On May 22, Tencent Keen Security Lab released 14 common security vulnerabilities on various models of BMW. These vulnerabilities could be triggered by physical contact and remote non-contact. According to its official blog, all vulnerabilities and The attack methods have all been confirmed by BMW.
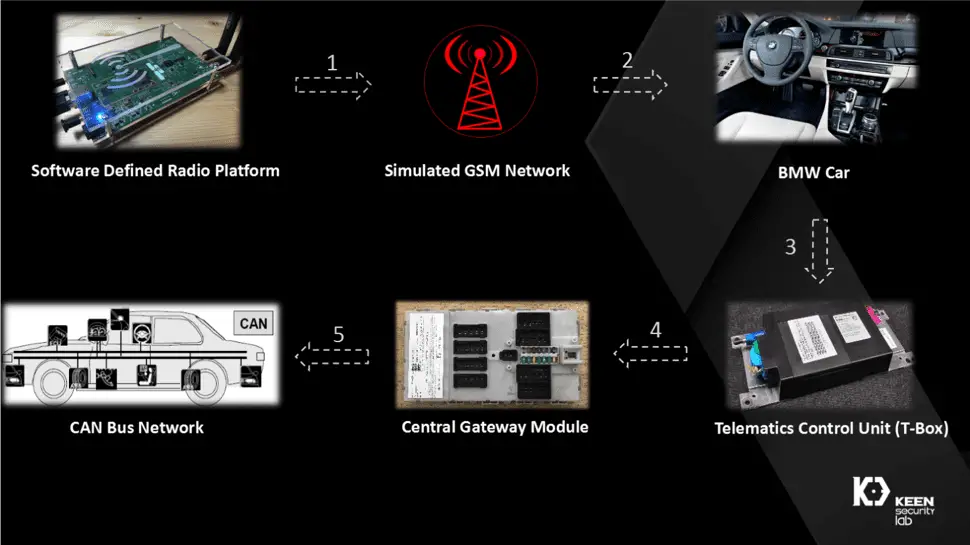
According to its official blog, the research began in January 2017. The laboratory conducted hardware implementation of head units, T-Boxes and Central Gateways of various BMW vehicles. After the study, the focus was placed on analyzing the vehicle’s exposure to the external attack surface (including GSM network, BMW remote service, BMW Internet driving system, remote diagnosis, NGTP protocol, Bluetooth protocol, USB, and OBD-II interface). The physical contact and remote non-contact attack of various models prove that it can remotely crack the car infotainment system, vehicle communication module, etc., and gain control over the CAN bus.
At present, Tencent Keen Security Lab has reported details of the vulnerabilities and attack chains to BMW and provided technical analysis and related repair suggestions.
After Tencent Keen Security Lab laboratory completed the cracking of the onboard communication module and infotainment system, after further analysis, the combined use of these security loopholes enabled a complete local attack chain and remote attack chain.
According to reports, the ultimate goal of the local and remote attack chains is to send diagnostic commands from the onboard gateway to different CAN buses (eg, PT-CAN, K-CAN) to affect the ECUs in the vehicle, which in turn affects the vehicle.
