A new vulnerability, whimsically named “Slippy-Book,” has emerged as a formidable threat to the integrity of popular Linux distributions. Discovered by security researcher Febin Mon Saji, this Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability, identified as CVE-2023-44451 for Xreader and CVE-2023-52076 for Atril, targets the very core of file parsing in Linux’s prominent document viewers.

Slippy-Book is a critical path traversal and arbitrary file write flaw. It resides in Atril and Xreader, the default document viewers for the MATE environment and Linux Mint respectively, and affects a range of widely-used operating systems, including Kali Linux, Parrot Security OS, Ubuntu-Mate, and Xubuntu. This vulnerability enables the writing of arbitrary files to any location on the file system accessible to the user, thus paving the way for remote command execution.
The Slippy-Book vulnerability can be exploited in various ingenious ways:
- Autostart Maneuver: By placing a malicious .desktop entry in the $HOME/.config/autostart/ directory, attackers can ensure execution upon user login, akin to the startup folder in Windows.
- SSH Key Writing: Writing to the authorized_keys file within the user’s .ssh/ directory, enabling immediate command execution via SSH if the system has SSH enabled.
- File Execution on Login: Placing files like .bash_profile or .bash_login with malicious commands in the user’s home directory can result in RCE, especially during non-GUI logins like SSH.
- Targeting Directories for Maximum Impact: Writing malicious files to directories like ~/.local/bin or ~/.local/lib/python3.x/site-packages/ can grant control over the target system.
The impact of Slippy-Book is profound, especially for security researchers and desktop users of Kali, Parrot OS, and Linux Mint. The vulnerability allows attackers to execute remote commands, compromising system integrity and user privacy. The fact that it doesn’t require overwriting existing files to achieve its malicious ends only adds to its stealth and potency.
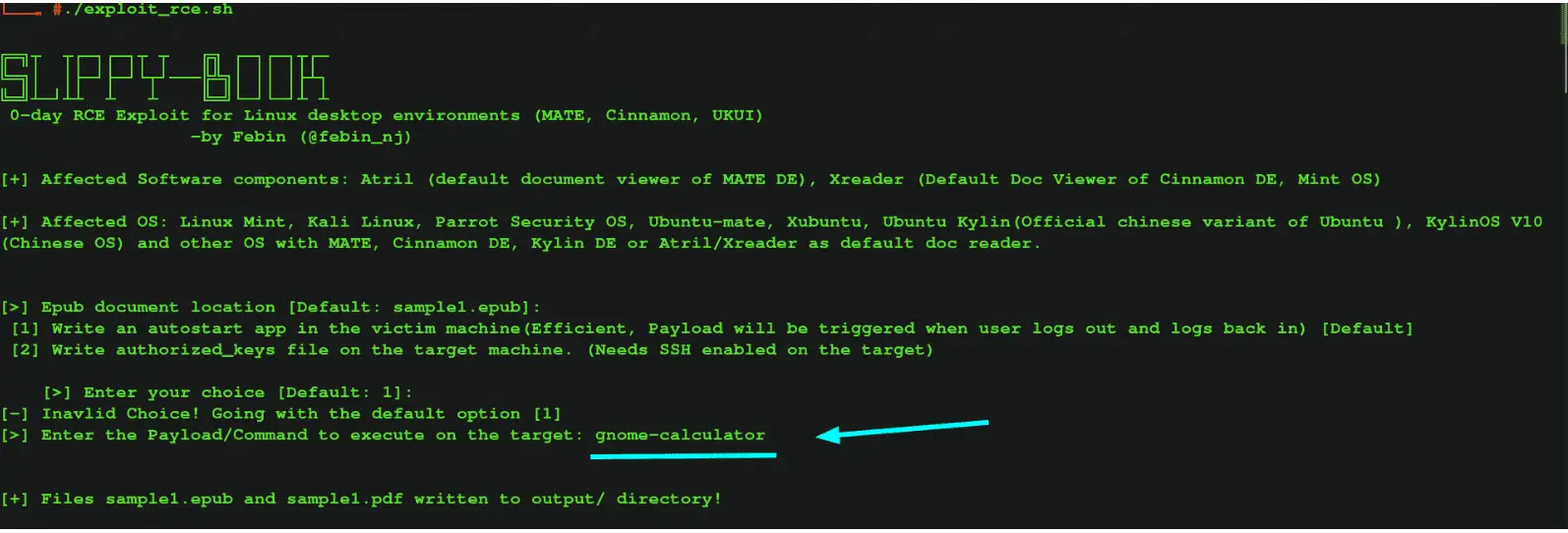
The publication of proof-of-concept code and a video demonstration by the researcher has sounded the alarm for users and administrators of affected Linux distributions. It is a stark reminder of the need for constant vigilance in the cyber world. Users must ensure timely updates and patches to their systems and maintain a keen eye on system behaviors and file integrity.
Also, the researcher revealed another critical one-click RCE/Command Injection vulnerability affecting popular Linux operating systems with MATE, Cinnamon, and some Xfce desktop environments.