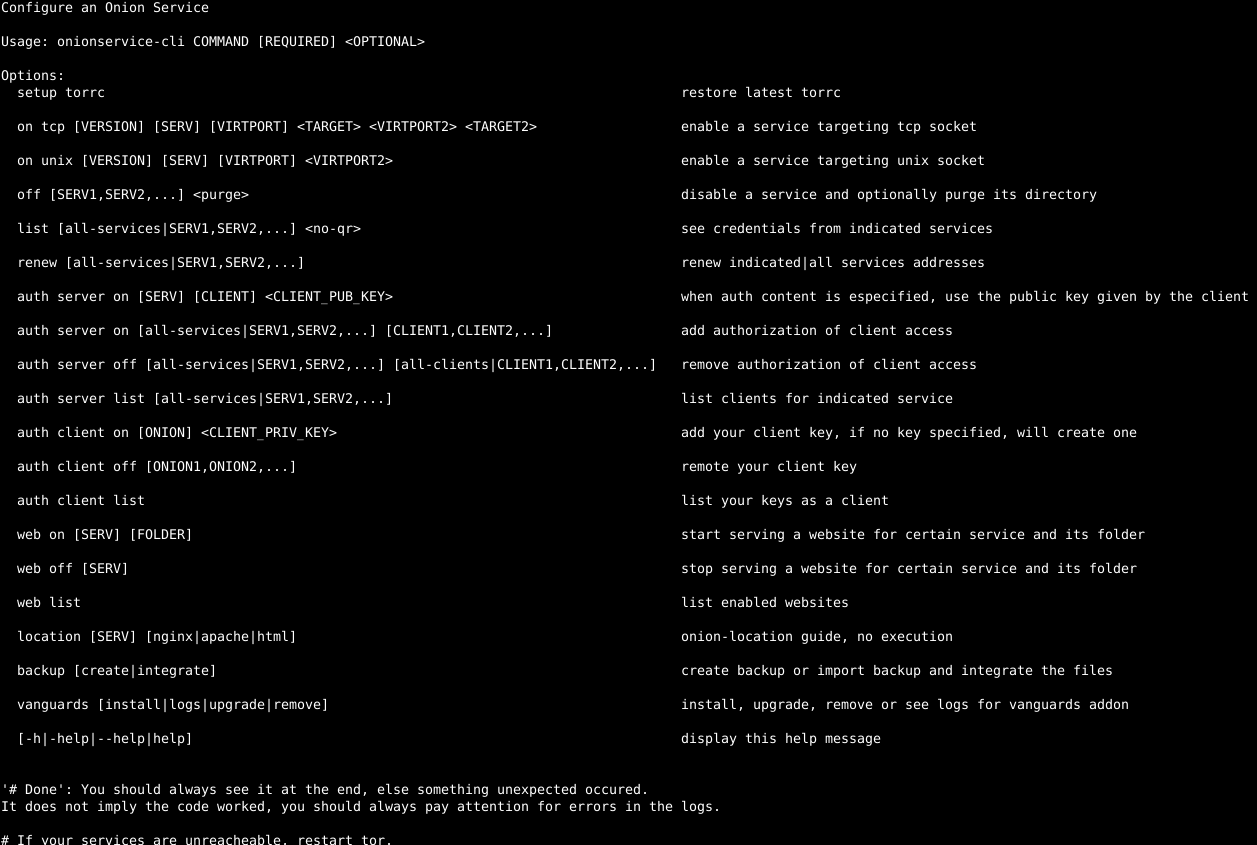
onionservice: Feature-rich Onion Service manager for UNIX-like operating systems
onionservice
Feature-rich Onion Service manager for UNIX-like operating systems written in POSIX conformant shellscript
A collection of Onion Services features implemented for Unix-like systems following the Portable Operating System Interface standard.
WARNING: do not trust this repo yet, backup your hs keys in another location. This project has not been released and should be considered for development only.
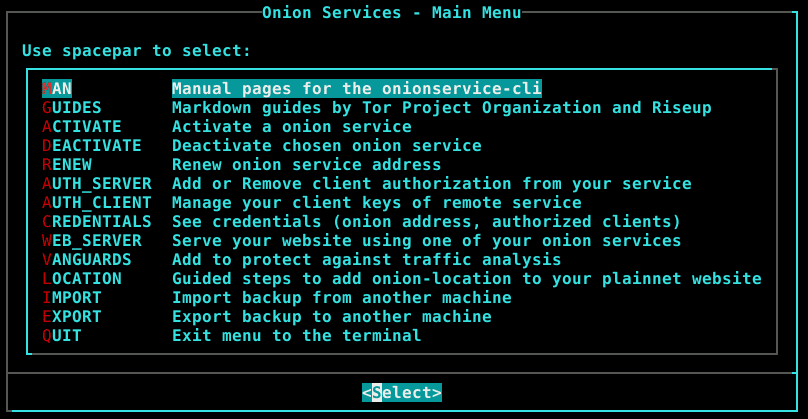
Echosystem
Onion Services are the Hidden Services of Tor which use onion routing as its base for stablishing private connections. They offer:
- Location hiding – IP address aren’t used, so your location is protected.
