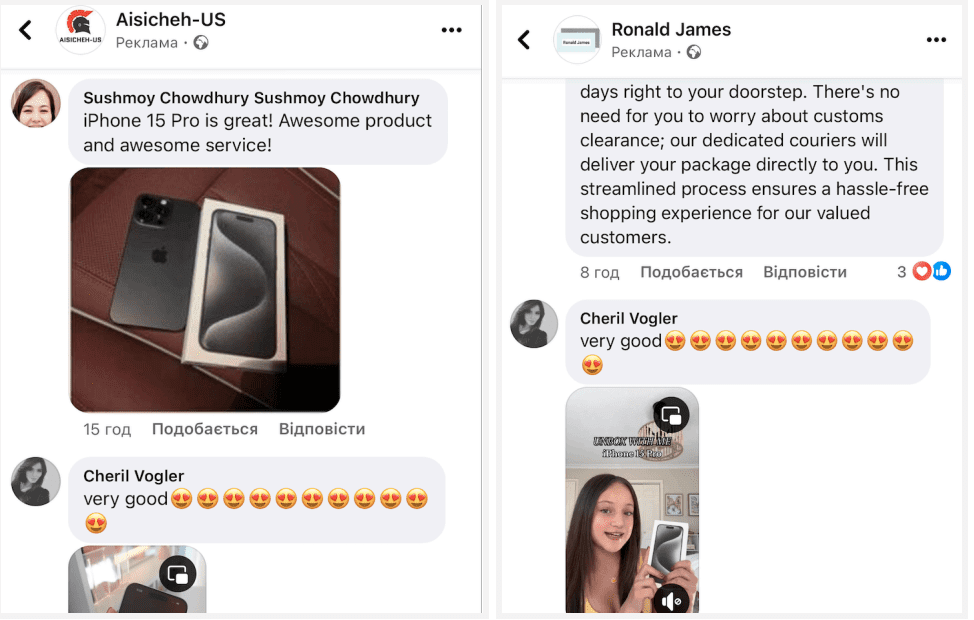
Identical comments from the user “Cheril Vogler” indicate a concerted effort to promote ads linked to the scam websites aisicheh[.]com (left) and debuited[.]com (right) (Source: facebook[.]com)
In a significant development in the fight against cyber fraud, Recorded Future’s Payment Fraud Intelligence team has identified a sophisticated scam campaign, dubbed “ERIAKOS.” This campaign leverages over 600 domains to disseminate fraudulent e-commerce websites, targeting victims primarily through mobile devices and social media ads.
The ERIAKOS scam campaign stands out due to its advanced tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). The campaign meticulously screens victims based on their access method, only presenting the scam websites to mobile users who reach them through ad lures. This strategy likely helps evade detection by automated scanners, making the scam more resilient and prolonging the lifespan of the malicious domains.
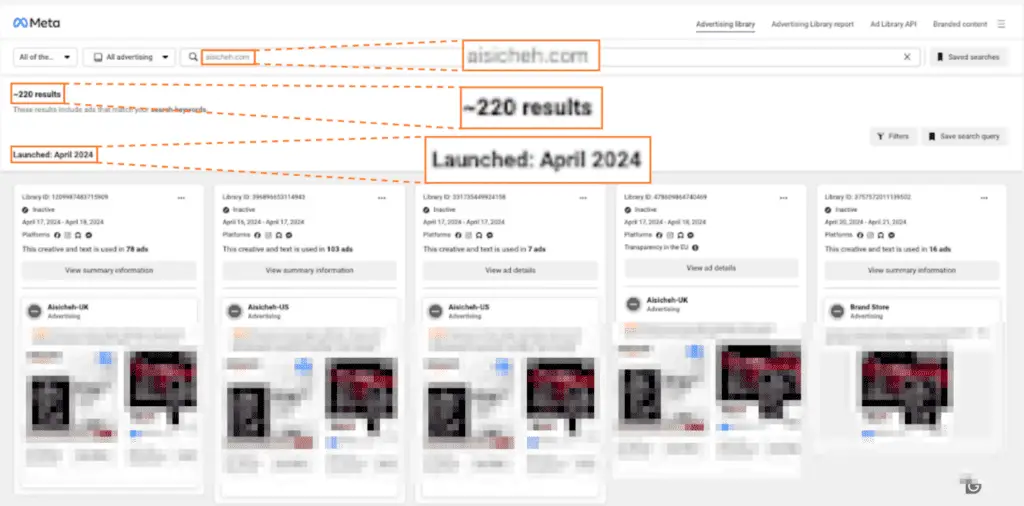
- Network of 608 Scam Domains: The ERIAKOS campaign utilizes a vast network of domains, each designed to deceive users into believing they are interacting with reputable brands.
- Mobile-Only Targeting: By focusing exclusively on mobile users accessing the sites via social media ads, the campaign reduces the risk of detection and increases its effectiveness.
- Brand Impersonation: The scam sites primarily impersonate two well-known brands, including a major e-commerce platform and a power tools manufacturer, to exploit brand trust and urgency through bogus sales offers.
- Fraudulent Transactions: Victims are led to complete transactions on these scam sites, where their financial and personal data is stolen.
Recorded Future identified four primary technical indicators associated with the scam websites:
- Content Delivery Network: All scam sites used oss[.]eriakos[.]com.
- Domain Registrar: Domains were registered with Alibaba Cloud Computing Ltd.
- IP Addresses: Two specific IP addresses (47[.]251[.]129[.]84 and 47[.]251[.]50[.]19) were consistently used.
- Domain Misconfiguration: The scam domains exhibited specific misconfigurations between their main domains and www subdomains.
The scam campaign also involves sophisticated exploitation of merchant accounts. These accounts process victim transactions through major card networks and Chinese payment service providers (PSPs). The integration of these merchant accounts complicates the detection and blocking of fraudulent transactions.
To mitigate this threat, Recorded Future recommends:
- Blocklisting Suspicious Merchant Accounts: Financial institutions should block customer transactions with the identified merchant accounts linked to the scam.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of customer transactions for signs of fraud associated with these accounts.
- Customer Awareness: Educating customers about the risks of interacting with unfamiliar e-commerce sites and the importance of verifying the legitimacy of online stores.
To read the entire analysis, click here to download the report as a PDF.
Related Posts:
- Phishing Scam targets iOS user in India
- Massive Scam Surge: Google Ads Fueling Fraud
- Cards on the Dark Web: Payment Fraud Booms