Source

Cloud computing has become a key component of today’s modern IT infrastructure. Cloud computing offers businesses a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution. Cloud Computing is particularly lucrative for small and medium-sized businesses because these companies only pay for the resources they actually use, and there is no requirement for significant upfront capital investment. As a result of the expansion of digital technologies, cloud computing has evolved into an essential component for businesses to implement if they wish to maintain efficient operations and maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
The cloud has changed how businesses handle their data, applications, and services. Companies may better satisfy client needs because of the cloud’s scalability, which lets them easily increase or decrease resources. Cloud computing also reduces capital costs by eliminating the need for expensive hardware and software, allowing businesses to focus on their core skills.
Additionally, a new obstacle related to cloud data security has emerged. In today’s world, businesses have a greater responsibility to protect not just their data but also their infrastructure. Encryption, multi-factor authentication, and a wide variety of other security measures are only some of the options available to organizations.
Cloud Security Challenges and Their Remediations
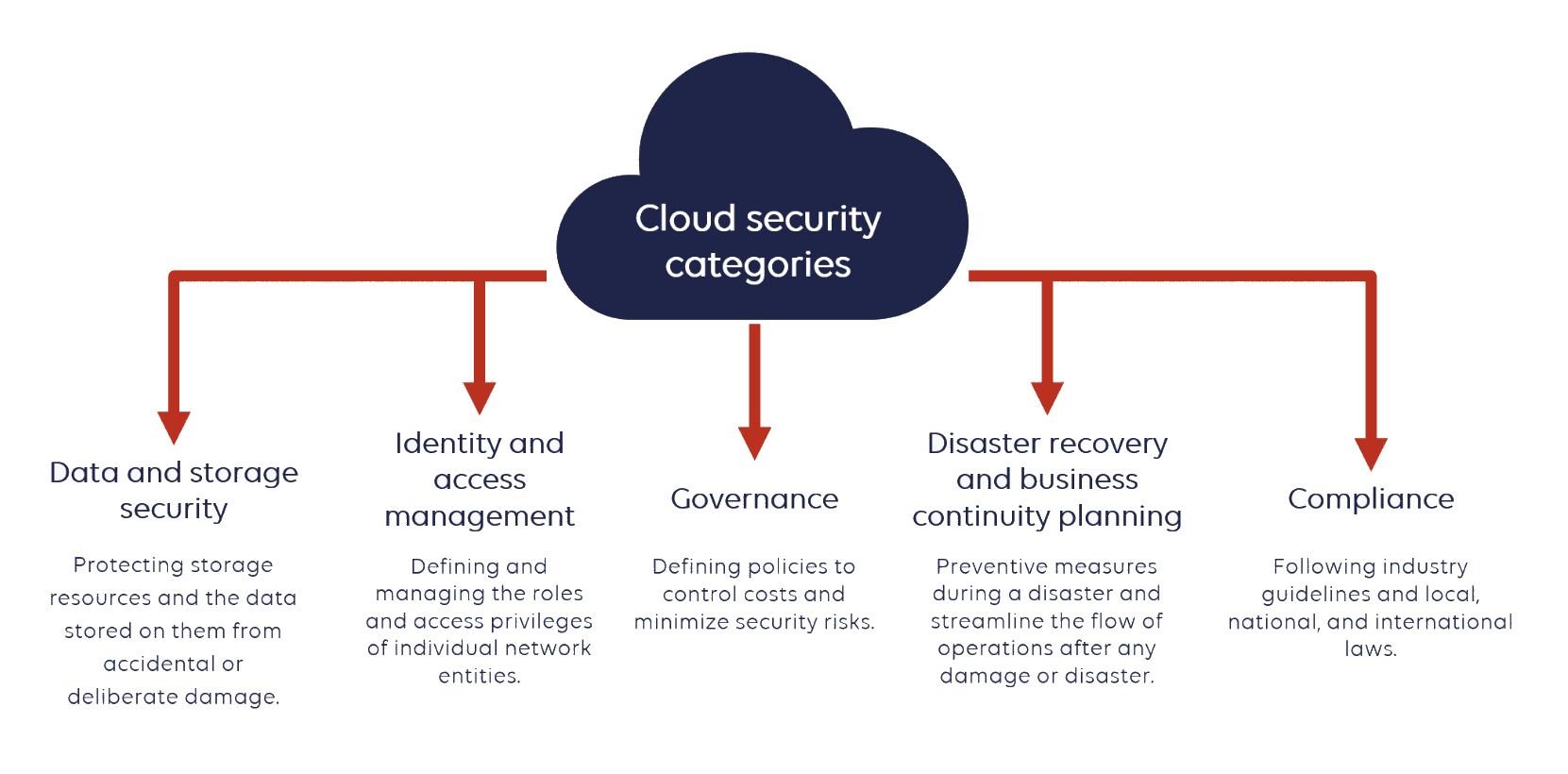
Since the cloud has become the foundational element of today’s IT infrastructure, this may give rise to a number of cloud data security issues. Given that the entire IT infrastructure is now hosted in the cloud, even small misconfigurations can result in significant issues. Let’s talk about some of the problems associated with cloud security and the remedies to those issues.
