Cacti, a popular open-source network monitoring and graphing tool, has recently released a crucial security update to address two significant vulnerabilities that could leave systems exposed to malicious attacks. These vulnerabilities were found in versions up to 1.3.x DEV and have since been addressed in the latest development updates.
Command Injection Flaw: CVE-2024-29895
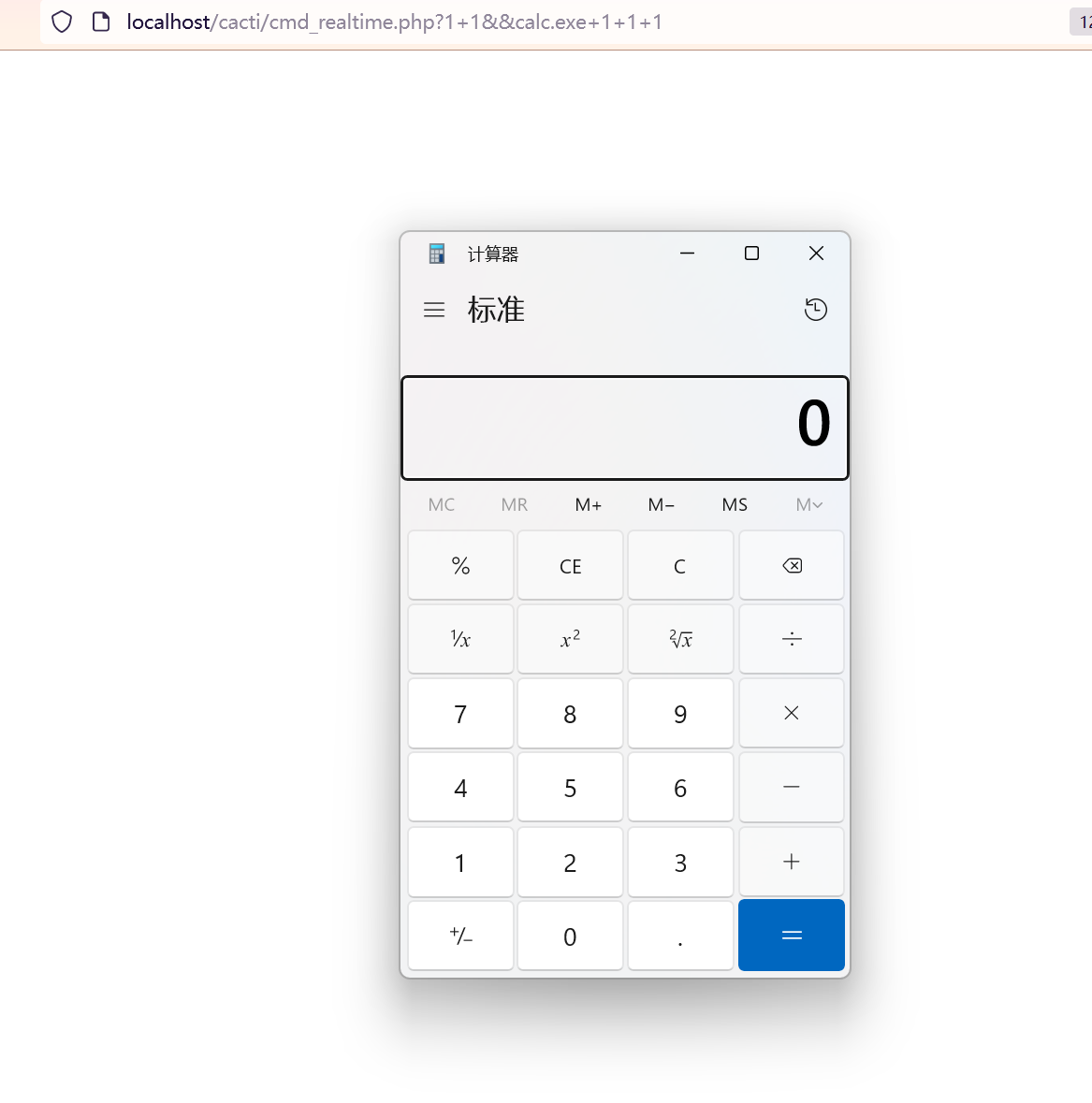
The first and more severe of the vulnerabilities, cataloged under CVE-2024-29895 with a CVSS score of 10, is a command injection flaw found within the cmd_realtime.php file of Cacti. This vulnerability allows unauthenticated users to execute arbitrary commands on the server. The flaw is particularly alarming due to the ease of its exploitation—a result of the register_argc_argv PHP option being enabled by default in many environments, including the main PHP Docker image.

