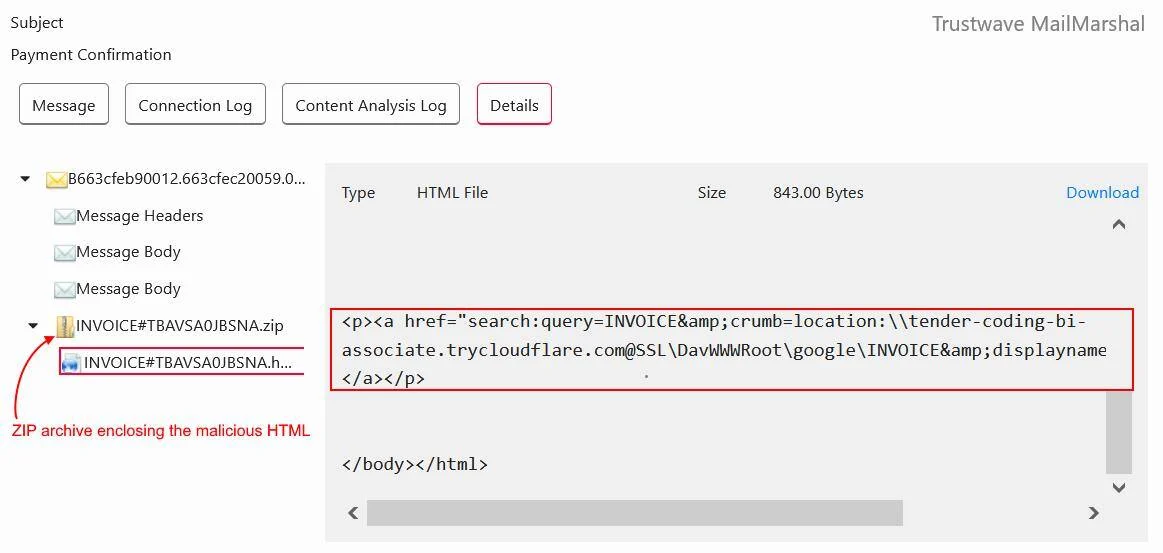
MailMarshal extracts the HTML file from the ZIP archive | Image: Trustwave SpiderLabs
A new, sophisticated malware campaign is targeting Windows users, leveraging the operating system’s built-in search functionality to deceive and potentially infect victims. This attack, dubbed “Search & Spoof” by Trustwave SpiderLabs, demonstrates a deep understanding of system vulnerabilities and user psychology.
The campaign begins with a seemingly innocuous phishing email containing an HTML attachment disguised as a routine document, such as an invoice. This attachment, when opened, triggers a chain of events designed to trick users into running malicious code:
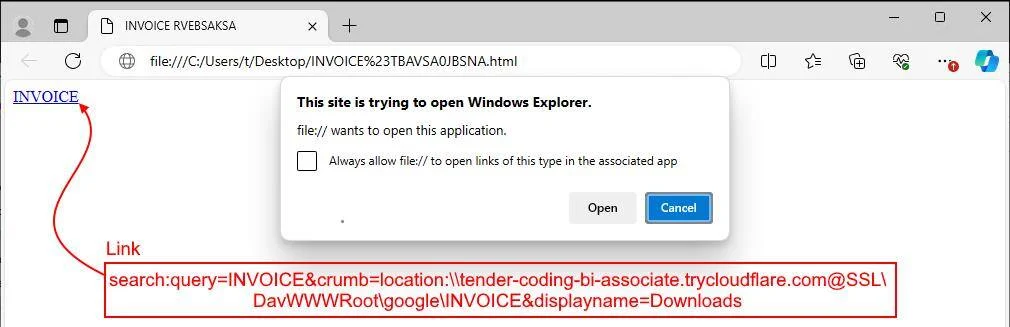
- Hidden Redirection: The HTML file contains code that instantly redirects the user’s browser to a malicious URL using the “search:” protocol.
- Exploiting Windows Search: This URL manipulates the Windows search function, making it appear as though the user is searching for a legitimate file in their “Downloads” folder.
- Malicious Shortcut: The search results display a shortcut file, which, when clicked, could execute a hidden batch script and potentially initiate further malicious activities.
The attackers cleverly abuse Cloudflare’s tunneling service to mask their malicious infrastructure, making the attack harder to detect. By exploiting the trust users place in familiar interfaces and routine actions like opening attachments, the attackers aim to bypass traditional security measures.
While the specific payload of this campaign remains unclear, the potential for harm is significant. Trustwave SpiderLabs recommends disabling the “search-ms” and “search” URI handlers in Windows to prevent exploitation of the search protocol. They have also deployed updates for their MailMarshal customers to detect and block emails containing the malicious HTML file.
To prevent the exploitation of the search-ms/search URI protocol, users can disable these handlers by deleting associated registry entries using the following commands:
This attack highlights the importance of user awareness and vigilance. Be wary of unsolicited emails and attachments, even those that appear to come from trusted sources. Always verify the legitimacy of links and files before clicking or opening them. Keep your operating system and security software updated to protect against known vulnerabilities.
By staying informed and taking proactive steps to secure your systems, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these types of attacks.