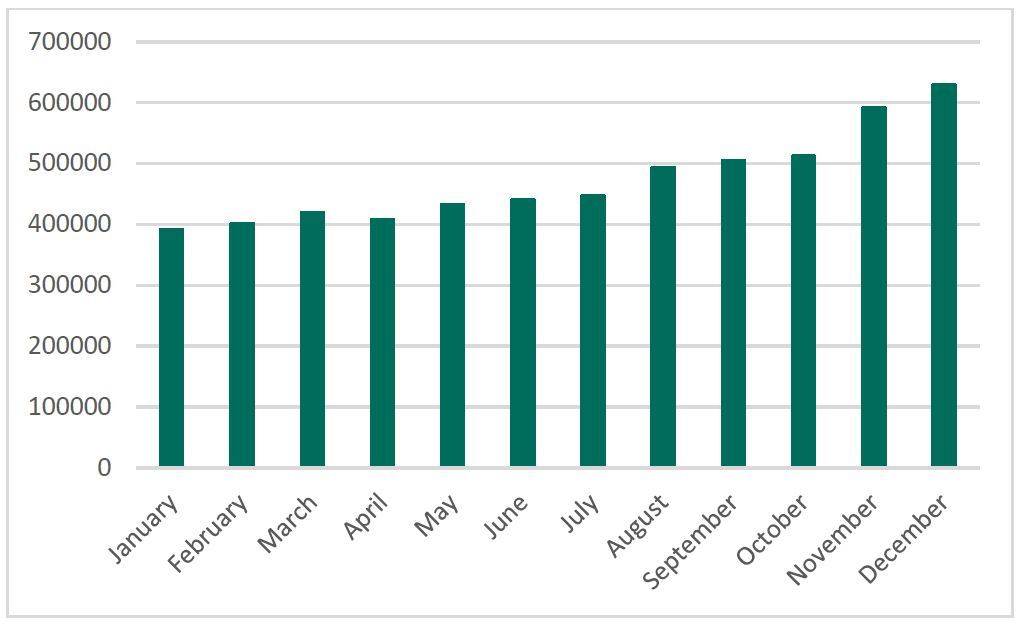
According to Kaspersky Lab’s Cyber Threat Research and securelist, cybercriminals use cryptocurrencies that exploit malicious scripts in their browsers to exploit the victim’s computer hardware resources and they use another technique to mine cryptocurrencies.
Image: Kaspersky Lab
In short, hackers use legitimate applications as containers for malicious code to pass the victim’s computer system’s defenses. Maliciously installed programs use the legitimate Windows utility msiexec to download and execute malicious modules from a remote server. In the next step, it installs a malicious scheduler task, which injects a mining program into the system, disguising itself as a legitimate system process and using process-hole techniques. If the victim tries to terminate this process, the Windows system will restart.
According to Kaspersky Lab data, “by the end of 2017, 2.7 million users had been attacked by malicious miners – this is almost 1.5 times higher than in 2016 (1.87 mln).” They have been falling victims as a result of adware, cracked games and pirated software used by cybercriminals to secretly infect their PCs. Another approach used was web mining through a special code located in an infected web page. The most widely used web miner was CoinHive, discovered on many popular websites.
Kaspersky Lab recommends users adhere to the following:
- Don’t click on unknown websites, or suspicious banners and ads
- Do not download and open unknown files from untrusted sources
- Use security solutions on endpoints and servers
Source: securelist