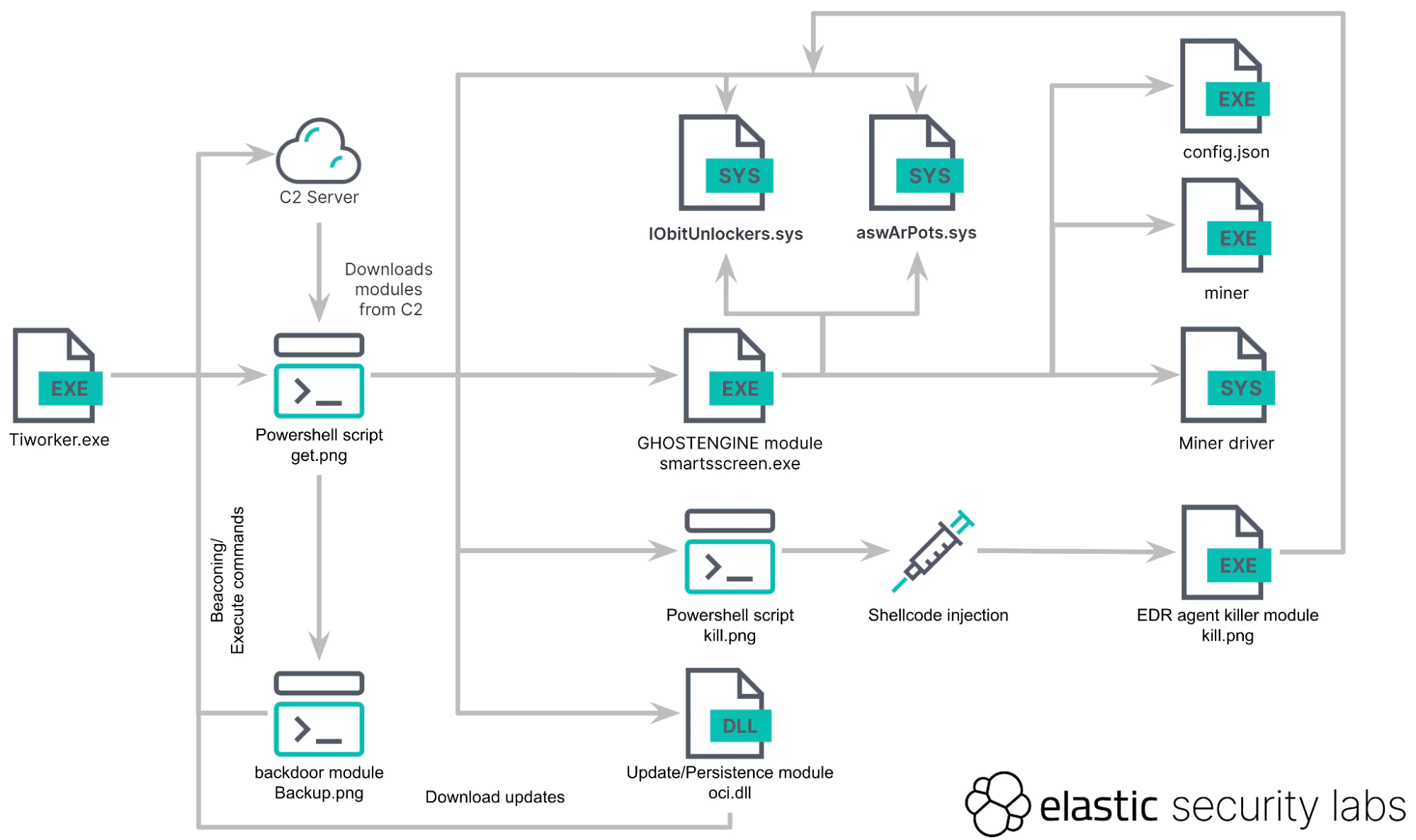
Elastic Security Labs has shed light on a complex and insidious crypto-mining operation codenamed REF4578, with its core payload, GHOSTENGINE, exhibiting an alarming degree of sophistication in evading detection and maximizing illicit profits. The malware, partially identified as HIDDENSHOVEL by Antiy researchers, demonstrates a multi-pronged attack strategy designed to bypass security measures and ensure persistence.

The intrusion began on May 6, 2024, with the execution of a PE file named Tiworker.exe, masquerading as the legitimate Windows TiWorker.exe file. This initiated the REF4578 intrusion, which involved deploying a known vulnerable driver. The Tiworker.exe file downloads and executes a PowerShell script that orchestrates the entire execution flow.
This binary executes a hardcoded PowerShell command to retrieve an obfuscated script, get.png, which downloads additional tools, modules, and configurations from the attacker’s command and control (C2) server.
GHOSTENGINE plays a pivotal role in retrieving and executing modules on the compromised machine. Primarily using HTTP, it downloads files from a configured domain, with a backup IP available. Additionally, FTP is used as a secondary protocol with embedded credentials. This script also performs various clean-up tasks, such as removing remnants of prior infections and clearing system logs.
To establish persistence, get.png creates multiple scheduled tasks as SYSTEM. These tasks include OneDriveCloudSync, DefaultBrowserUpdate, and OneDriveCloudBackup, ensuring the continuous execution of malicious services and scripts. The script also includes mechanisms to terminate redundant processes, download updated binaries, and manage DNS resolution.
Beyond evasion, GHOSTENGINE employs a suite of specialized modules to further its agenda:
- EDR Agent Controller and Miner Module (smartsscreen.exe): This module terminates active EDR agent processes using a combination of vulnerable drivers from Avast and IObit. It then downloads and installs the XMRIG client mining program, starting the mining process.
- Update/Persistence Module (oci.dll): This service DLL is loaded by msdtc to maintain system persistence and download updates from the C2 servers.
- EDR Agent Termination Module (kill.png): This PowerShell script injects shellcode into the current process, decrypting and loading a PE file into memory. It replicates techniques used in smartsscreen.exe to continuously scan for and terminate new EDR processes.
- PowerShell Backdoor Module (backup.png): This backdoor allows remote command execution on the system, sending encoded commands and receiving results.
The ultimate objective of REF4578 is to deploy and relentlessly operate the XMRig crypto miner, a legitimate mining software repurposed for illicit gains. By extracting the miner’s configuration file, researchers were able to pinpoint the Monero Payment ID associated with the operation, enabling them to track the flow of stolen cryptocurrency on the blockchain. Although the identified payment ID might not reflect an astronomical sum, it serves as a testament to the campaign’s success and hints at the potential for substantial cumulative profits across a wider network of victims.
The emergence of GHOSTENGINE underscores the escalating sophistication of crypto-mining malware and the constant need for heightened vigilance.