In the shadowy corners of the digital world, where the battle between cybersecurity defenders and attackers unfolds with relentless intensity, a new adversary has emerged, wielding the sophisticated tool of deception and evasion: LODEINFO malware. This fileless menace, which has haunted cyberspace since December 2019, represents a significant shift in the tactics of cybercriminals, particularly those targeting the Japanese sector, including media, diplomacy, public institutions, defense industries, and think tanks. Recently, security researchers from ITOCHU Cyber & Intelligence Inc. analyzed each version of the LODEINFO malware and identified changes.
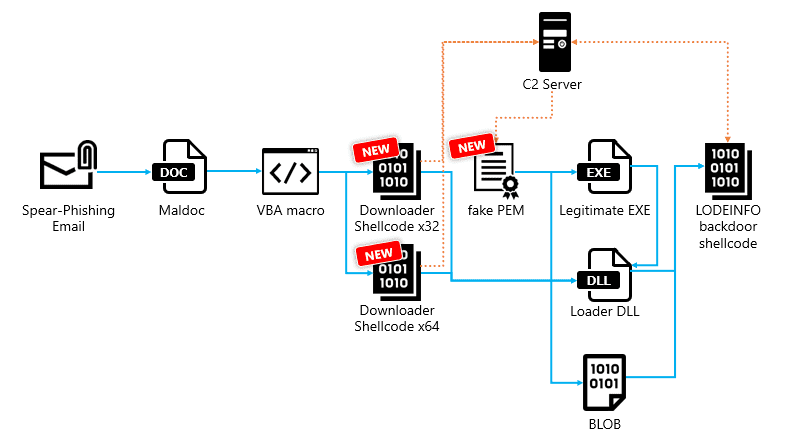
LODEINFO, a spearhead in the arsenal of the infamous APT group APT10, showcases the alarming evolution of cyber threats. It infiltrates systems through seemingly innocuous spear-phishing emails, employing malicious Word documents to execute its sinister agenda. Initially, Excel files were also used, but the attackers have refined their methods to increase their success rate.

The malware’s infection process is a masterclass in subterfuge and technological prowess. Once the malicious document is opened, LODEINFO injects itself into the system’s memory, sidestepping traditional detection mechanisms with ease. The malware’s ability to adapt is evident in its continuous development, with multiple versions being unveiled as the attackers refine their approach to exploit and conquer.
Among the most innovative tactics employed by LODEINFO is the use of Remote Template Injection. This technique abuses Microsoft Word’s template feature to execute malicious macros hosted on an attacker-controlled server, making detection by security solutions a formidable challenge. The malware’s design is a labyrinth of evasion techniques, including obfuscation through Base64 encoding and sophisticated payload deployment methods that ensure its malicious operations go undetected.
Despite efforts to counteract its spread, LODEINFO remains a potent threat, with new versions such as v0.7.3 demonstrating the attackers’ commitment to evolving their techniques. The malware’s complex architecture, including its downloader shellcode and backdoor capabilities, highlights a disturbing trend toward more resilient and adaptable cyber threats.
The persistence and sophistication of LODEINFO malware underline the critical need for advanced defensive strategies. Cybersecurity professionals recommend the adoption of memory scanning technologies capable of detecting fileless malware, alongside a comprehensive approach to security that encompasses the latest research and countermeasures.