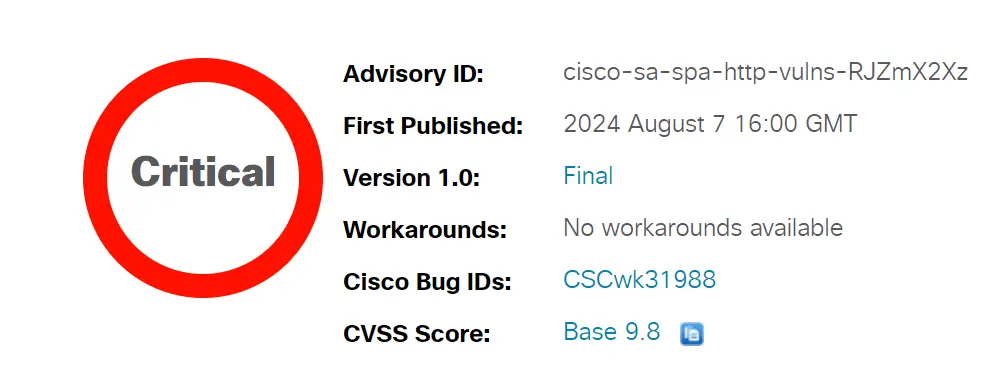
In a recent security advisory, Cisco disclosed multiple critical vulnerabilities affecting their Small Business SPA300 and SPA500 Series IP Phones. These vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2024-20450, CVE-2024-20452, CVE-2024-20454, CVE-2024-20451, and CVE-2024-20453, pose significant security risks, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary commands or cause denial of service (DoS) conditions.
Unpatched and Unprotected
The web-based management interface of the affected IP phone series is at the heart of these vulnerabilities. The most severe vulnerabilities, CVE-2024-20450, CVE-2024-20452, and CVE-2024-20454, each carry a CVSS score of 9.8. They permit unauthenticated remote attackers to execute arbitrary commands with root privileges on the underlying operating system. These vulnerabilities arise due to improper error checking of incoming HTTP packets, leading to potential buffer overflow conditions. By sending specially crafted HTTP requests, attackers can exploit this flaw to gain root-level access and execute commands on the device.
Similarly, vulnerabilities CVE-2024-20451 and CVE-2024-20453, each with a CVSS score of 7.5, can lead to DoS conditions. These vulnerabilities also stem from improper error checking of HTTP packets. Exploitation can result in the affected devices reloading unexpectedly, thereby disrupting normal operations.
Alarmingly, Cisco has announced it will not release software updates to address these flaws, as the affected phone models have reached their end-of-life. This leaves businesses with no immediate solution to mitigate the risks.
What Can You Do?
While Cisco has not provided a direct fix, businesses can take the following steps to minimize their exposure:
- Isolate: If possible, disconnect the affected phones from your network to prevent remote attacks.
- Firewall: Implement strict firewall rules to limit access to the web management interface of the phones.
- Monitor: Closely monitor network traffic for any suspicious activity.
- Replace: Consider replacing the vulnerable phones with newer, supported models that receive security updates.
Related Posts:
- Hackers use Cisco Router flaws to attack Iran, 3,500 routers hacked
- Cisco releases patch to fix three high security bugs