
A sophisticated cyber campaign orchestrated by the threat actor Earth Minotaur has been uncovered by Trend Micro researchers, exposing their reliance on the MOONSHINE exploit kit and a previously unreported DarkNimbus backdoor. This campaign primarily targets Tibetan and Uyghur communities via Android devices and is now identified as a multi-platform threat.
First identified in 2019, the MOONSHINE exploit kit has been linked to attacks against Tibetan communities. Over the years, it has evolved significantly, with Trend Micro identifying 55 active MOONSHINE servers by 2024. The toolkit now includes new vulnerabilities and enhanced protections to evade analysis.
The report highlights, “MOONSHINE exploits multiple known vulnerabilities in Chromium-based browsers and applications, requiring users to update software regularly to prevent attacks.” Vulnerabilities in widely used applications, including WeChat and Tencent Browser Server, provide a pathway for attackers to compromise devices.
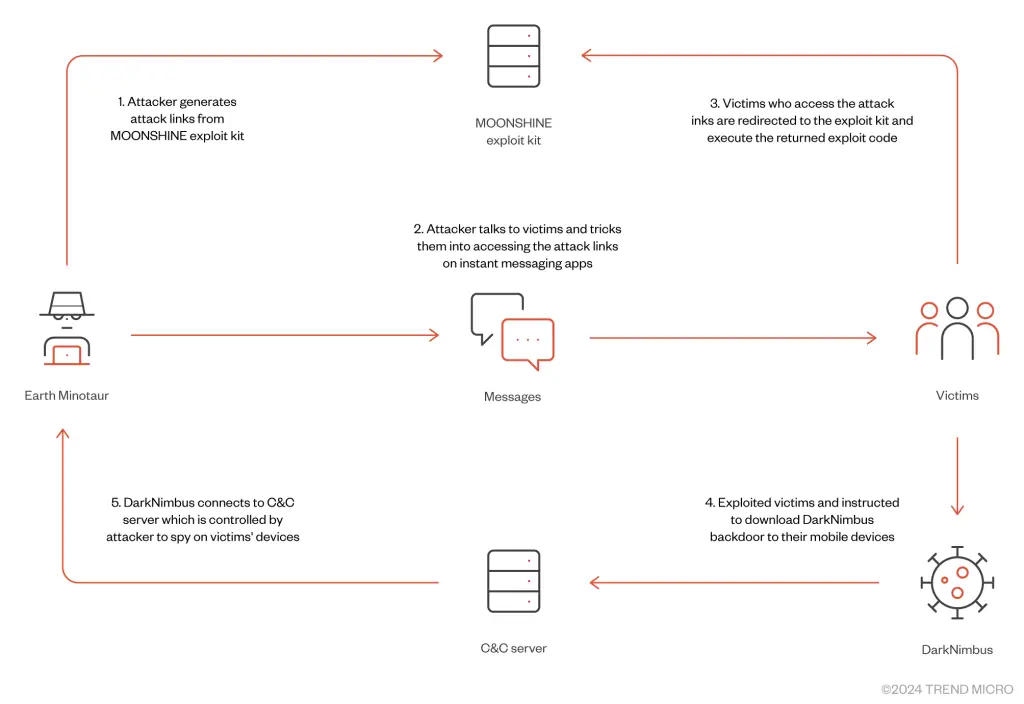
The DarkNimbus backdoor, revealed as part of the campaign, operates on both Android and Windows platforms. The Android version of DarkNimbus is a comprehensive surveillance tool capable of collecting device information, stealing personal data, recording calls, capturing screenshots, and more. The report explains, “DarkNimbus abuses Android’s Accessibility Service to monitor and pilfer conversations from instant messaging apps.”
On Windows, DarkNimbus employs techniques such as keystroke logging and browser credential harvesting. It uses sophisticated protocols to communicate with command-and-control servers, further highlighting its adaptability and sophistication.
Earth Minotaur employs social engineering to distribute malicious links disguised as legitimate content. Victims are lured through messages related to government announcements, COVID-19 news, or cultural topics. These links redirect victims to MOONSHINE servers, which assess the victim’s device and browser vulnerabilities before delivering exploit code.
A unique aspect of MOONSHINE is its ability to downgrade browser engines to exploit older vulnerabilities. “The MOONSHINE exploit kit supports an interesting phishing technique meant to downgrade an app’s browser engine: When the server detects a version of TBS that is not vulnerable to the exploits supported in MOONSHINE, it doesn’t deliver the exploit code. Instead, the server returns a phishing page informing the victim that the version of browser engine used in the app is outdated and needs to be upgraded with a provided download link,” the report notes.
Once the exploit succeeds, a trojanized browser core is implanted, enabling the delivery of the DarkNimbus backdoor.
While MOONSHINE has been attributed to multiple groups, including Earth Minotaur and POISON CARP, the report emphasizes the complexity of attribution. Trend Micro states, “We believe that Earth Minotaur is an intrusion set which hasn’t been publicly reported… highlighting the connections that exist between multiple campaigns attributed to Chinese operations.”
Related Posts:
- Zero-Day Vulnerability: 18 Years of Exploiting the ‘0.0.0.0’ Flaw
- Trojan Malware Infiltrates Browser Extensions, Impacts 300,000 Users
- CVE-2024-21887 and More: How Earth Estries APT Group Exploits VPNs & Servers
- Earth Estries’ Evolving Toolkit: A Deep Dive into Their Advanced Techniques
- New Chrome and Firefox malicious extensions prevent user removal to hijack browsers