Image: The Shadowserver Foundation
Enterprise security firm Proofpoint has issued a critical warning regarding active exploitation attempts against Synacor’s Zimbra Collaboration platform. A recently disclosed security flaw, tracked as CVE-2024-45519, has been under attack since late September 2024, prompting urgent calls for patching. This vulnerability, affecting Zimbra’s postjournal service, allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary commands on compromised systems, posing a severe threat to the platform’s global user base.
CVE-2024-45519 is a command injection vulnerability discovered by independent security researcher Alan Li (alias lebr0nli), and patched by Synacor in early September 2024. The flaw stems from insufficient sanitization of user inputs passed to the popen function in the unpatched versions of Zimbra’s postjournal service. This service, designed to handle journaled emails, can be abused by attackers to remotely execute commands on vulnerable systems without requiring authentication. While the postjournal feature is not enabled on all systems, its presence on certain Zimbra servers has already led to widespread exploitation attempts.
Proofpoint began observing malicious campaigns targeting CVE-2024-45519 on September 28, 2024. The attackers have adopted a novel strategy, sending spoofed Gmail messages to bogus CC addresses to trick Zimbra servers into processing the emails as commands. These emails contain Base64-encoded strings that, once parsed, are executed by the Zimbra server using the sh utility. The exploit allows attackers to gain remote control over vulnerable servers.
The first signs of exploitation emerged just one day after Project Discovery, a vulnerability research group, released technical details of the flaw. The release gave attackers the information necessary to launch attacks, leading to a sharp rise in exploitation attempts. As a result, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added CVE-2024-45519 to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies have been given an October 24, 2024, deadline to remediate the vulnerability.
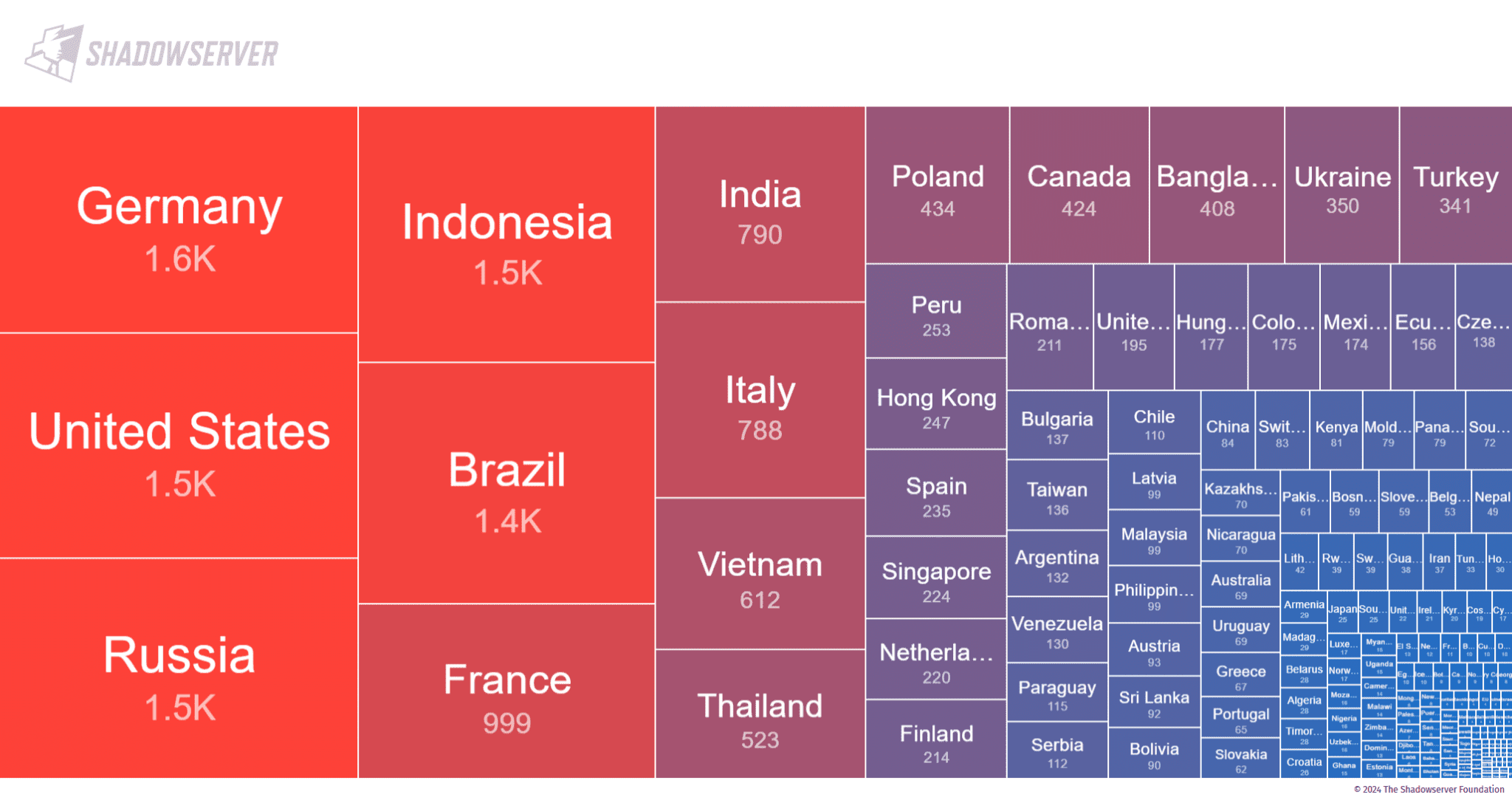
According to the Shadowserver Foundation, as of October 4, 2024, more than 19,600 unpatched Zimbra instances remain exposed to this vulnerability. Germany, the U.S., and Russia top the list of affected countries, each with over 1,500 vulnerable servers.
We are scanning for & reporting Zimbra IPs likely vulnerable to CVE-2024-45519 (CVSS 9.8 RCE, NVD entry: https://t.co/2GAEUJdy8a)
Over 19.6K unpatched instances seen on 2024-10-04.
Top: Germany (1.6K), US (1.6K), Russia (1.5K).Country tree map: https://t.co/Dycn7ePVfX pic.twitter.com/ytjfLMgiBo
— The Shadowserver Foundation (@Shadowserver) October 5, 2024
Zimbra administrators are urged to apply the latest security patches immediately. The vulnerability has been addressed in the following patched versions of Zimbra Collaboration:
- 8.8.15 Patch 46
- 9.0.0 Patch 41
- 10.0.9
- 10.1.1
Security engineer Ashish Kataria from Synacor emphasized the importance of applying these updates, stating: “While the postjournal feature may not be enabled on all systems, patching is critical to prevent potential exploitation.” For systems where the postjournal feature is not used, Kataria recommended removing the postjournal binary temporarily until the patch can be applied.
Related Posts:
- Zimbra Email Servers Under Attack: CISA Flags CVE-2024-45519 as Actively Exploited
- PoC Exploit Releases for Zimbra RCE Flaw CVE-2024-45519: Mass Exploitation Detected
- CVE-2023-41106: Zimbra Collaboration Suite Vulnerability Could Allow Unauthenticated Access
- CVE-2024-33533 to 33536: Zimbra Users at Risk of XSS and LFI Attacks
- New APT Exploits Zimbra Vulnerability to Target European Military and Diplomatic Entities