
The cybersecurity landscape in Q2 2024 was marked by a notable increase in new vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques targeting both applications and operating systems. According to Kaspersky Labs’ latest report, the quarter witnessed a significant rise in attacks exploiting vulnerable drivers as a primary means of privilege escalation. This trend signals a growing threat, as attackers increasingly turn to outdated drivers as a vector for infiltrating systems, bypassing traditional security measures.
Kaspersky’s report highlights a concerning trend: the number of registered vulnerabilities in Q2 2024 exceeded the figures from the same period last year, with a strong possibility of surpassing 2023’s total by year’s end. The increase is consistent with the upward trajectory observed since 2019, suggesting that vulnerabilities are being discovered—and potentially exploited—at an accelerating pace.
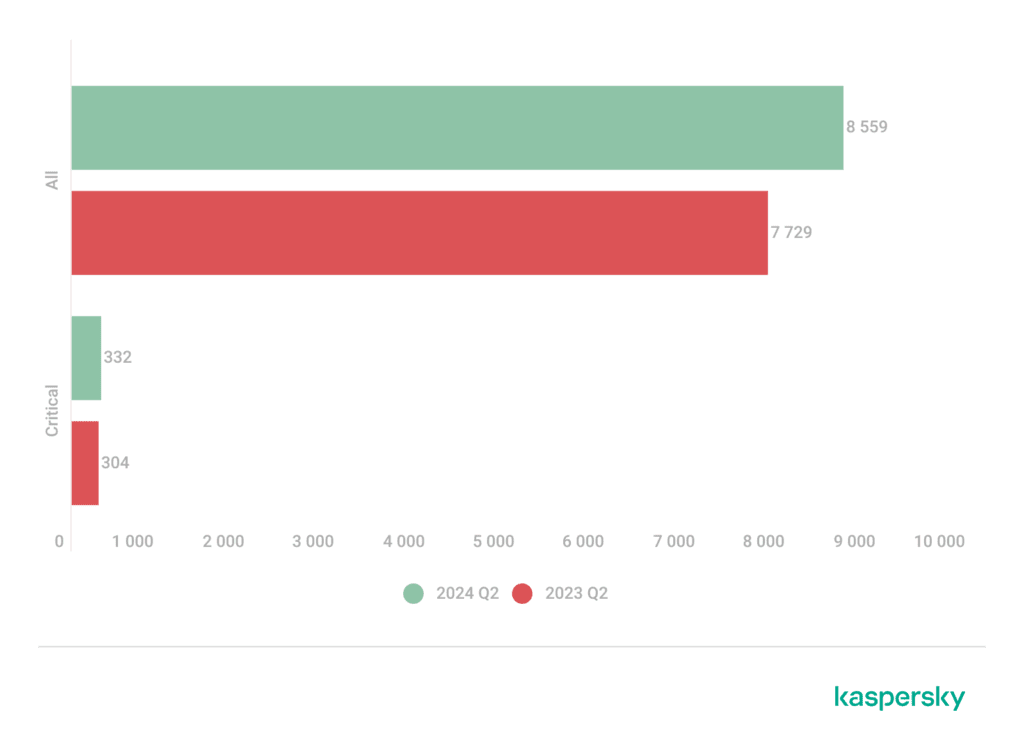
Despite this growth, the share of vulnerabilities classified as critical has seen a slight decrease compared to 2023. However, it’s these critical vulnerabilities that pose the most significant risks to organizations. Notably, the report emphasizes the challenges posed by unclassified critical vulnerabilities, which remain unaddressed and continue to threaten system integrity.
One of the standout findings in the report is the prevalence of attacks using the Bring Your Own Vulnerable Driver (BYOVD) technique. This method involves attackers deliberately installing unpatched, vulnerable drivers on a target system to exploit weaknesses for privilege escalation or other malicious activities. Initially popularized by creators of game cheats, BYOVD has now been widely adopted by cybercriminals for more nefarious purposes.
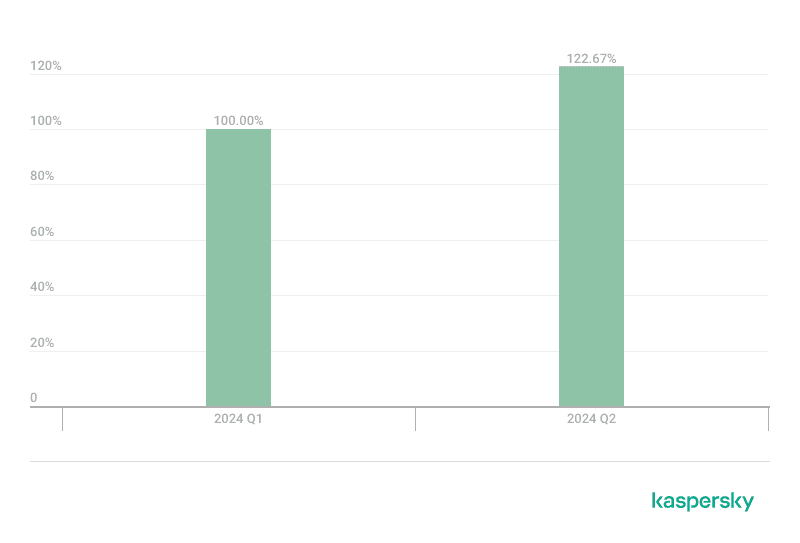
The report notes a significant increase in the use of vulnerable drivers since 2023, with attackers leveraging them to bypass security mechanisms and gain unauthorized control over systems. Kaspersky’s data indicates that hundreds of vulnerable drivers are currently being exploited, with new ones appearing regularly. To combat this, Kaspersky has been enhancing its detection and blocking capabilities, aiming to mitigate the growing threat posed by BYOVD attacks.
