Infection flow | Image:
Researchers at FortiGuard Labs have uncovered the inner workings of Byakugan, a versatile malware strain employing a mix of legitimate and malicious components to steal sensitive user data while flying under the radar. This analysis delves into its infection methods, features, and the dangers it poses.
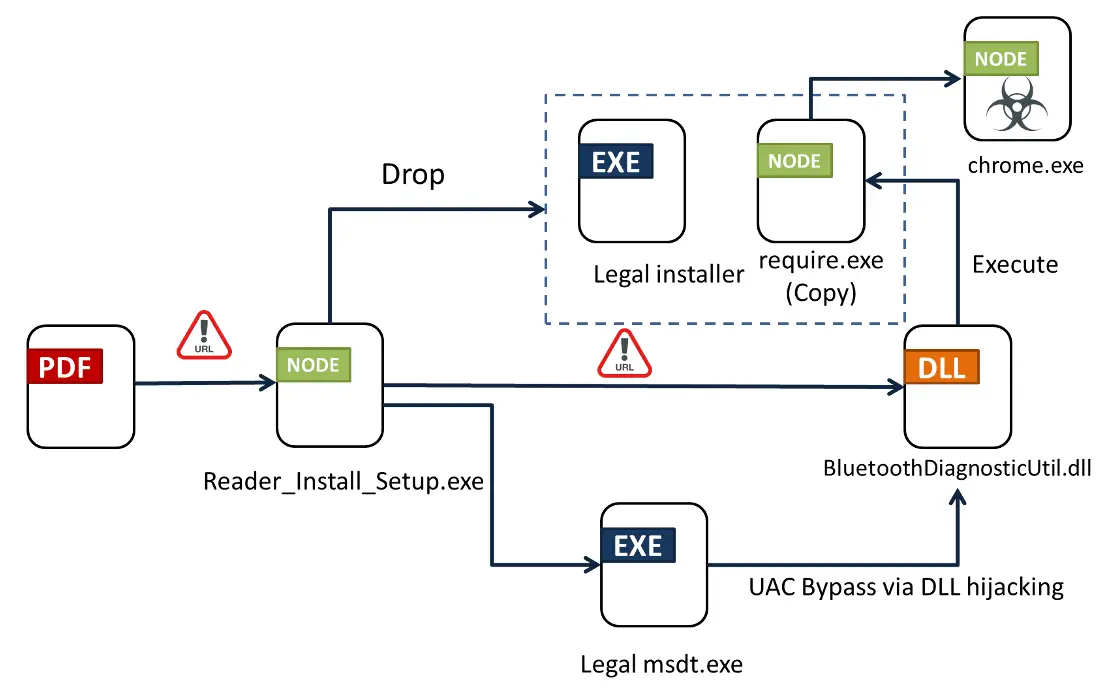
The campaign’s initial touchpoint is a seemingly innocuous PDF file, written in Portuguese. This document, however, is anything but harmless. It features a blurred table, enticing the victim to click on a malicious link purportedly to clear up the image. This action triggers the download of a downloader—a Trojan horse laying the groundwork for Byakugan’s infiltration.

The ingenuity of Byakugan’s infection vector lies in its multi-stage process. Upon clicking the PDF’s malicious link, the victim unwittingly initiates the download of a downloader tool. This tool, disguised under the benign guise of “require.exe,” proceeds to download a DLL. This DLL is then executed through DLL-hijacking, a technique that exploits the legitimate process of “require.exe” to download Byakugan’s main module, misleadingly named “chrome.exe.”
The command and control (C2) server of Byakugan, hosted on thinkforce[.]com[.]br, is a testament to the malware’s sophistication. This server not only orchestrates the delivery of files and commands to the infected machine but also potentially serves as the attacker’s dashboard. A login page on port 8080 reveals the extent of Byakugan’s capabilities, offering a peek into the malware’s operational backbone.
Byakugan distinguishes itself through a diverse arsenal of features, each designed to exploit different aspects of the victim’s digital life:
- Surveillance Suite: It can monitor the victim’s screen (leveraging OBS Studio) and take screenshots, potentially capturing login credentials, confidential documents, or private conversations.
- Crypto-miner with a Twist: Byakugan’s mining capabilities are designed to avoid detection, dynamically adjusting intensity to prevent system slowdowns when the victim is likely using the computer for resource-intensive tasks like gaming.
- Keylogger and Data Exfiltration: Every keystroke is fair game, allowing the malware to steal passwords, financial data, and other sensitive information. It then sends this pilfered data back to the attacker’s control server.
- Manipulating Your Browser: Byakugan targets popular web browsers, aiming to steal cookies, credit card details, saved passwords, and download histories. It can even inject its own malicious cookies for further attacks.
Byakugan’s developers have clearly prioritized evasion tactics:
- Mimicking Legitimacy: It disguises itself as a benign memory management tool, terminating if its filename or location raises suspicion.
- Manipulating Security Tools: Byakugan brazenly adds itself to Windows Defender’s exclusion list and tweaks firewall rules to prevent detection.
- Resilient Persistence: It establishes a foothold by creating a scheduled task that triggers its execution upon every system startup.
Byakugan spotlights the growing trend of malware authors blending clean and malicious elements to hinder security software analysis. This deceptive approach creates more noise, making it harder for automated tools and even human analysts to pinpoint the threat accurately.