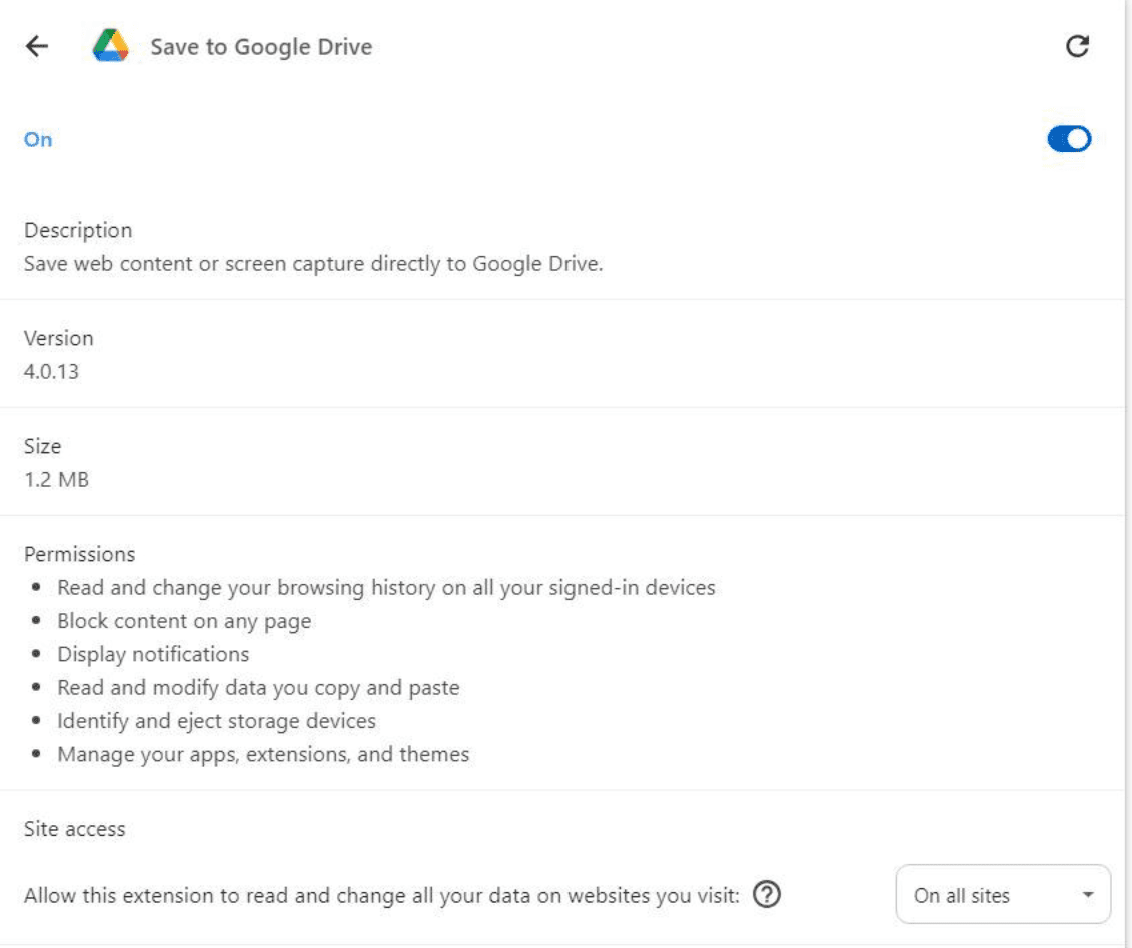
Malicious Chrome extension | Image: TRU
A new and sophisticated malware campaign has been detected by eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU), leveraging DLL side-loading to distribute the LummaC2 stealer and a malicious Chrome extension. This multi-stage attack, initiated through a deceptive drive-by download, ultimately aims to steal sensitive financial information and manipulate browser behavior.
The attack begins with victims inadvertently downloading a malicious ZIP archive, often triggered by a seemingly innocuous email or compromised website. The archive contains an MSI installer file, which, upon execution, cunningly uses a legitimate executable to sideload a malicious DLL. This DLL then downloads and decrypts the LummaC2 stealer and a PowerShell script from a command-and-control (C2) server.
Once the malicious DLL is loaded, it triggers a chain of events that ultimately deploys LummaC2 stealer. The stealer retrieves a PowerShell script encoded in base64, which downloads the next-stage payload from two-root[.]com. This payload, after being decrypted using two rounds of XOR operations, installs a malicious Chrome extension named “Save to Google Drive.”
This extension, however, is not the helpful tool it claims to be. Instead, it secretly interacts with popular services like Facebook, Coinbase, and Google Pay, potentially allowing attackers to manipulate financial transactions and steal sensitive data such as account balances and cryptocurrency addresses.
The malicious Chrome extension goes far beyond simply stealing financial data. It collects extensive device information, including system and hardware details, installed browser extensions, and cookies. It generates a unique identifier (UUID) for the compromised machine and sends all collected data back to the attackers’ C2 server.
The extension also has a browser manipulation component, opening nearly invisible popup windows to monitor specific URLs, such as Google Pay, YouTube, and Facebook pages. By doing so, it can intercept and manipulate user interactions, potentially capturing sensitive input like login credentials or two-factor authentication (2FA) codes.
Moreover, the extension targets popular email platforms like Gmail, Outlook, and Yahoo Mail. It dynamically injects web content to steal sensitive information, particularly targeting 2FA processes that use email verification codes. This makes it a particularly dangerous tool for intercepting authentication data.
The extension also includes CursedChrome, an implant that turns compromised Chrome browsers into HTTP proxies, enabling attackers to browse the web using the victim’s authenticated session across all websites. This technique allows attackers to impersonate victims and access sensitive online accounts undetected.
The C2 infrastructure supporting this attack is sophisticated. The malware communicates with C2 servers by decoding addresses embedded in Blockchain and mempool URLs. These URLs return data about a specific Bitcoin address and are used to manage communications between the malware and its operators. The attackers also rely on Base58-decoding techniques to extract C2 addresses, further obfuscating their activities.
Organizations and users are strongly advised to stay vigilant, avoid downloading suspicious files, and ensure that browser extensions are from trusted sources. Updating security software and monitoring for unusual browser behavior can also help mitigate the risks posed by this evolving threat.
Related Posts:
- LummaC2 Malware Uses Gaming Platform as C2 Server
- Beware! Fake Notion Installer Spreads Data-Stealing Malware
- LummaC2 and Raccoon Stealer: The Rise of Certificate Abuse in Malware
- ClearFake Campaign Employs Novel Social Engineering Tactic to Deliver LummaC2 Infostealer