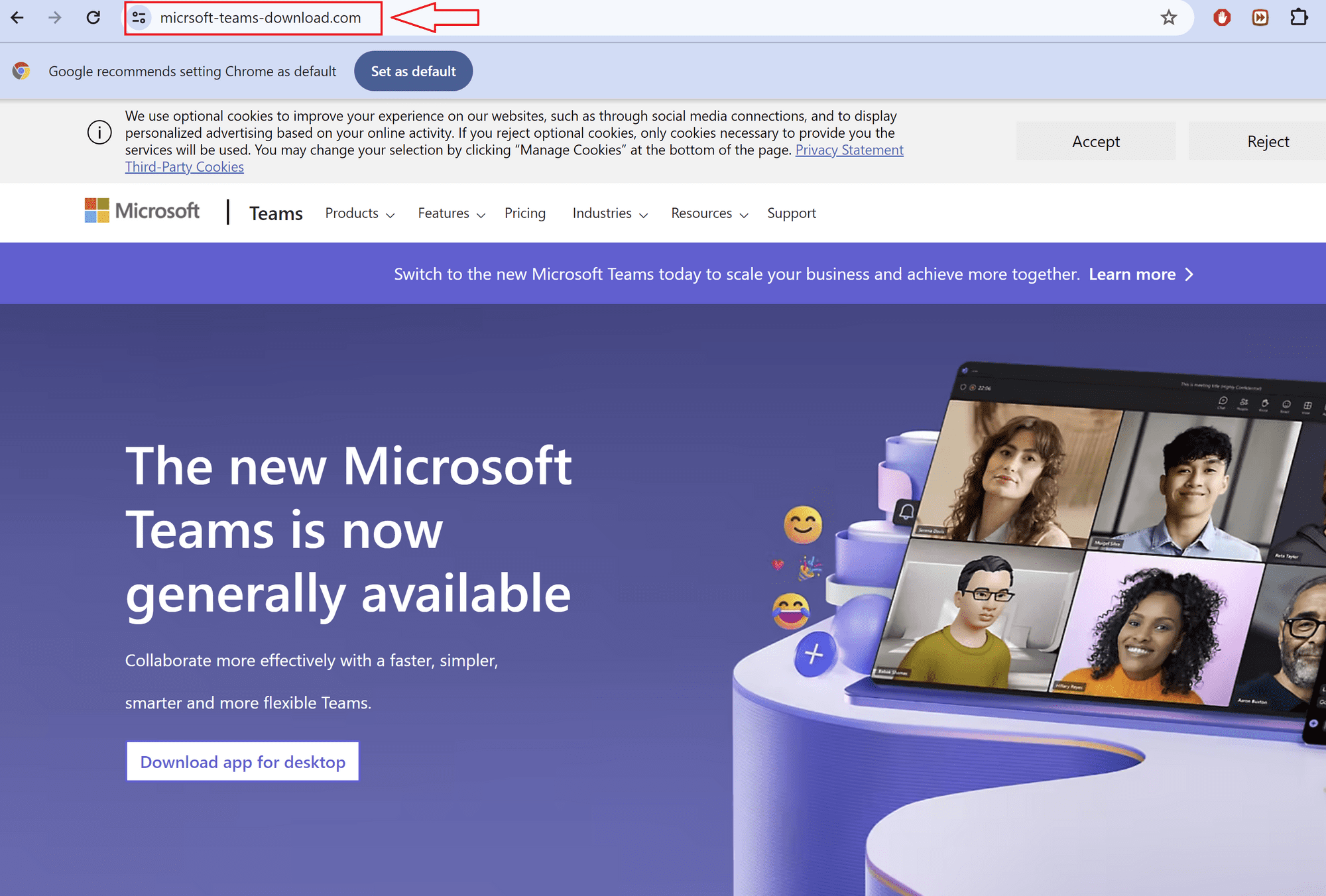
Fake Microsoft Teams Website
Rapid7, a cybersecurity firm, has uncovered a recent malvertising campaign using fake software installers to distribute the Oyster backdoor, also known as Broomstick. This sophisticated malware targets users searching for popular downloads like Google Chrome and Microsoft Teams, luring them to malicious websites that mimic legitimate platforms.
In three separate incidents, Rapid7 observed users downloading supposed Microsoft Teams installers from typo-squatted websites. These websites, designed to resemble legitimate Microsoft Teams sites, misled users into downloading malicious software. For instance, users navigating to URLs like hxxps://micrsoft-teams-download[.]com downloaded a binary named MSTeamsSetup_c_l_.exe. This binary was signed with an Authenticode certificate issued to “Shanxi Yanghua HOME Furnishings Ltd.”
Searching VirusTotal revealed other installers signed by the same entity, each impersonating legitimate software. Another related incident involved a binary named TMSSetup.exe, signed by “Shanghai Ruikang Decoration Co., Ltd.” This certificate was revoked by May 30, 2024, but not before causing significant harm.
Oyster, also known as Broomstick or CleanUpLoader, is a malware family first identified in September 2023 by IBM researchers. It is typically delivered via a loader called Oyster Installer, which masquerades as a legitimate software installer. This installer drops the backdoor component, Oyster Main, which gathers information about the compromised host, communicates with hard-coded command-and-control (C2) addresses, and allows remote code execution.
In recent incidents, Rapid7 has observed the direct deployment of Oyster Main without the intermediary Oyster Installer.
This campaign underscores the growing threat of malvertising, where cybercriminals abuse legitimate advertising channels to disseminate malware. The sophisticated tactics employed by Oyster, such as typo-squatting and code obfuscation, highlight the need for heightened awareness and robust cybersecurity measures.
Rapid7 has taken proactive steps to combat this threat by releasing a Python script on GitHub to help decode obfuscated Oyster configurations. To protect themselves, users are strongly advised to exercise caution when downloading software, always verify the legitimacy of websites, and keep their security software up-to-date.