PSAUX Ransomware is Exploiting Two Max Severity Flaws (CVE-2024-51567, CVE-2024-51568) in CyberPanel
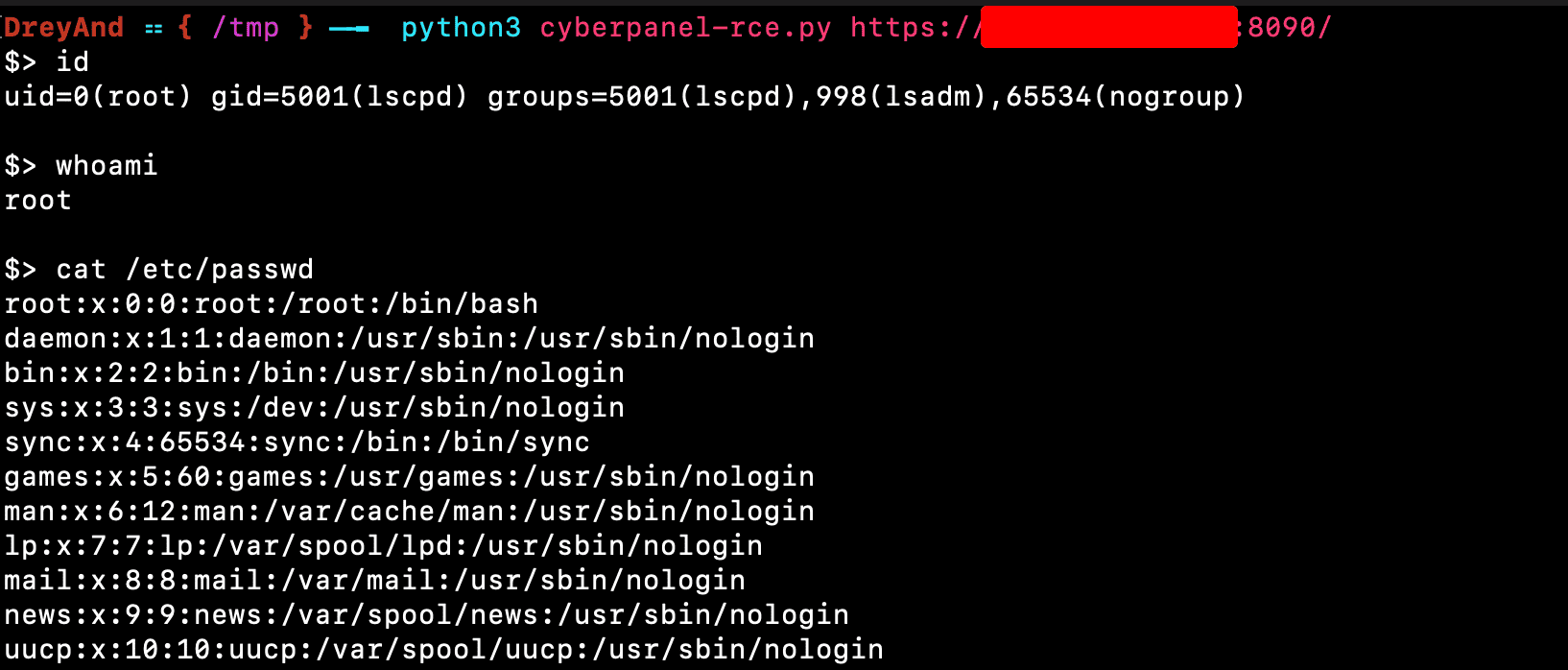
Three critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities impacting CyberPanel, a widely used web hosting control panel, are under active exploitation. Threat actors are leveraging these vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2024-51567, CVE-2024-51568, and CVE-2024-51378, to compromise servers and deploy PSAUX ransomware. The vulnerability affects CyberPanel versions 2.3.6 and 2.3.7 and permits unauthenticated attackers to gain root access, enabling complete control over affected systems.
The PSAUX ransomware campaign exploited multiple zero-day vulnerabilities in CyberPanel versions 2.3.6 and possibly 2.3.7, as disclosed by cybersecurity researchers DreyAnd and Luka Petrovic. The vulnerabilities, which allow for unauthenticated remote root access, were designated with the following CVEs, each assigned a maximum CVSS score of 10:
- CVE-2024-51567: This vulnerability lies in the upgrademysqlstatus function within CyberPanel’s databases/views.py. By bypassing security middleware and leveraging shell metacharacters in the statusfile property, attackers gain remote command execution capability.
