Although Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a disgusting feature for audio and video enthusiasts, it does not mean that it cannot play an active role in other aspects. According to foreign media reports, Google decided to introduce some form of DRM for the Play Store application to improve the real security of Android application installation package (APK) files. It reports that this mechanism is very similar to the driver signature on the Windows platform.
The purpose of adding a DRM signature to an app is simple—to improve the Android user’s security experience. Google is not referring to the new system as DRM, saying instead that it is adding a “small amount of security metadata on top of APKs to verify that the APK was distributed by Google Play.”

Image: Android
Google said one of the reasons for the introduction of this mechanism is to help developers reach out to a broader user community, especially those regional markets where p2p application sharing has become commonplace due to limited connectivity and expensive data packages.
“We’ll be able to determine app authenticity while a device is offline, add those shared apps to a user’s Play Library, and manage app updates when the device comes back online. This will give people more confidence when using Play-approved peer-to-peer sharing apps.
This also benefits you as a developer as it provides a Play-authorized offline distribution channel and, since the peer-to-peer shared app is added to your user’s Play library, your app will now be eligible for app updates from Play.”
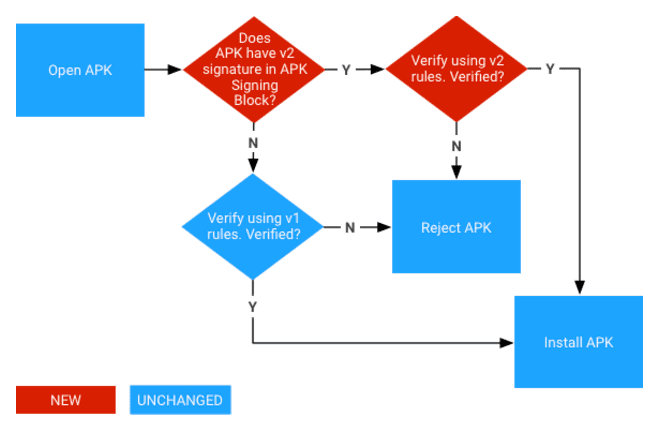
“No action is needed by developers or by those who use your app or game. We’re adjusting Google Play’s maximum APK size to take into account the small metadata addition, which is inserted into the APK Signing Block. In addition to improving the integrity of Google Play’s mobile app ecosystem, this metadata will also present new distribution opportunities for developers and help more people keep their apps up to date.”
Source: BetaNews