- End-to-end authentication – Only the owner of the hs secret key can host the same onion, so no impersonation is possible, no man-in-the-middle.
- End-to-end encryption – Traffic is encrypted from the client to the onion host, no need to trust CAs which are a fallible model.
- NAT punching – On a firewalled network, no need to open ports
For a deeper understanding, read the Rendezvous Specification and Tor design.
Onion Routing tries to solve most of these problems but it is still centralized by the Directory Authorities, and referencing Matt Traudt’s blog post: replacing it for something more distributed is not a trivial task.
On the Tor echosystem, from TPO metrics, comparing only Free and Open Source Operating Systems, Linux dominates on relays by platform and Tor Browser downloads by platform over BSD. Data regarding which operating system the onion service operator can not be easily acquired for obvious reasons. That was on the network level, but know on the user system, even if one chooses a Free and Open Source Operating System, GNU/Linux dominates a big share over *BSD, having a huge impact on the main software used for the kernel (Linux), shell (bash), service manager (systemd).
Goal
The goal of this project is:
- facilitates onion service management, from activating service to adding client authorization to it, giving the full capabilities of editing files manually would have but with less tipying.
- show that managing the onion service is much more than just using a web server with your pages.
- distribution, from the source code level (FOSS) to the effect it takes when it allows anyone to run the code on any operating system, shell or service manager. Mitigation from a single point of failure
Descentralization from a single point of failure:
- Kernel from predominant
Linuxto alsoBSD. - Shell from predominant
bashto also any POSIX shell such asksh,(y,d)ashandzsh(emulating sh). - Service manager from predominant
systemdto alsoOpenRC.
Editing the tor configuration file (torrc) is not difficult, but automation solves the problem of misconfiguration and having:
- less time spent
- complete uniformity
- graphical interface to help newbies
Features
- Enable service – Create directory if not existent (HiddenServiceDir), select onion version (HiddenServiceVersion), custom socket type being unix or tcp, up to two virtual ports, up to two targets (HiddenServicePort).
- Disable service – Remove service configuration from the torrc, the service will not be acessible anymore, but you can enable it again any time you want. Optionally purge the service, deleting its configuration and directory, which will delete its keys permanently.
- Renew service address – Focused on private onion services, if you ever leak its address, you can change its hostname, beware all of your authorized clients will be disconnected and the service keys will be permanently deleted.
- Credentials – Show hostname, clients, torrc block, qrencoded hostname.
- Onion authentication – For v3 onion services only. This depends on client and server side configuration and works with a key pair, the client holds the private key part either generate by him (more safe) or given by the service operator and the onion service operator holds the public part. If any if
- Server – Generate key pair or add public part, list client names and their public keys from
<HiddenServiceDir>/authorized_clients/<client>.auth. If any client is configured, the service will not be acessible without authentication. - Client – Generate key pair or add public part, list your
<ClientOnionAuthDir>/<SOME_ONION>.auth_private.
- Server – Generate key pair or add public part, list client names and their public keys from
- Onion-Location – For public onion services You can redirect your plainnet users to your onion service with this guide for nginx, apache2 and html header attributes.
- Backup – Better be safe.
- Create – Backup of your
torrclines containing hidden service configuration, all of your directories ofHiddenServiceDirandClientOnionAuthDir. Guide to export the backup to a remote host with scp. - Integrate – Integrate hidden serivces lines configuration from
torrcand the directoriesHiddenServiceDirandClientOnionAuthDirto your current system. This option should be used after creating a backup and importing to the current host. Guide to import backup to the current host with scp.
- Create – Backup of your
- OpSec – Operation Security
- Vanguards – This addon protects against guard discovery and related traffic analysis attacks. A guard discovery attack enables an adversary to determine the guard node(s) that are in use by a Tor client and/or Tor onion service. Once the guard node is known, traffic analysis attacks that can deanonymize an onion service (or onion service user) become easier.
- Unix socket – Support for enabling an onion service over unix socket to avoid localhost bypasses.
- Web server – Serve files with your hidden service using Nginx or Apache2 web server.
- Bulk – Some commands can be bulked with
all-clients,all-services,[SERV1,SERV2,...]and[CLIENT1,CLIENT2,...], the command will loop the variables and apply the combination. - Optional – Some commands are optional so less typing. Also they may behave differently depending on how much information was given to be executed and that is expected. They are specified inside
<>(e.g.<VIRTPORT2>) - Fool-proof – The script tries its best to filter invalid commands and incorrect syntax. The commands are not difficult but at first sight may scare you. Don’t worry, if it is invalid, it won’t run to avoid tor daemon failing to reload because of invalid configuration. If an invalid command runs, please open an issue.
Install & Use
Copyright (c) 2021 OnionService developers