Recently, FireEye released a security analysis report that an Iranian hacker named TEMP.Zagros (also known as MuddyWater) launched a large-scale phishing campaign against Asia and the Middle East from January to March 2018. In a recent activity, the hackers used the latest code execution and persistence technologies to distribute a macro-based malicious document to these areas. In contrast, the document deleted a VBS file and a PowerShell command that contains Base64 encoding. INI file. Once successfully executed, malicious documents will install a POWERSTATS back door.
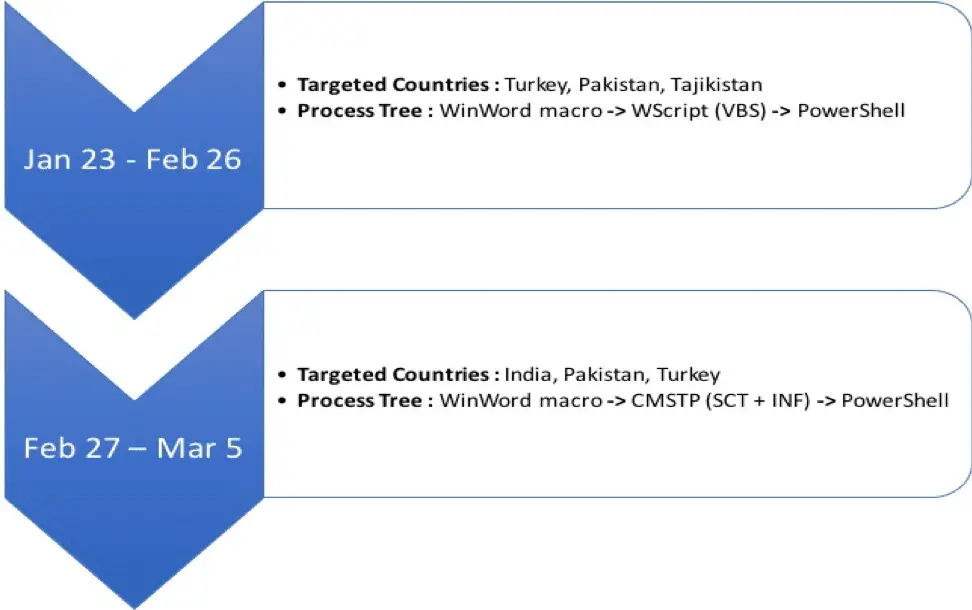
In this malicious activity, TEMP. Zagros’s tactics, techniques, procedures, and goals have undergone major changes within a month. The above picture shows the brief timeline of the fishing activity.
TEMP.Zagros usually uses phishing attack emails and malicious macro files that have geopolitical themes, such as documents claiming to come from the Pakistani National Assembly or Banking Technology Development and Research Institute. While analyzing these files, FireEye observed that TEMP.Zagros reused AppLocker bypass and horizontal movement techniques for indirect code execution. In addition, the researchers found Chinese strings in the malicious code used by TEMP.Zagros. These strings were left as false flags, making it more difficult to locate the query.
FireEye Analysis Report:
Iranian Threat Group Updates Tactics, Techniques and Procedures in Spear Phishing Campaign
Source: SecurityAffairs