Google has just released an update for its Chrome web browser, addressing two high-severity vulnerabilities that malicious actors could exploit. Users are strongly urged to update their browsers immediately to version 130.0.6723.116/.117 for Windows and Mac, and 130.0.6723.116 for Linux.
The vulnerabilities, tracked as CVE-2024-10826 and CVE-2024-10827, are both classified as “use-after-free” flaws. These types of vulnerabilities occur when a program continues to use a memory location after it has been freed, potentially allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code or crash the browser.
- CVE-2024-10826 resides in the “Family Experiences” component of Chrome. While details are scarce to prevent further exploitation, this feature relates to parental controls and account sharing, suggesting a potential risk for families who utilize these functions.
- CVE-2024-10827 exists within the “Serial” component, which likely deals with communication ports and data transfer. This vulnerability could allow attackers to intercept or manipulate data transmitted through the browser.
Both vulnerabilities were reported by anonymous researchers. Google has acknowledged their contributions and swiftly patched these critical flaws.
What should you do?
Updating your Chrome browser is crucial to protect yourself from potential attacks. Here’s how:
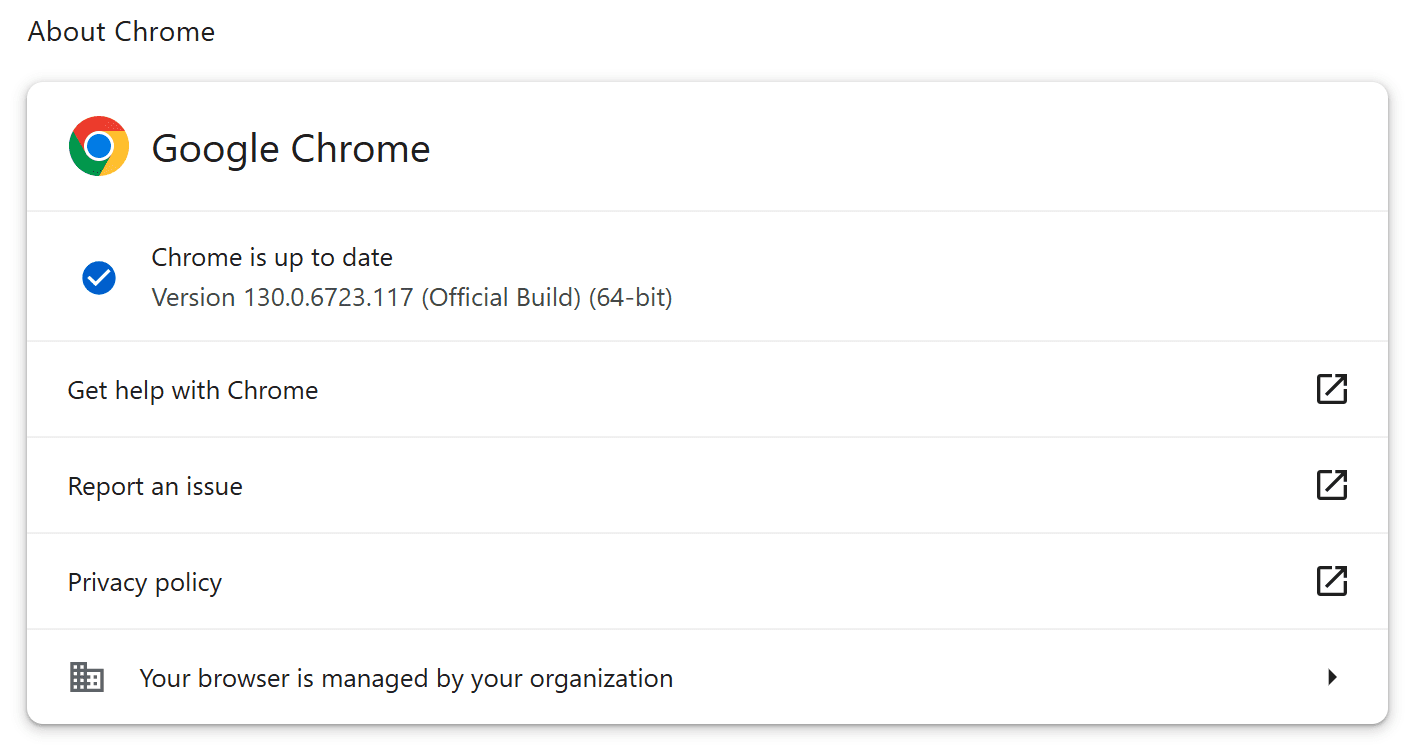
- Check your Chrome version: Go to
chrome://settings/helpin your address bar. - Update Chrome: If you’re not on the latest version (130.0.6723.116/.117), Chrome will automatically download and install the update.
- Relaunch your browser: To ensure the update takes effect, restart Chrome.