SugarGh0st RAT Targets U.S. Artificial Intelligence Experts
Proofpoint, a leading cybersecurity firm, has uncovered a concerning campaign targeting American organizations and individuals involved in artificial intelligence (AI) research. The campaign, dubbed UNK_SweetSpecter, utilizes a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) known as SugarGh0st to infiltrate systems and exfiltrate sensitive data.
SugarGh0st RAT, a customized variant of the older Gh0stRAT, has historically been utilized by Chinese-speaking threat actors. Initially reported by Cisco Talos in November 2023, the SugarGh0st RAT was primarily seen targeting users in Central and East Asia. However, the recent shift in focus to American AI experts marks a significant development in its deployment.

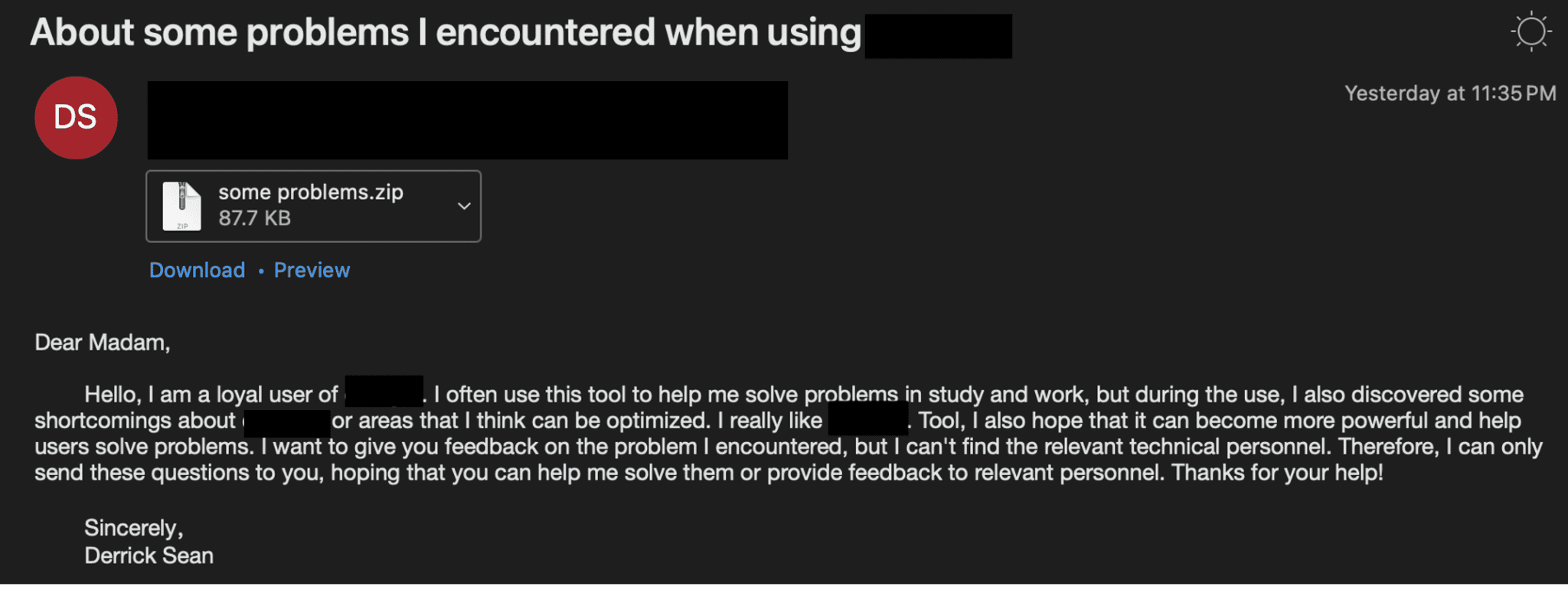
Lure email | Image: Proofpoint
In the May 2024 campaign, UNK_SweetSpecter used a free email account to send AI-themed lures to targeted individuals. These emails contained a zip archive, enticing the recipients to open it. Once the zip file was opened, the infection chain closely mimicked “Infection Chain 2” as previously described by Cisco Talos.
Upon delivery of the zip file, the attached LNK shortcut file deployed a JavaScript dropper. This LNK file bore a striking resemblance to those publicly available from Talos’ research, featuring similar metadata artifacts and spoofed timestamps. The JavaScript dropper then executed a multi-stage process:
- Decoy Document: A decoy document was displayed to the recipient to mask the malicious activity.
- ActiveX Tool: The dropper registered and abused an ActiveX tool for sideloading.
- Base64 Encoding: It deployed an encrypted binary, all encoded in base64.
While the decoy document distracted the recipient, the JavaScript dropper installed the necessary libraries to run Windows APIs directly from the JavaScript. This setup enabled the execution of a multi-stage shellcode derived from DllToShellCode, which then XOR decrypted and aplib decompressed the SugarGh0st payload. This payload facilitated keylogging, command and control (C2) communications, and data exfiltration.
Proofpoint’s analysis revealed that UNK_SweetSpecter had shifted its C2 communications from previously observed domains to a new domain: account.gommask[.]online. This domain shared hosting with account.drive-google-com[.]tk on IP address 103.148.245[.]235 before moving to 43.242.203[.]115. All identified infrastructure appears to be hosted on AS142032.
While Proofpoint cannot definitively attribute these campaigns to a specific state actor, the involvement of Chinese language operators is strongly suggested by linguistic artifacts found in the malware. The timing of this campaign coincides with a May 8, 2024, report from Reuters, which revealed heightened U.S. efforts to limit Chinese access to generative AI technologies. This context supports the hypothesis that Chinese-aligned cyber actors are targeting American AI experts to advance Chinese AI development goals.
This campaign underscores the growing threat of cyber espionage targeting the AI industry. Organizations and researchers in this field must be extra vigilant in their security practices.