Cloud Sprawl
Cloud sprawl is when an organization uses several cloud services or providers simply to implement a multi-account configuration, that too without having a centralized management strategy in place. Because of this, an organization’s visibility into its resources is restricted, which can lead to problems such as an insufficient view of the resources being deployed, misconfigurations during deployment, and an inability to monitor all of the resources properly.
Organizations should implement a centralized cloud management strategy to tackle the issue of cloud sprawl. This strategy should include connecting all of the services and their logs in a centralized system, including inventory management and asset management, enforcing appropriate security policies, and adding appropriate visibility through the use of SIEM. Easily gaining visibility and effectively managing an organization’s resources are made easier by adding each of these governance policies.
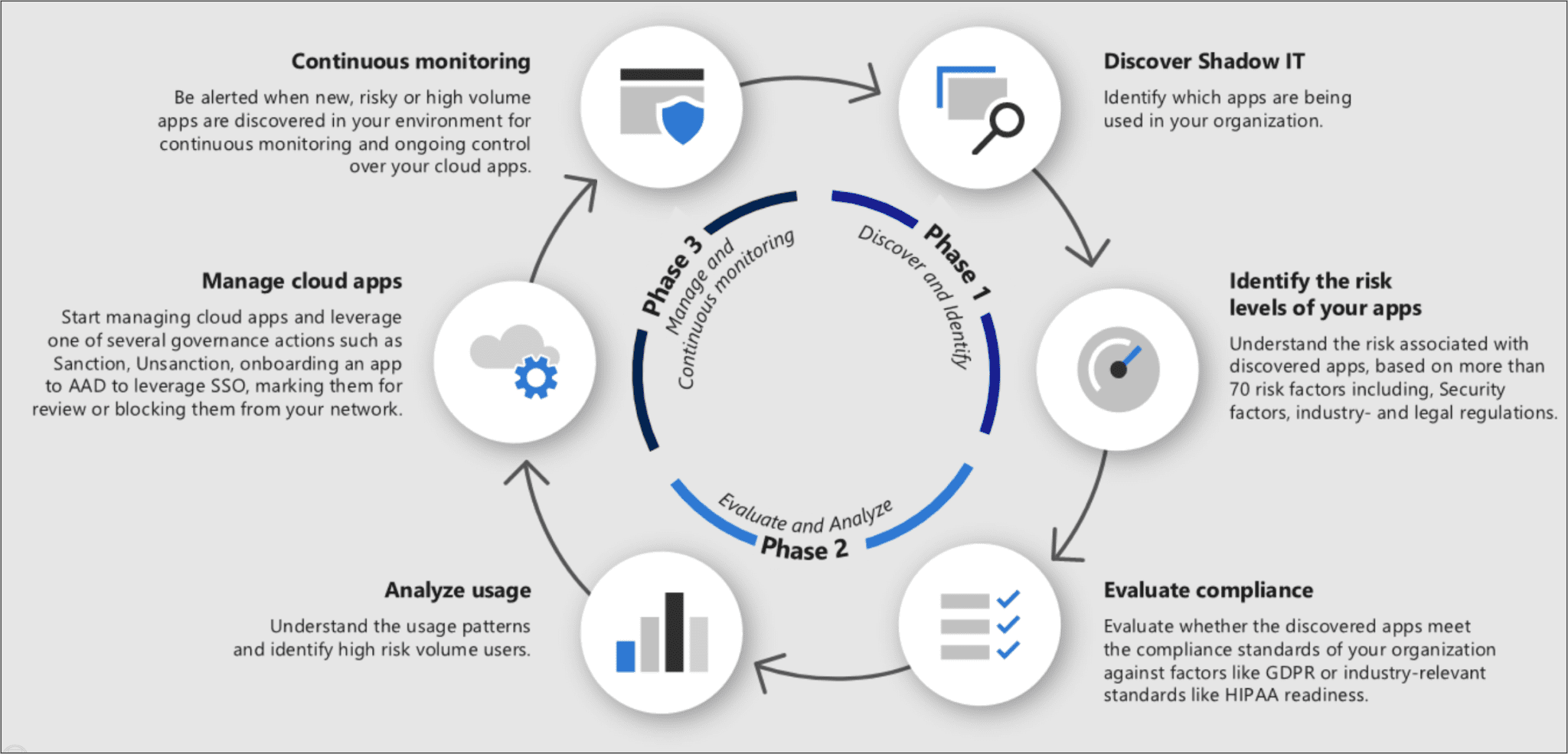
Shadow IT

The term “shadow IT” refers to employees working for an organization using unauthorized cloud services or apps to access or store information related to the organization or its clients. This can occur when employees bypass the organization’s IT department and acquire cloud services directly, usually without sufficient vetting or security controls being in place. Shadow IT can expose businesses to many risks, including compromising sensitive data, violating rules and regulations, and increasing operating expenses.
The issue can be tackled using cloud monitoring technologies that can assist businesses in identifying unauthorized cloud usage and shadow IT. This can include tools that monitor network traffic, log behavior, and track how cloud services are used. In addition, further reducing the risks associated with Shadow IT, and establishing and implementing appropriate IT policies and IAM policies might be of value.
Policy Misconfigurations
Misconfiguration of security policies is a typical root cause of cloud security incidents, which can lead to data breaches, account hijacking, and other types of security issues. These issues occur when infrastructure is deployed using improper practices, such as creating S3 buckets without disabling public access or not putting access restrictions related to public IPs on internal EC2 instances. In addition, some other issues may arise due to policy misconfiguration, such as access control issues, etc.
