Malicious website
In January 2024, eSentire’s Threat Response Unit (TRU) uncovered a sophisticated malware campaign unleashed against Latin American users. This insidious scheme, centered around the Fenix Botnet, employs cunning tactics to compromise victims and inflict significant financial damage.
The Infection Chain

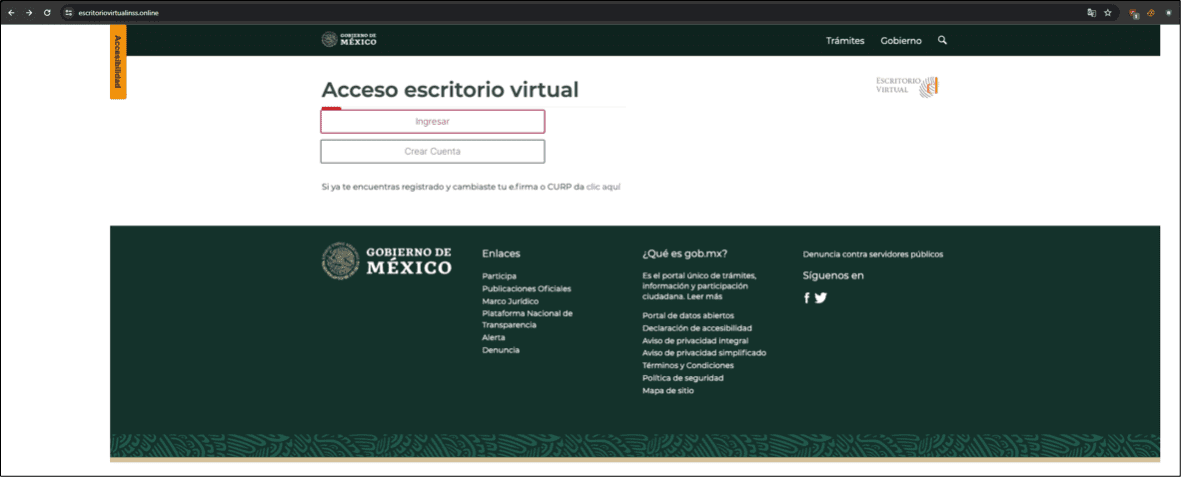
The attack begins with a deceptive lure. Victims are tricked into visiting a website that convincingly masquerades as an official Government of Mexico portal. There, they are misled into downloading a malicious ZIP archive presented as a legitimate tool.
Once the archive is downloaded and executed, a Remote Access Trojan (RAT) is stealthily installed. This RAT boasts information-stealing capabilities and swiftly conscripts the compromised machine into the Fenix Botnet.
A Focus on Financial Fraud
The most disturbing aspect of Fenix is its specialized functionality designed to target Latin American financial institutions. The RAT employed in this campaign is equipped to monitor banking activity and intercept sensitive credentials. This directly endangers the financial wellbeing of both individuals and businesses in the region.
Dissecting the Attack
Let’s delve into the technical details of this attack:
-
Social Engineering: The initial infection hinges on social engineering, with users being tricked into believing the malicious website is an authentic government portal.
-
Malicious Payload: The downloaded ZIP archive cleverly masks its harmful contents. It includes an Internet Shortcut file and a text file with instructions to launch it. The Internet Shortcut is a key component, in retrieving further malicious files from the Internet.
-
Obfuscation and Delivery: The attackers use obfuscated JSE code to download another payload, hiding their true intentions.
-
Shellcode Execution: Employing a technique known as QueueUserAPC process injection, a vital Windows process (AuthHost.exe) is manipulated to execute a malicious shellcode.
-
Payload Evolution: The shellcode dynamically fetches payloads from a remote server. The specific payload served can be either ‘NarniaRAT’ or ‘BotnetFenix’, each with its sinister objectives.
Capabilities of the Payloads
-
NarniaRAT:
- Data Exfiltration: NarniaRAT meticulously gathers files from sensitive system locations including Desktops, Documents, and the User Profile.
- System Reconnaissance: It gleans valuable computer information such as IP addresses, location, installed antivirus software, and system uptime.
- Surveillance: NarniaRAT can secretly capture screenshots and log keystrokes
- The Banking Angle: Most worryingly, NarniaRAT retrieves a list of targeted banks predominantly operating in Latin America, indicating its focus on financial theft.
-
BotnetFenix
- Versatile Toolkit: This Rust-based malware is a potent tool for executing remote commands. It can download additional payloads, run PowerShell scripts, and even deploy a specialized credential stealer.
- Communications Infrastructure: BotnetFenix utilizes a network of compromised machines (the botnet) and hardcoded command and control (C2) servers to coordinate future attacks.
Key Takeaways
The Fenix Botnet and its associated payloads highlight the growing sophistication of cyberattacks in Latin America. Here’s what you need to keep in mind:
- Constant Vigilance: Always be cautious when downloading files or visiting unfamiliar websites, even if they appear legitimate.
- Robust Security Solutions: Implement strong antivirus and endpoint protection software to detect and block malware.
- User Awareness: Educate yourself and others on the tactics used in social engineering attacks to avoid falling victim.