Beware of Fake Advanced IP Scanner: Malicious Installer Delivers CobaltStrike Backdoor
Trustwave SpiderLabs has uncovered a dangerous cyberattack campaign targeting users of the popular network scanning tool, Advanced IP Scanner. Threat actors are distributing a compromised version of the installer through a typo-squatted domain, which ranks highly in search engine results.
Advanced IP Scanner is a widely-used free network scanner for Windows, employed by IT administrators to analyze local area networks (LANs) and gather information about connected devices. However, for the past year, this tool has been targeted in a watering hole attack. Cybercriminals have been mimicking the legitimate Advanced IP Scanner website and leveraging Google Ads to ensure their malicious site ranks highly in search results for “Advanced IP Scanner.”
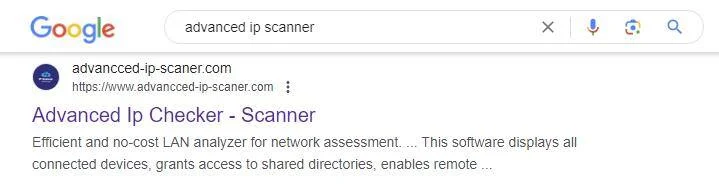
Search results for Advanced IP Scanner may direct users to a malicious domain | Image: Trustwave SpiderLabs
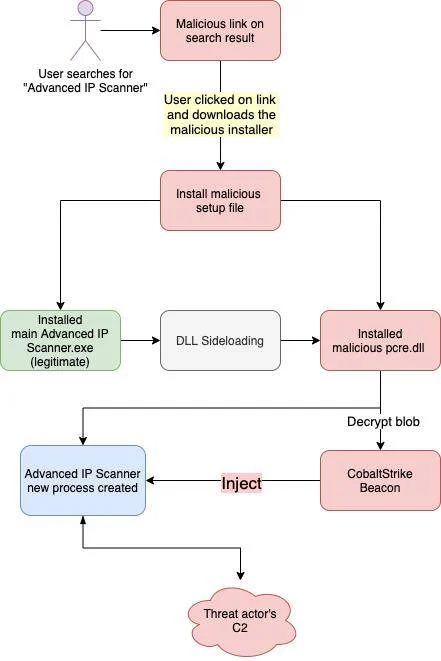
The malicious installer, Advanced_IP_Scanner_2.5.4594.1.exe (MD5: 723227f3a71001fb9c0cd28ff52b2636), downloaded from the fake website contains a DLL named pcre.dll (MD5: 21cdd0a64e8ac9ed58de9b88986c8983), identified as malicious. In the genuine software, this DLL provides a Perl Compatible Regular Expressions library. However, in the compromised version, it is side-loaded to inject a CobaltStrike beacon into a newly created parent process.
The attack sequence is as follows:
- Initial Execution: The main Advanced IP Scanner program calls the “pcre_study” module from the malicious DLL, which allocates memory in the parent process’s address space and copies the encrypted CobaltStrike beacon into it.
- Decryption and Injection: The program then calls the “pcre_exec” module, which decrypts the CobaltStrike beacon. A new process for Advanced IP Scanner is created, and the decrypted CobaltStrike beacon is injected into this new process using the process hollowing technique.

Execution chain overview | Image: Trustwave SpiderLabs
Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly creative in their attack strategies, employing techniques such as typo-squatting, search engine optimization (SEO), and fake advertisements. To combat these threats, it’s essential to remain vigilant and continuously update cybersecurity practices.
This incident underscores the critical importance of downloading software only from trusted, official sources. IT administrators and security professionals must exercise caution when acquiring network tools and implement robust security measures, including endpoint protection and regular monitoring for unusual network activity.