Attackers can manipulate the $poller_id variable, which is derived from $_SERVER['argv'] and can be influenced via URL parameters when the register_argc_argv option is active. An example provided for a proof of concept shows how a simple URL could trigger the execution of unwanted commands like opening a calculator app on the server, which indicates the potential for more malicious actions.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerability: CVE-2024-30268
The second vulnerability, identified as CVE-2024-30268 with a CVSS score of 6.1, involves a reflected Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) issue in the settings.php file. This flaw could enable attackers to capture the cookies of an administrator or any user interacting with the compromised settings interface. By manipulating the filter parameter in the URL without proper sanitization, attackers can inject arbitrary JavaScript code, which executes when the parameter value is output in the user’s browser.
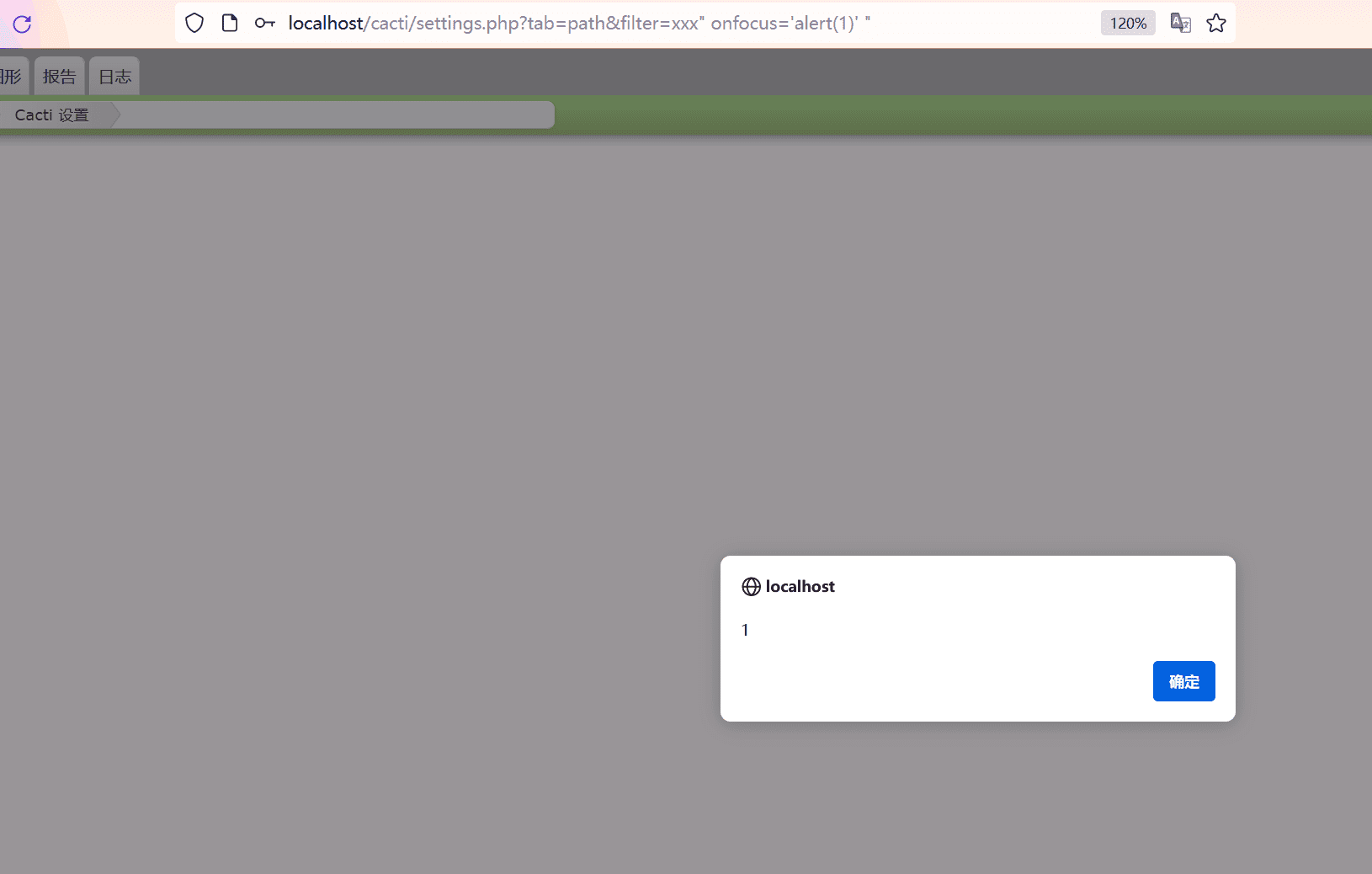
This XSS flaw could be exploited to perform actions such as stealing session cookies and impersonating users, potentially leading to unauthorized actions being performed on the platform.
Mitigations
Both vulnerabilities were discovered by security researcher LioTree, who promptly reported them to the Cacti development team. Fortunately, the issues have been promptly addressed in the latest Cacti 1.3.x DEV release.
Users of Cacti are strongly advised to upgrade their installations to the patched version immediately to protect themselves from potential exploitation. Delaying the update could leave systems vulnerable to compromise, leading to data breaches, unauthorized access, and other serious security incidents.