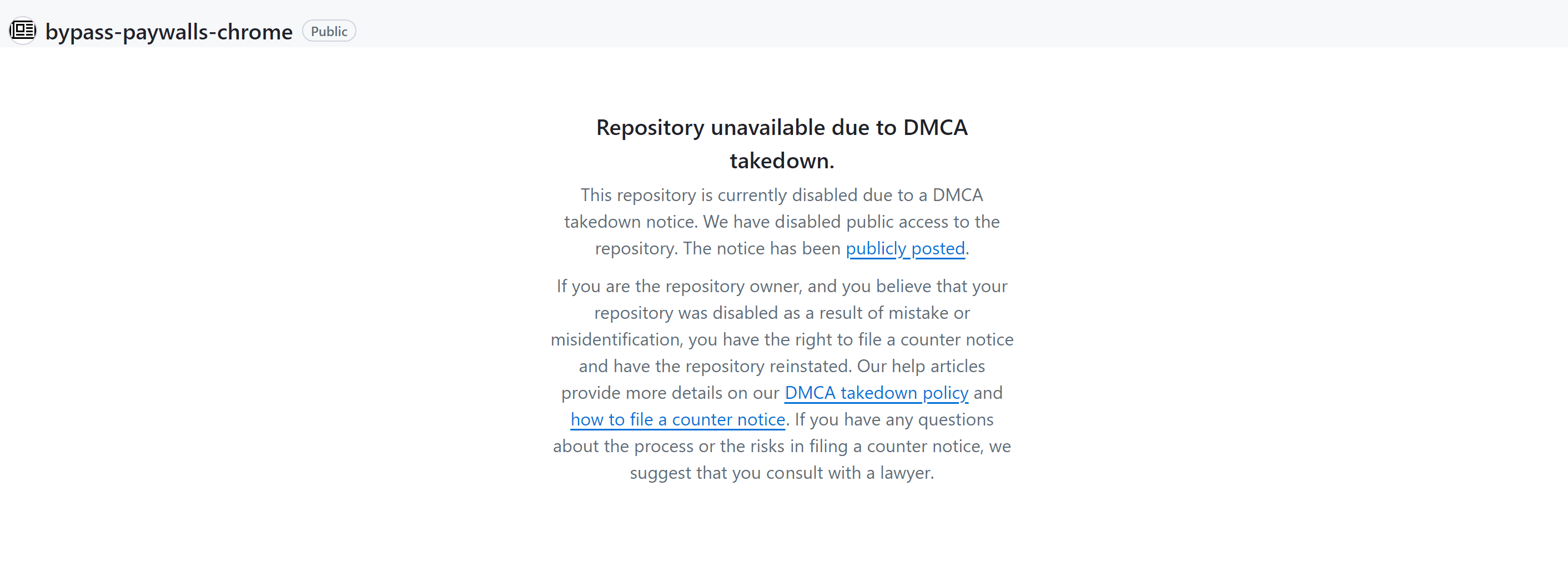
The browser extension Bypass Paywalls Clean (BPC), which allowed users to circumvent paywalls and access content on websites without subscribing, has been blocked along with its 3,879 forks. The cause was a complaint filed by the News Media Alliance (NMA) to the GitHub platform, where the extension’s code was hosted. The organization, representing the interests of more than 2,200 publishers of news, magazines, and digital media, pointed out that BPC violates its members’ rights by bypassing technological measures protecting content, which contravenes the provisions of the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA).
With the advent of digital technologies, the media landscape has undergone significant changes. Internet platforms quickly became the primary means for disseminating and consuming content. On one hand, this opened new opportunities for publishers, but on the other, it led to serious challenges. Free access to digital versions of newspapers and magazines resulted in a significant decline in print sales. Initially, advertising was the main source of revenue for online publications, but over time, this stream began to dry up. The popularity of ad-blocking programs grew as users sought to shield themselves from intrusive and aggressive ads.
In the face of declining revenue, many publishers began implementing paywalls, restricting access to their materials only to subscribers. This move allowed some publications not only to survive but also to improve their financial standing. However, technical solutions enabling users to bypass these paywalls were not long in coming. One of the most well-known tools for this was Bypass Paywalls Clean, which users could easily install in Chrome and Firefox browsers.
For publishers hoping for increased subscription revenue, the emergence of BPC became a significant problem. The extension allowed users to access content without payment, threatening the subscription-based financial model. In April 2023, the first complaint against BPC was filed on the GitLab platform, where the main repository of the extension was hosted. The repository was subsequently removed and not restored.
In August 2023, NMA filed a similar complaint with GitHub. Unlike the previous case, GitHub published the full details of the complaint, including information about the complainant and the legal grounds for the content’s removal. In letters sent to GitHub, NMA explained that the complaint concerned not only copyright infringement but also the circumvention of technological measures protecting content, which directly violates Section 1201 of the DMCA.
NMA identified four repositories containing software products that violate the law. Among them were “bypass-paywalls-chrome,” “bypass-paywalls-firefox,” “bpc_updates,” and “bypass-paywalls-clean-filters.” Each of these repositories included code that allowed users to bypass paywalls on sites protected by various technological measures. Depending on the content protection system used, some publications provide access to a limited number of free articles (a so-called “soft” paywall), while others completely block access without a subscription (a hard paywall).
NMA emphasized that all these repositories contain tools that violate the DMCA’s provisions by circumventing technological content protection measures. GitHub, after reviewing the complaint and conducting its own investigation, found NMA’s claims to be justified. As a result, the platform disabled all 3,879 repositories, including the main BPC repository, delivering a severe blow to the developer and user community supporting the extension.
The removal may signify the end of Bypass Paywalls Clean on the GitHub platform. While some projects may continue to exist on other platforms, the future support and development of BPC remain in question, as the extension requires regular updates to function effectively.
Related Posts:
- Australian Department sues Facebook for violating privacy policy
- X Faces GDPR Heat Over AI Training on 60 Million European Users’ Data