kit_hunter: basic phishing kit scanner for dedicated and semi-dedicated hosting
Kit Hunter: A basic phishing kit detection tool
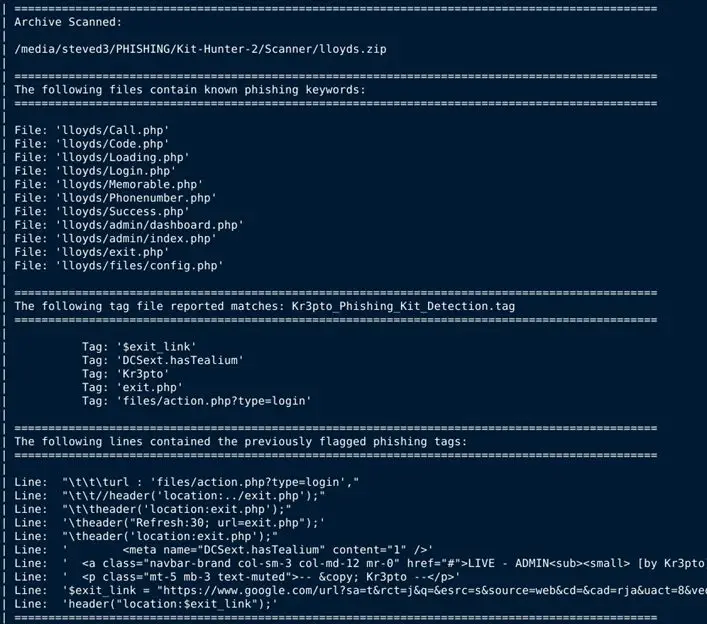
Kit Hunter is a personal project to learn Python and a basic scanning tool that will search directories and locate phishing kits based on established markers. As detection happens, a report is generated for administrators.
By default, the script will generate a report that shows the files that were detected as potentially problematic, list the markers that indicated them as problematic (a.k.a. tags), and then show the exact line of code where the detection happened.

Install
git clone https://github.com/SteveD3/kit_hunter.git
Once downloaded, you will need to place the tag folders somewhere on the system, and then edit kit_hunter_2.py and make sure the paths are set.
You’ll find these paths at the top of the script, just below the acknowledgments. The sections you’ll need to edit are below. I’ve included what is in my configuration as an example.
kh_shell_scan = ‘/lab/steved3/PHISHING/Kit-Hunter-2/tag_files/shell_scan/’
kh_quick_scan = ‘/lab/steved3/PHISHING/Kit-Hunter-2/tag_files/quick_scan/’
kh_full_scan = ‘/lab/steved3/PHISHING/Kit-Hunter-2/tag_files/’
Use
Help
To get quick help: python3 kit_hunter_2.py -h
Default scan
To launch a full scan using the default settings: python3 kit_hunter_2.py
Quick scan
To launch a quick scan, using minimal detection rules: python3 kit_hunter_2.py -q
Custom scan
To launch a custom scan: python3 kit_hunter_2.py -c
Note: When using the -c switch, you must place a tag file in the same location as Kit Hunter. You can name this file whatever you want, but the extension must be .tag. Please remember that the formatting is important. There should only be one item per line, and no whitespaces. You can look at the other tag files if you need examples.
Directory selected scanning
You can run kit_hunter_2.py from any location using the -d switch to select a directory to scan:
python3 kit_hunter_2.py -d /path/to/directory
However, it is easier if you place kit_hunter_2.py in the directory above your webroot (e.g. /www/ or /public_html/) and call the script from there.
The final report will be generated in the directory being scanned.
In my usage, I call Kit Hunter from my /kit/download/ directory where new phishing kits are saved. My reports are then generated and saved to that folder. However, if I call Kit Hunter and scan my /PHISHING/Archive/ folder using the -d switch, then the report will save to /PHISHING/Archive/.
Shell detection
This latest release of Kit Hunter comes with shell detection. Shell scripts are often packaged with phishing kits or used to deploy phishing kits on webservers. Kit Hunter will scan for some common shell script elements. The process works exactly the same way as regular scanning, only the shell detections are called with the -s switch. This is a standalone scan, so you can’t run it with other types. You can however leverage the -m and -l flags with shell scanning. See the script’s help section for more details.
Once the scanning is complete, output from the script will point you to the location of the saved scan report.
Copyright (C) 2021 SteveD3
Source: https://github.com/SteveD3/