The report provides a detailed breakdown of the most common types of vulnerabilities exploited during the quarter:
- CWE-434: Unrestricted Upload of File with Dangerous Type
- CWE-89: Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL Command (SQL Injection)
- CWE-22: Improper Limitation of a Pathname to a Restricted Directory (Path Traversal)
These vulnerabilities, particularly in web applications, continue to be the most critical, as they often grant attackers access to sensitive data. The report underscores the importance of securing web applications, given their role in handling crucial functions such as file sharing, VPN access, and cloud services.
Kaspersky’s telemetry shows a rise in exploit activity targeting both Windows and Linux platforms. For Windows, the most exploited vulnerabilities are within the Microsoft Office suite, particularly in components like Equation Editor and MSHTML. These exploits, including those for vulnerabilities such as CVE-2018-0802 and CVE-2021-40444, are primarily delivered through phishing emails, aiming to gain initial access to systems.
Linux, increasingly prevalent in corporate environments, has also seen a rise in exploits targeting the kernel. Vulnerabilities such as CVE-2022-0847 (Dirty Pipe) and CVE-2023-2640 in the Ubuntu kernel are frequently exploited for privilege escalation, allowing attackers to persist within compromised systems.
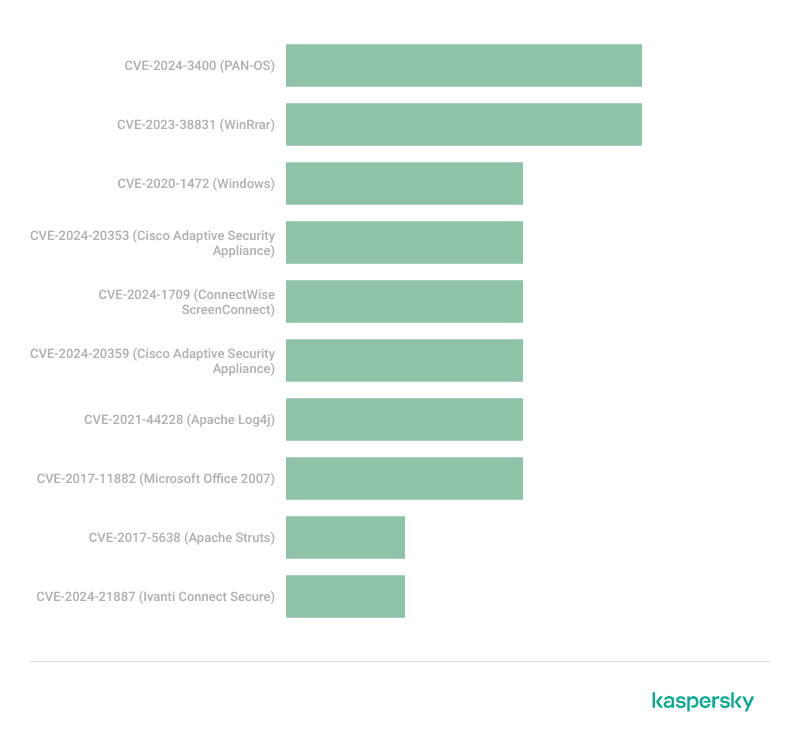
The report reveals a shift in the distribution of critical vulnerabilities exploited in Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) attacks. APT groups have been quick to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in remote access services, access control mechanisms, and office applications, underscoring the need for vigilant monitoring and rapid response.
Interestingly, the share of exploits targeting operating systems saw a noticeable increase in Q2, attributed to the release of Proof of Concept (PoC) exploits ahead of the cybersecurity conference season. This uptick highlights the importance of proactive patch management and the need to stay ahead of emerging threats.
With the rise in vulnerabilities and the resurgence of previously patched exploits, organizations must adopt a proactive approach to cybersecurity. The BYOVD technique, in particular, is expected to become even more prevalent, as cybercriminals continue to exploit vulnerable drivers to compromise systems.
To mitigate these risks, Kaspersky recommends:
- Thorough Infrastructure Monitoring: Understanding and keeping track of your infrastructure is critical to maintaining security, especially at the network perimeter.
- Effective Patch Management: Implementing a robust patch management strategy is essential to detect and eliminate vulnerabilities promptly, including those related to BYOVD.
- Comprehensive Security Solutions: Utilizing security solutions that offer strong protection, early detection, and prevention of complex attacks is crucial. These solutions should also provide real-time cyberattack data and promote digital literacy among employees.
For a detailed look at the full report and specific recommendations, visit Kaspersky Labs’ official website.
Related Posts:
- Unpacking Kasseika: The Latest Ransomware to Exploit BYOVD Tactics
- New VMware Findings: Kernel Drivers’ Vulnerabilities Risk Total Device Takeover
- Kaspersky Report: Criminals earning millions through mining malware
- Kaspersky Report: Energy Industry becomes the largest area affected by vulnerabilities in industrial automation systems