WordPress Ultimate Member Plugin Under Active Attack: Critical Flaw (CVE-2024-1071) Impacts 200k Sites
A critical unauthenticated SQL Injection vulnerability was found in Ultimate Member, a popular WordPress plugin boasting over 200,000 active installations. This critical flaw, identified as CVE-2024-1071, carries a high-severity CVSS score of 9.8, underscoring the grave risk it poses to websites utilizing this widely adopted plugin.
The vulnerability came to light by Christiaan Swiers, who identified and responsibly reported this flaw via the Wordfence Bug Bounty Program. Swiers earned a bounty of $2,063.00 during the Wordfence Bug Bounty Program Extravaganza.

Image: Wordfence
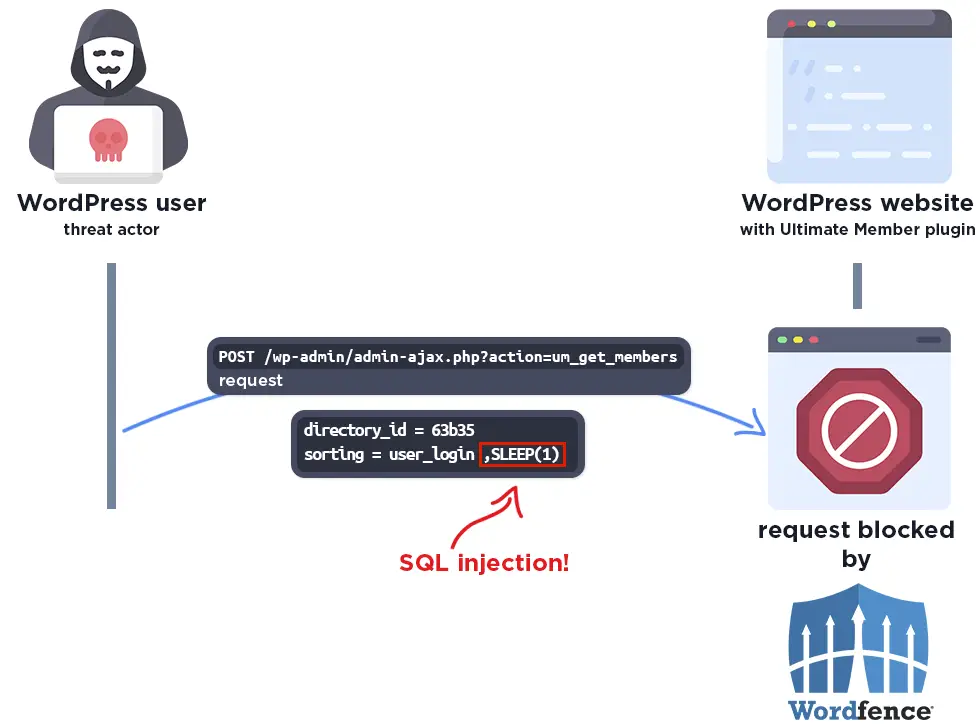
CVE-2024-1071 manifests in versions 2.1.3 to 2.8.2 of the Ultimate Member plugin. The flaw is rooted in an insecure implementation related to the plugin’s user query functionality, specifically through the ‘sorting’ parameter. This parameter, due to insufficient escaping and preparation of SQL queries, becomes an open door for unauthenticated attackers to manipulate and inject additional SQL commands. These nefarious actions can lead to the extraction of sensitive information from the database, including password hashes.
The crux of the vulnerability lies within the ajax_get_members() function of the Member_Directory_Meta class. This function, responsible for querying WordPress users for the member directories feature, fails to adequately secure the ‘sorting’ parameter against SQL injection. While attempts were made to sanitize inputs using the sanitize_text_field() function, this measure falls short of thwarting SQL injection attacks.
The most alarming aspect is the absence of the WordPress wpdb prepare() function in appending the ORDER BY statement to the SQL query. The prepare() function is crucial for parameterizing and safely executing SQL queries in WordPress, serving as a bulwark against SQL injection threats.

Wordfence reported blocking 522 attacks targeting this flaw within a mere 24-hour window, underscoring the active threat posed by this vulnerability. Attackers have leveraged a Time-Based blind approach, utilizing SQL CASE statements coupled with the SLEEP() command. This method allows attackers to pilfer database information by observing the response time of their injected commands, a sophisticated technique that has proven effective in breaching database security.
Upon discovery, Wordfence promptly notified the Ultimate Member team on January 30, 2024. The developer’s swift response and cooperation led to the release of a patch on February 19, 2024. The updated version 2.8.3 of the Ultimate Member plugin addresses and rectifies this critical vulnerability.
The Ultimate Member development team has released a patch in version 2.8.3. If your website utilizes this plugin, immediate updating to the latest version is strongly advised.