To tackle misconfiguration, organizations should implement practices such as ensuring that buckets or infrastructure can only be deployed using cloud formation templates, further adding incident response if a policy is violated. Organizations should perform proper vulnerability scanning and penetration testing to identify such issues related to configuration.
Lack of Visibility and Control
Insider threats are one of the most serious risks now associated with cloud security. This is because employees frequently have access to sensitive data and critical systems, such as the systems that include personally identifiable information (PII) or sensitive data related to clients. Insider risks can originate from hostile employees who intentionally breach sensitive information for financial gain. Insider threats can also originate from employees who use credentials that are easy to guess or are overly simplistic and, as a result, pose a greater risk of being compromised and exposing sensitive information.

Organizations should use multi-factor authentication to restrict cloud resource access to authorized personnel. This can protect critical data and systems from compromised accounts. To detect suspicious or abnormal behavior in the cloud, organizations should monitor employee activities such as data access, logins, and network activity.
Usage of Outdated Software and Packages
When it comes to cloud security, using outdated applications and packages is a major challenge many companies face. Outdated softwares and packages may have security flaws that, if exploited, could allow unauthorized users to gain access to the cloud environment or steal sensitive data. These packages can be found in services that have been deployed for a significant amount of time and have not been reviewed for updates. As a result, they have some critical security flaws.
To tackle this issue, businesses should do reviews of the services and instances they have deployed at regular intervals, such as every 30 or 90 days. If they discover any packages or specifics that are outdated, they should be updated. And if an instance or program in question is not required, it should be withdrawn.
Conclusion
Organizations face a wide variety of challenges due to the complexity and constant change that characterize cloud security. Several risks need to be addressed to shore up the security of cloud settings, including threats posed by insiders and software and packages that have become obsolete. However, there are measures that companies may take to strengthen their cloud security and address these concerns. Organizations can overcome these issues by employing appropriate policies, monitoring systems, and educating their employees.