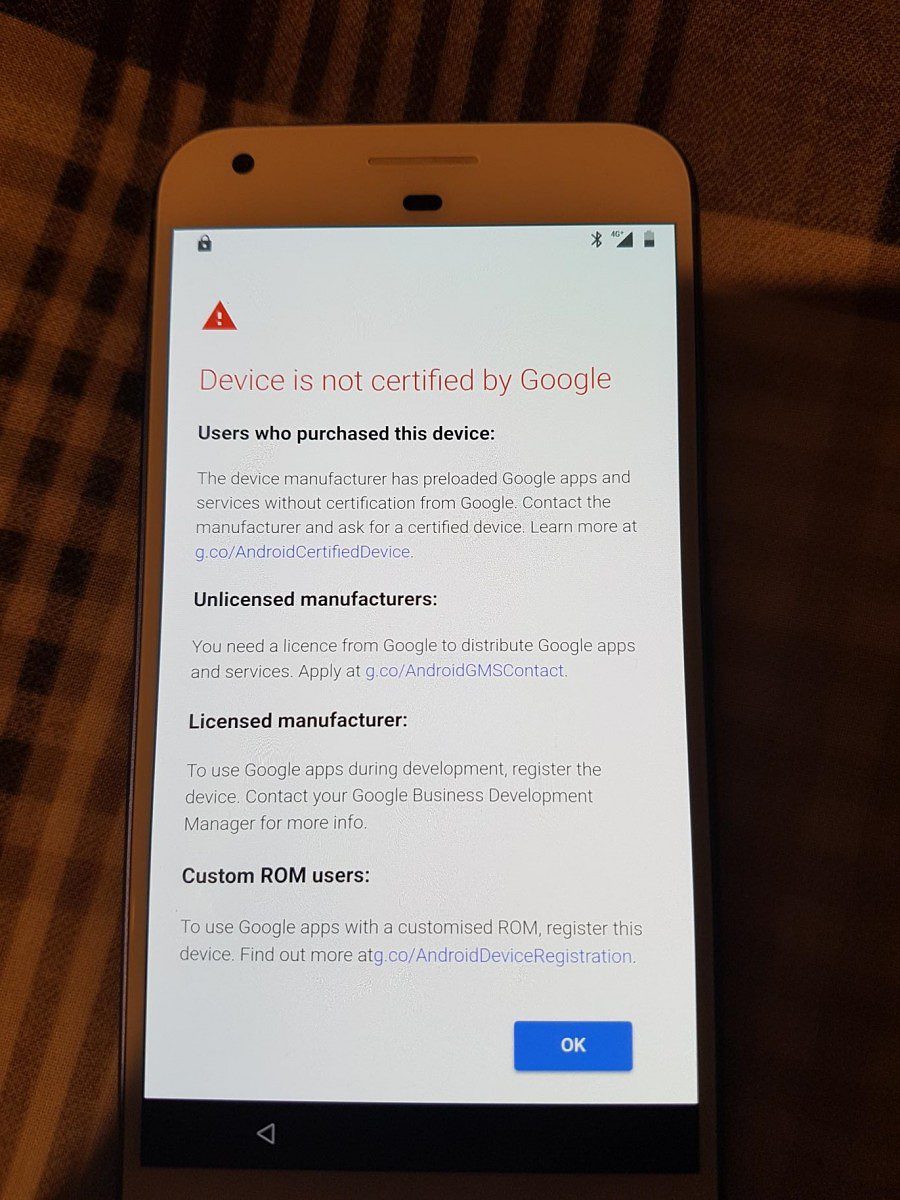
Android is an open source operating system, so there are countless various devices. If the device is certified by Google, then Google’s official Android application (eg Play Store, Maps, etc.) can be distributed on the device. However, if the device does not pass Google certification, such as Amazon Fire OS tablet and most Chinese manufacturers’ mobile phones, then they will not be allowed to install these applications.

Some users often install Google applications in various ways when needed, and some manufacturers install Google applications without permission. But now Google has begun to take corresponding measures. When a user tries to run a Google application, Google now checks the generation date of the Android system image. If it is an unauthenticated device and it is running a version of the Android operating system that was compiled after March 16, 2018, the Google app will not be available.
Fortunately, users who have installed custom ROMs can use Android IDs to register their own devices to allow Google applications to run on the device. Each user has 100 device limits, which may not be enough for ROM testers, but it is sufficient for most people.
It is not yet clear how this will affect users who want to run the Play Store on their Amazon Fire OS tablet or any other “uncertified” device that runs the manufacturer’s system, and what is “custom” ROM”? We are expecting the response from Google about this.
Source, Image: xda-developers