Image: VulnCheck
Security researchers from VulnCheck have disclosed a critical unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in BigAntSoft BigAnt Server, tracked as CVE-2025-0364 (CVSS 9.8). This flaw allows attackers to escalate privileges and execute arbitrary code on affected systems without authentication.
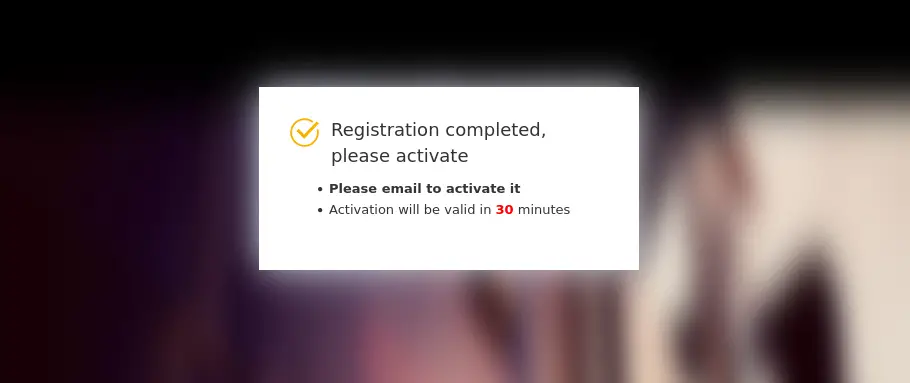
BigAntSoft BigAnt Server is an on-premises Windows-based business messaging solution. The vulnerability arises from an exposed SaaS registration feature that permits an attacker to solve a simple CAPTCHA and create an administrative user account. With this access, the attacker can exploit the Cloud Storage Add-in to upload malicious PHP files, which are then executed without authentication.
According to VulnCheck, this issue affects all versions up to BigAnt Server 5.6.06. The researchers noted: “An attacker can gain full remote code execution unauthenticated via a chain of 10 requests.” They further confirmed that public exploits are now available.
The vulnerability was identified while investigating CVE-2024-54761, which was initially misclassified due to incorrect privilege requirements. Upon further examination, researchers uncovered additional insecure programming practices that led to the discovery of CVE-2025-0364.
The exploit chain involves:
- Bypassing authentication via exposed SaaS registration.
- Leveraging a CAPTCHA-solved admin account to access the Cloud Storage Add-in.
- Uploading a malicious PHP payload.
- Executing arbitrary commands remotely.
Upon running the exploit, researchers successfully obtained SYSTEM privileges:
“The target appears to be a vulnerable version! Registering SaaS org with password: kyLZiAddnH”
“Attempting to upload JQsaYCKEOu.php to cloud drive addin…“
“Caught new shell from 10.0.0.104:51690”
A critical aspect of the exploit is that it does not require user interaction beyond solving the CAPTCHA, making it a significant risk for exposed servers.
At the time of discovery, VulnCheck found around 50 publicly exposed BigAnt servers online. By the time of publication, this number had decreased to approximately 30 instances, likely due to administrators taking precautionary actions.
With no authentication required and direct remote code execution capabilities, the vulnerability poses severe security risks. Attackers can exploit this flaw to:
- Gain full control over affected servers.
- Exfiltrate sensitive business communications.
- Deploy ransomware or establish persistent access.
BigAntSoft has yet to release an official patch for CVE-2025-0364. As a temporary mitigation, administrators are urged to:
- Disable SaaS registration if not required.
- Restrict public access to the BigAnt Server admin interface.
- Monitor logs for suspicious new account registrations.
- Apply web server restrictions to prevent execution of PHP files from unauthorized locations.
Security teams should also consider network segmentation and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to prevent exploit attempts.
Related Posts:
- Mozilla Confirms: Intel CPU Vulnerability Could Be Used To Extract User Information
- Apple Confirmed that All Mac and iOS Devices Are Affected by Chip Vulnerability
- Mozilla Confirms Active Attacks on Tor Browser via Firefox Vulnerability