- CVE-2024-51568: Another severe flaw, this issue involves command injection via completePath in the ProcessUtilities.outputExecutioner() function. Attackers are able to execute arbitrary commands through file upload in the File Manager, achieving remote code execution without authentication.
- CVE-2024-51378: Recently disclosed by Petrovic, this vulnerability affects the getresetstatus function in dns/views.py and ftp/views.py. Similar to the others, it allows remote command execution by bypassing the middleware, making it a high-risk flaw.
Threat intelligence from LeakIX, a known vulnerability search engine, revealed that 21,761 exposed CyberPanel instances were online as of October 26, with nearly half located in the United States. These instances collectively managed over 152,000 domains and databases, forming a massive target for ransomware operators.
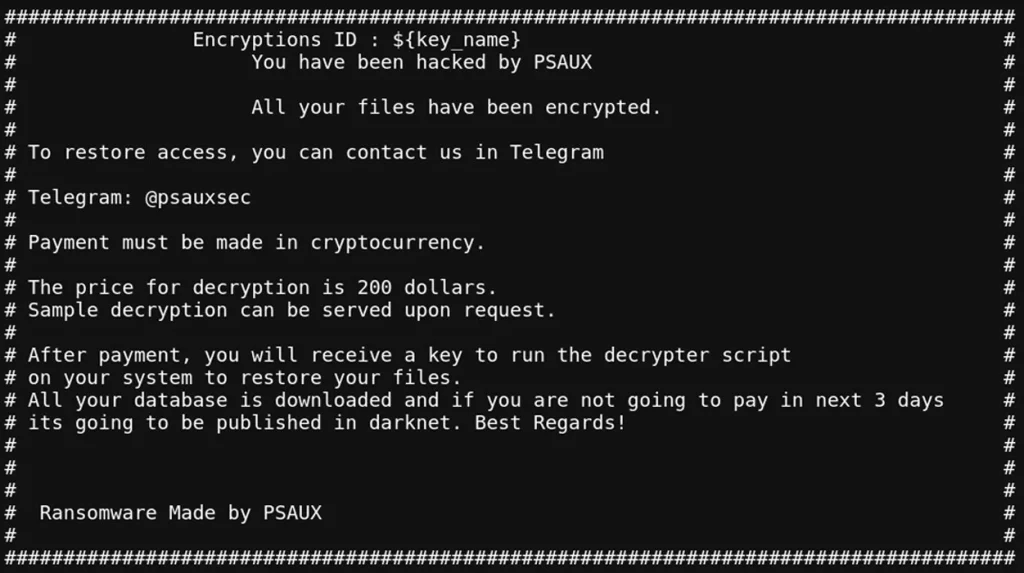
PSAUX ransom note | Image: LeakIX
The PSAUX ransomware, which first surfaced in June 2024, is designed to infiltrate web servers through both vulnerabilities and configuration weaknesses. Upon exploitation, PSAUX performs the following malicious actions:
- Encryption: Generates unique AES keys for encrypting files, rendering server data inaccessible.
- Ransom Notes: Creates index.html ransom notes in every directory and displays a copy in /etc/motd, visible upon login.
- RSA Encryption: Encrypts the AES keys and Initialization Vector (IV) with an embedded RSA key, saving the results as /var/key.enc and /var/iv.enc.
This attack leveraged specialized scripts, including ak47.py for exploiting CyberPanel’s vulnerabilities and actually.sh for file encryption.
In response to the attack, LeakIX and cybersecurity researcher Chocapikk managed to obtain scripts related to the PSAUX operation. LeakIX subsequently released a decryptor for PSAUX-encrypted files. However, administrators are cautioned to exercise care: the decryptor’s success relies on the ransomware operators’ use of known encryption keys. If an incorrect decryption key is applied, it could result in irreversible data loss. Users are advised to create backups before attempting decryption.
On October 29, CyberPanel issued an official statement acknowledging the vulnerabilities, crediting the researchers for their rapid reporting, and detailing remediation steps for affected users:
- For Users with SSH Access: Follow CyberPanel’s update guide to patch the vulnerabilities.
- For Users without SSH Access: In cases where SSH access has been restricted, contact hosting providers to temporarily lift IP blocks or enable port 22 to facilitate updating.
CyberPanel users are strongly urged to update their installations to the latest patched versions available on GitHub.



