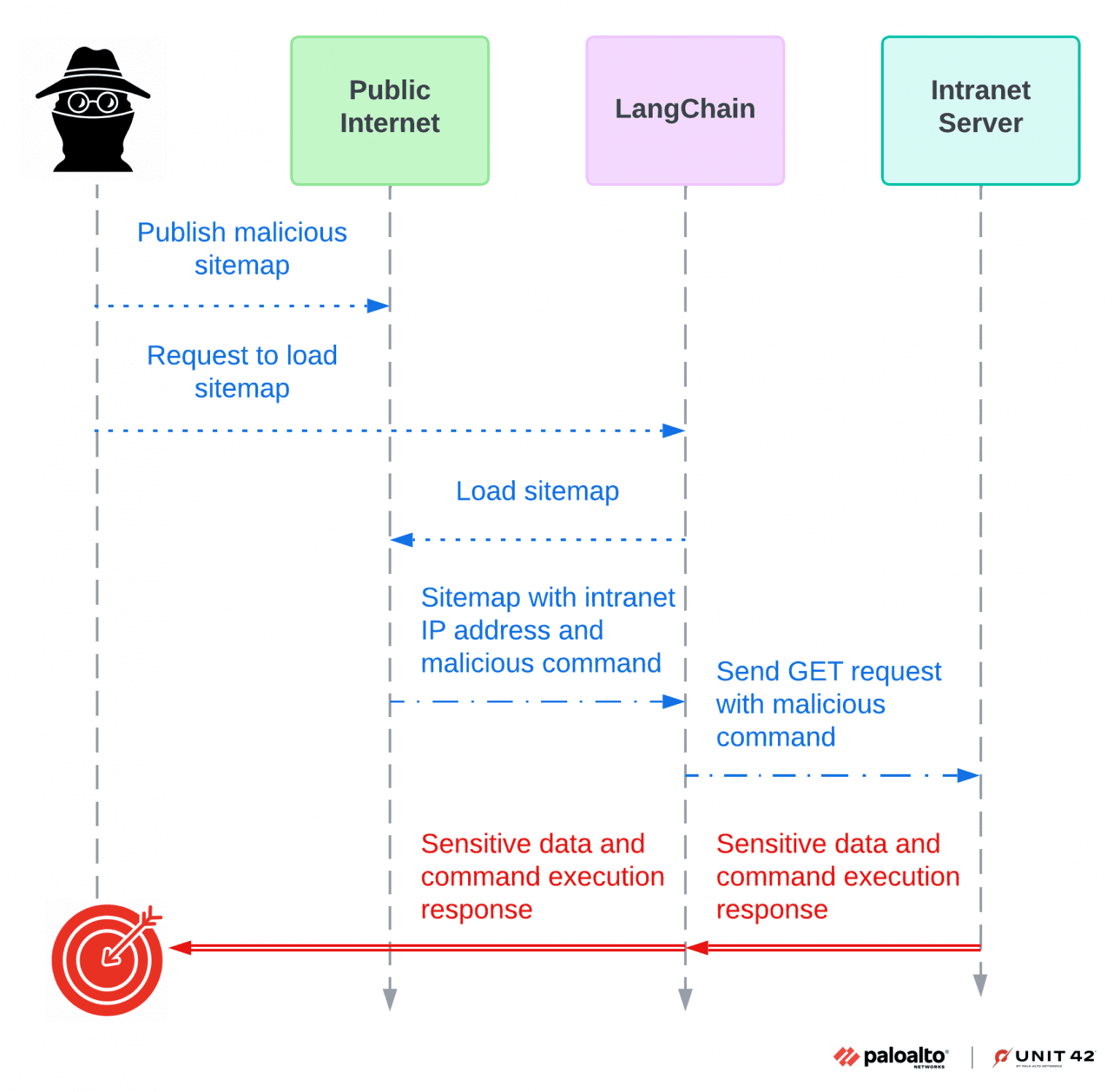
CVE-2023-46229 attack sequence diagram
Researchers from Palo Alto Networks have recently detailed two significant security vulnerabilities in LangChain, a widely used open-source generative AI framework boasting nearly 90,000 stars on GitHub. These vulnerabilities, identified as CVE-2023-46229 and CVE-2023-44467, have the potential to allow attackers to execute arbitrary code and access sensitive data, respectively. With over one million developers relying on LangChain’s tools, this discovery exposes a significant risk to the security of countless AI-powered applications.
- CVE-2023-46229: Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
LangChain versions earlier than 0.0.317 are vulnerable to SSRF through crafted sitemaps. This vulnerability allows attackers to obtain sensitive information from intranets, potentially bypassing access controls. Palo Alto Networks discovered this flaw on October 13, 2023, and immediately informed LangChain support. The vulnerability was promptly patched in the pull request langchain#11925, released in version 0.0.317.
- CVE-2023-44467: Critical Prompt Injection in LangChain Experimental
CVE-2023-44467 is a severe prompt injection vulnerability affecting LangChain Experimental versions before 0.0.306. LangChain Experimental is a separate Python library designed for research and experimental purposes, including integrations that can be exploited through malicious prompts. This vulnerability specifically affects PALChain, a feature that enhances language models with the ability to generate code solutions through program-aided language models (PAL).
This flaw allows attackers to exploit PALChain’s processing capabilities with prompt injections, enabling them to execute harmful commands or code. Such exploitation could result in unauthorized access or manipulation, posing significant security risks. Palo Alto Networks identified this vulnerability on September 1, 2023, and promptly informed the LangChain development team, which issued a warning on the LangChain Experimental PyPI page the following day.
LangChain’s popularity has soared in recent months, driven by the growing demand for LLM applications in various industries. Its extensive library of pre-built components and integrations has made it a go-to choice for developers seeking to harness the power of AI. However, this widespread adoption also amplifies the potential impact of these vulnerabilities.
Developers and organizations using LangChain are strongly urged to update their installations to the latest patched versions. For detailed technical information and proof-of-concept exploit codes, please visit the Palo Alto Networks blog.
Related Posts:
- Apache HTTP Server Hit by Triple Vulnerabilities – Users Urged to Update
- A New Set of Tools for Cyber Espionage: Targeting the Middle East, Africa, and the US
- Palo Alto Networks’ Unit 42 Reveals a New Cyber Threat in China: Financial Fraud APKs
- Palo Alto Firewalls Under Attack: Critical Flaw Exploited to Deploy Cryptojacking Malware
- CVE-2024-3400 (CVSS 10): Critical 0-Day Flaw in Palo Alto Networks Firewall Software Exploited in the Wild