Thousands of VMware ESXi Instances Exposed to Critical CVE-2024-22252 Vulnerability
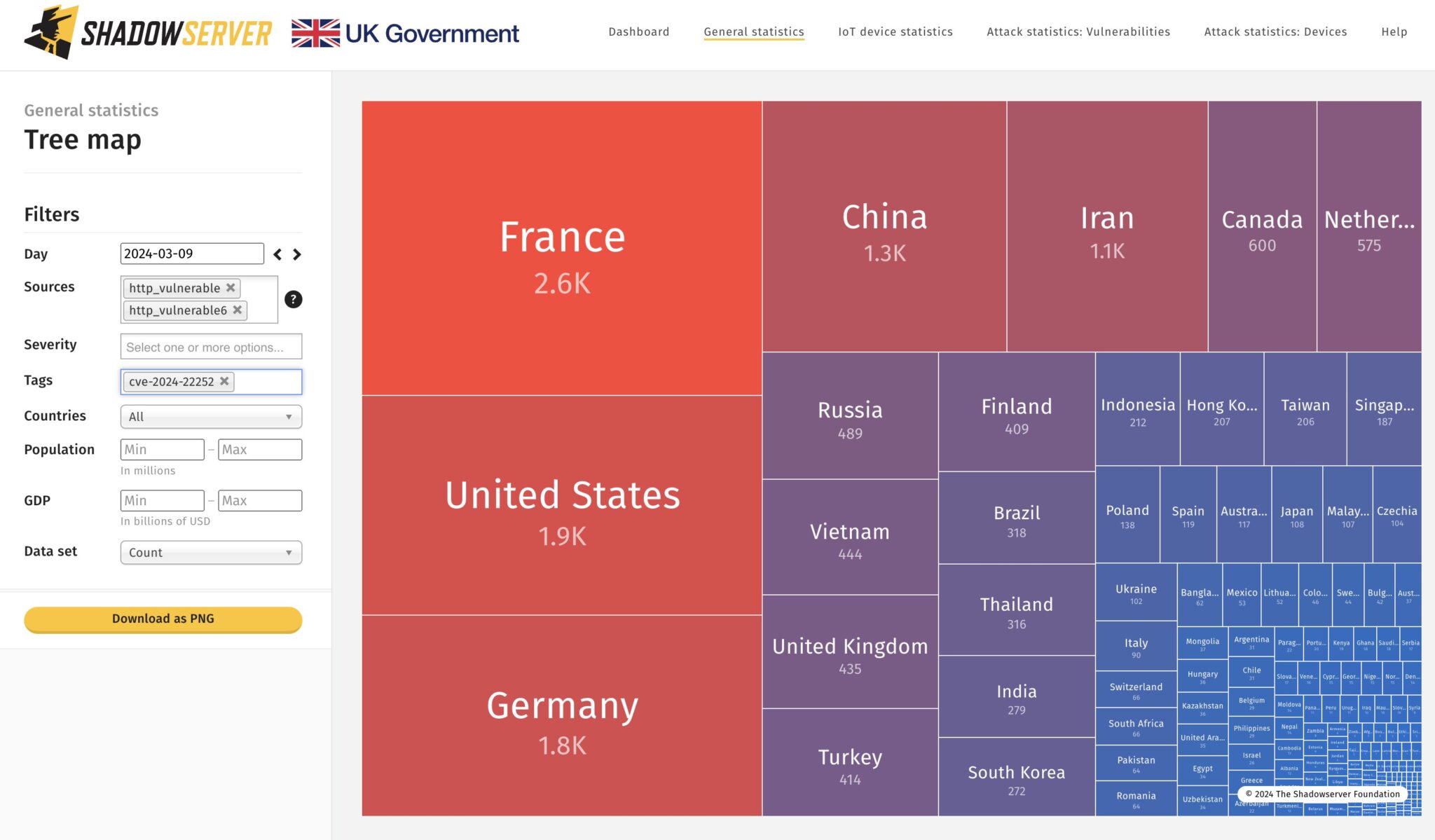
Today, Security researchers at The Shadowserver Foundation have sounded the alarm after discovering approximately 16,500 VMware ESXi instances exposed to a critical security flaw. The vulnerability, designated as CVE-2024-22252, could potentially allow attackers to execute malicious code on affected systems.
VMware addressed the vulnerability (a use-after-free bug in the XHCI USB controller) last week. However, the new data from Shadowserver highlights the vast number of systems still at risk. The vulnerability has been rated as Critical for VMware Workstation/Fusion installations (CVSS score 9.3) and Important for ESXi implementations (CVSS score 8.4).

Image: The Shadowserver Foundation
Key Points:
- Exploitation: Attackers with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine could exploit the vulnerability to execute code with increased privileges on the host system.
- Worst-Case Scenario: In Workstation and Fusion setups, successful exploitation could lead to compromise of the entire machine where these products are installed.
- Geographical Distribution: The Shadowserver data further reveals a geographical distribution of the vulnerability, with France leading the pack with 2,600 vulnerable instances. It is closely followed by the United States, with 1,900 instances, and Germany, with 1,800.
Call to Action
VMware strongly recommends that all organizations running affected software apply the available patches immediately. Failure to patch leaves systems open to potential attacks that could result in data theft, system disruption, or even ransomware deployment.
Additional Considerations:
- Organizations that lack the resources or ability to patch immediately should consider disabling USB controllers in their virtual machines to mitigate the risk, though this will impact usability.
- The widespread nature of this vulnerability underscores the importance of timely patch management in enterprise environments.
Security experts advise organizations to remain vigilant and prioritize critical security updates, especially for widely-used virtualization platforms like VMware ESXi.





