Image: Malwarebytes
A sophisticated cyberattack campaign is underway, cleverly impersonating the popular PuTTY software to target unsuspecting system administrators. Malwarebytes has uncovered a scheme where threat actors exploit malvertising and a custom malware loader built in Go to deliver the notorious Rhadamanthys information stealer.
The Scheme
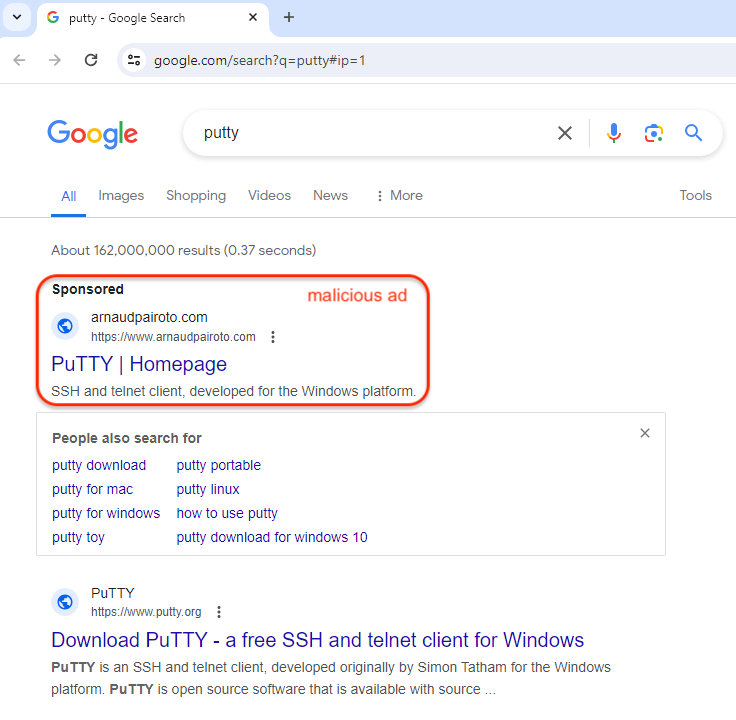
- Malicious Ads: Attackers purchase misleading Google ads designed to appear at the top of search results for “PuTTY”. These ads lead to a meticulously crafted fake PuTTY website.
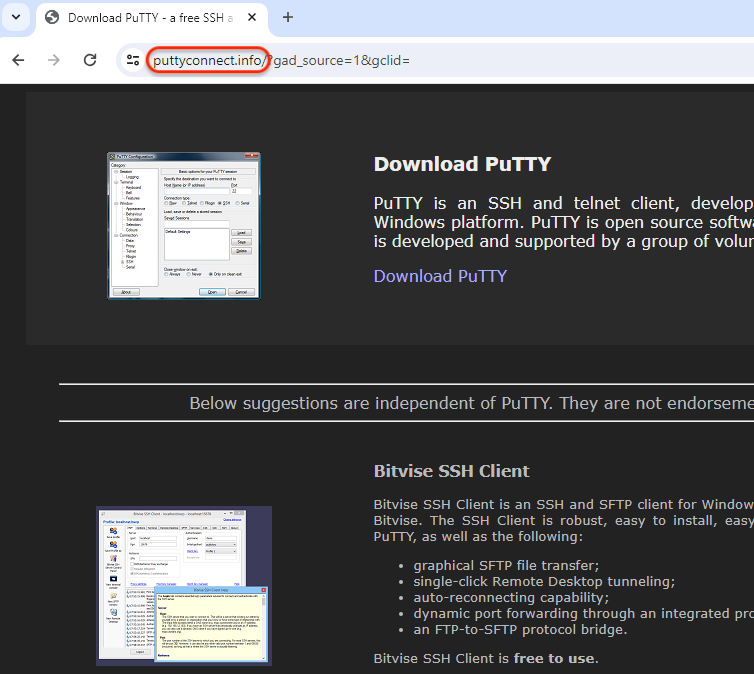
- Selective Targeting: Clicking on the deceptive ad leads users to an attacker-controlled domain designed to bypass security checks by presenting a seemingly legitimate page to non-targeted visitors, such as crawlers or sandboxes. Real victims, especially those from the US, find themselves redirected to a counterfeit site meticulously crafted to mimic putty.org, save for a critical difference—the download link.
- Go-Based Loader: The downloaded “PuTTY.exe” is not the real tool, but a malware dropper written in Go. It carefully checks the victim’s IP address to ensure it matches the profile of someone who likely clicked the malicious ad.
- The Rhadamanthys Payload: If the IP check passes, the loader uses the SSH protocol to discreetly download the Rhadamanthys stealer from a compromised server. This potent malware is then executed to begin data theft.
Introducing the Malicious Go Loader: Dropper 1.3

The payload, disguised as PuTTY.exe, is a malware dropper crafted in the Go programming language (version 1.21.0), possibly dubbed “Dropper 1.3” by its author. The execution of this dropper involves an IP check to ensure the victim’s public IP address matches those targeted through the malicious ad.
Successful verification prompts the retrieval of a follow-up payload from a separate server, employing the SSHv2 protocol for a more covert malware download process. The payload in question is Rhadamanthys, a notorious stealer executed by the dropper, designed to siphon off valuable information.
Why It Matters
- Trusted Tools Subverted: This attack highlights the dangers of supply chain attacks where attackers compromise the very tools IT professionals use daily.
- Sophisticated Techniques: The use of Go-based loaders and covert SSH communication demonstrates the lengths attackers will go to avoid detection.
- Info Stealer Threat: Rhadamanthys has a history of stealing sensitive data, including passwords, browser information, and cryptocurrency wallets.