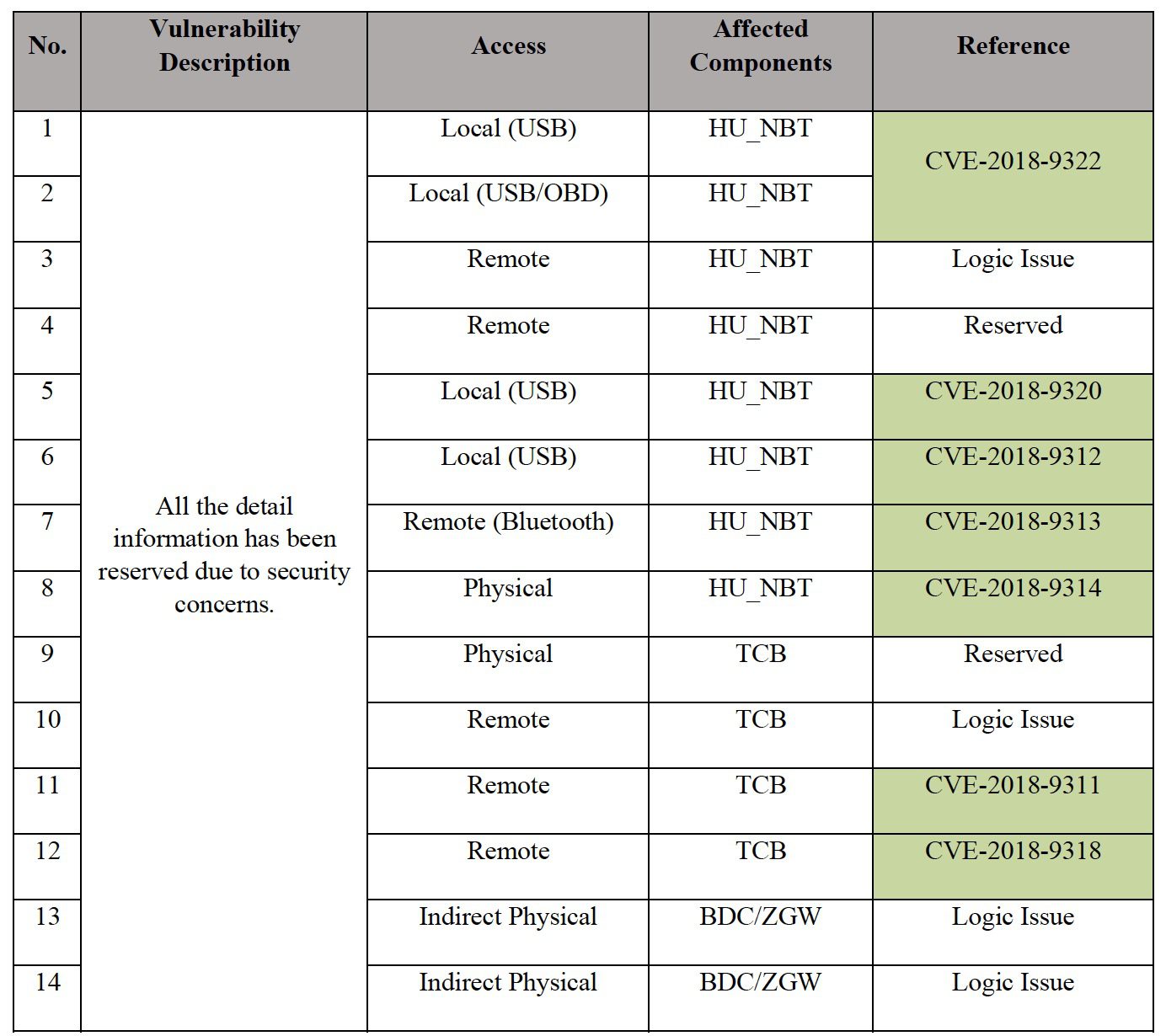
The loopholes mainly exist in the three modules of the head unit, T-Box and Central Gateway. Based on experimental experience, loopholes in the in-vehicle infotainment system can affect BMW. The models include the iSeries, the X Series, the 3 Series, the 5 Series, and the 7 Series. The vulnerabilities in the onboard communication module affect all BMW models equipped with this module since 2012.
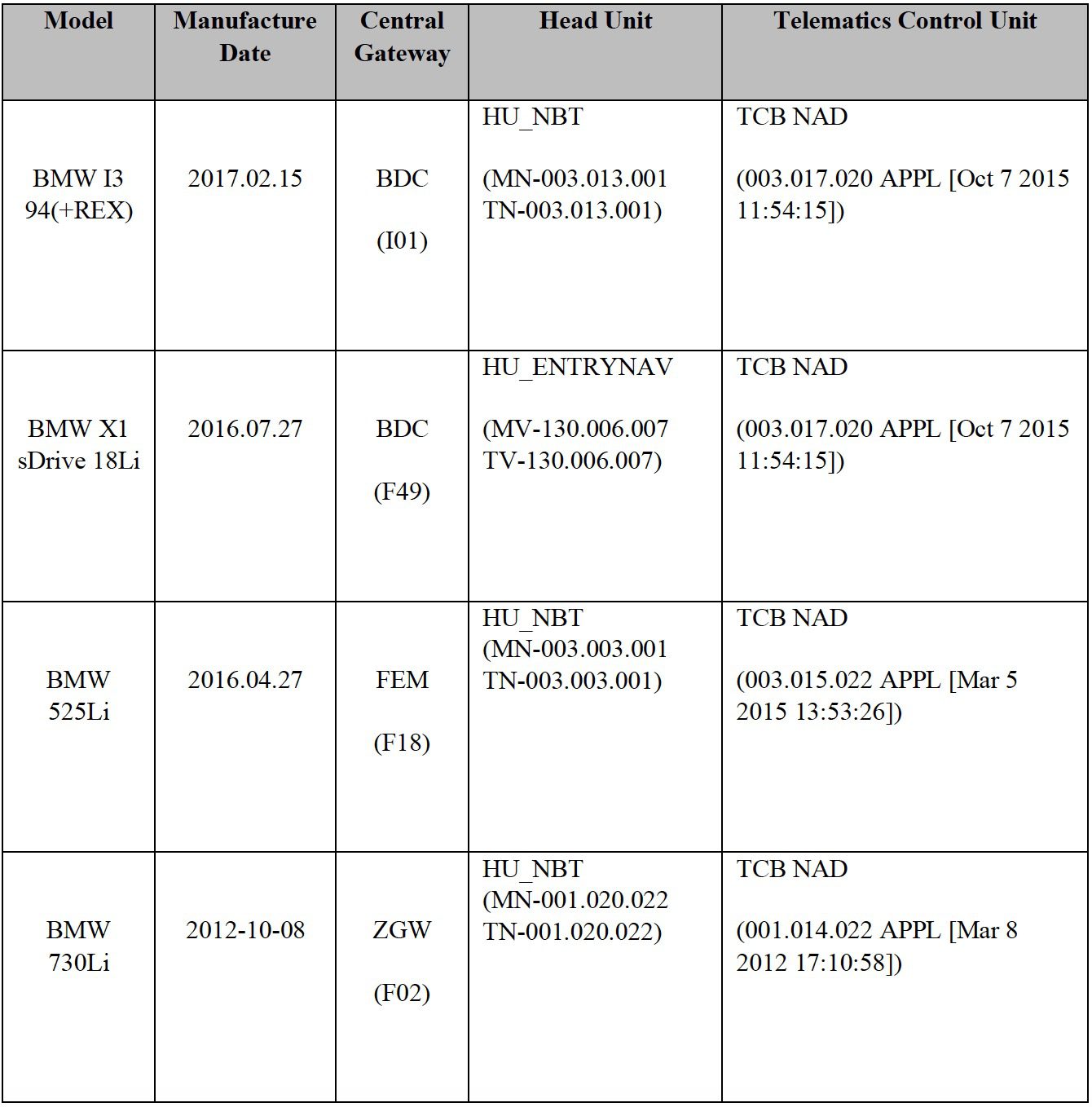
It is reported that all attacks that can be initiated through the cellular network, BMW has started repair measures in March 2018, these measures have been pushed out through the BMW configuration file update function in mid-April.
The remaining safety mitigation measures are being developed by BMW. Follow-up will be through optional software security patching methods that the owner can obtain through BMW’s official repair channels.
Concerning the specific details of the loopholes, Keen Security Lab plans to officially release the BMW Security Report containing all the details of the vulnerability in 2019.
Source, Image: Tencent