Mandiant Azure AD Investigator: PowerShell module for detecting artifacts
Mandiant Azure AD Investigator
This repository contains a PowerShell module for detecting artifacts that may be indicators of UNC2452 and other threat actor activity. Some indicators are “high-fidelity” indicators of compromise, while other artifacts are so-called “dual-use” artifacts. Dual-use artifacts may be related to threat actor activity, but also may be related to legitimate functionality. Analysis and verification will be required for these. For a detailed description of the techniques used by UNC2452 see our blog.

This tool is read-only. It does not make any changes to the Microsoft 365 environment.
In summary, this module will:
- Do the best effort job at identifying indicators of compromise that will require further verification and analysis
It will not:
- Identify a compromise 100% of the time, or
- Tell you if an artifact is legitimate admin activity or threat actor activity.
Features
Federated Domains (Invoke-MandiantAuditAzureADDomains)
This module uses MS Online PowerShell to look for and audit federated domains in Azure AD. All federated domains will be output to the file federated domains.csv.
- Signing Certificate Unusual Validity Period – Alerts on a federated domain where the signing certificates have a validity period of > 1 year. AD FS managed certificates are valid for only one year. Validity periods that are longer than one year could be an indication that a threat actor has tampered with the domain federation settings. They may also be indicative of the use of a legitimate custom token-signing certificate. Have your administrators verify if this is the case.
- Signing Certificate Mismatch – Alerts on federated domains where the issuer or subject of the signing certificates do not match. In most cases, the token-signing certificates will always be from the same issuer and have the same subject. If there is a mismatch, then it could be an indication that a threat actor has tampered with the domain federation settings. Have your administrators verify if the subject and issuer names are expected and if not consider performing a forensic investigation to determine how the changes were made and to identify any other evidence of compromise.
- Azure AD Backdoor (any.sts) – Alerts on federated domains configured with
any.stsas the Issuer URI. This is indicative of the usage of the Azure AD Backdoor tool. Consider performing a forensic investigation to determine how the changes were made and to identify any other evidence of compromise. - Federated Domains – Lists all federated domains and the token issuer URI. Verify that the domain should be federated and that the issuer URI is expected.
- Unverified Domains – Lists all unverified domains in Azure AD. Unverified domains should not be kept in Azure AD for long in an unverified state. Consider removing them.
Service Principals (Invoke-MandiantAuditAzureADServicePrincipals)
This module uses Azure AD PowerShell to look for and audit Service Principals in Azure AD.
- First-party Service Principals with added credentials – First-party (Microsoft published) Service Principals should not have added credentials except in rare circumstances. Environments that are or were previously in a hybrid-mode may have credentials added to Exchange Online, Skype for Business, and AAD Password Protection Proxy Service Principals. Verify that the Service Principal credential is part of a legitimate use case. Consider performing a forensic investigation if the credential is not legitimate.
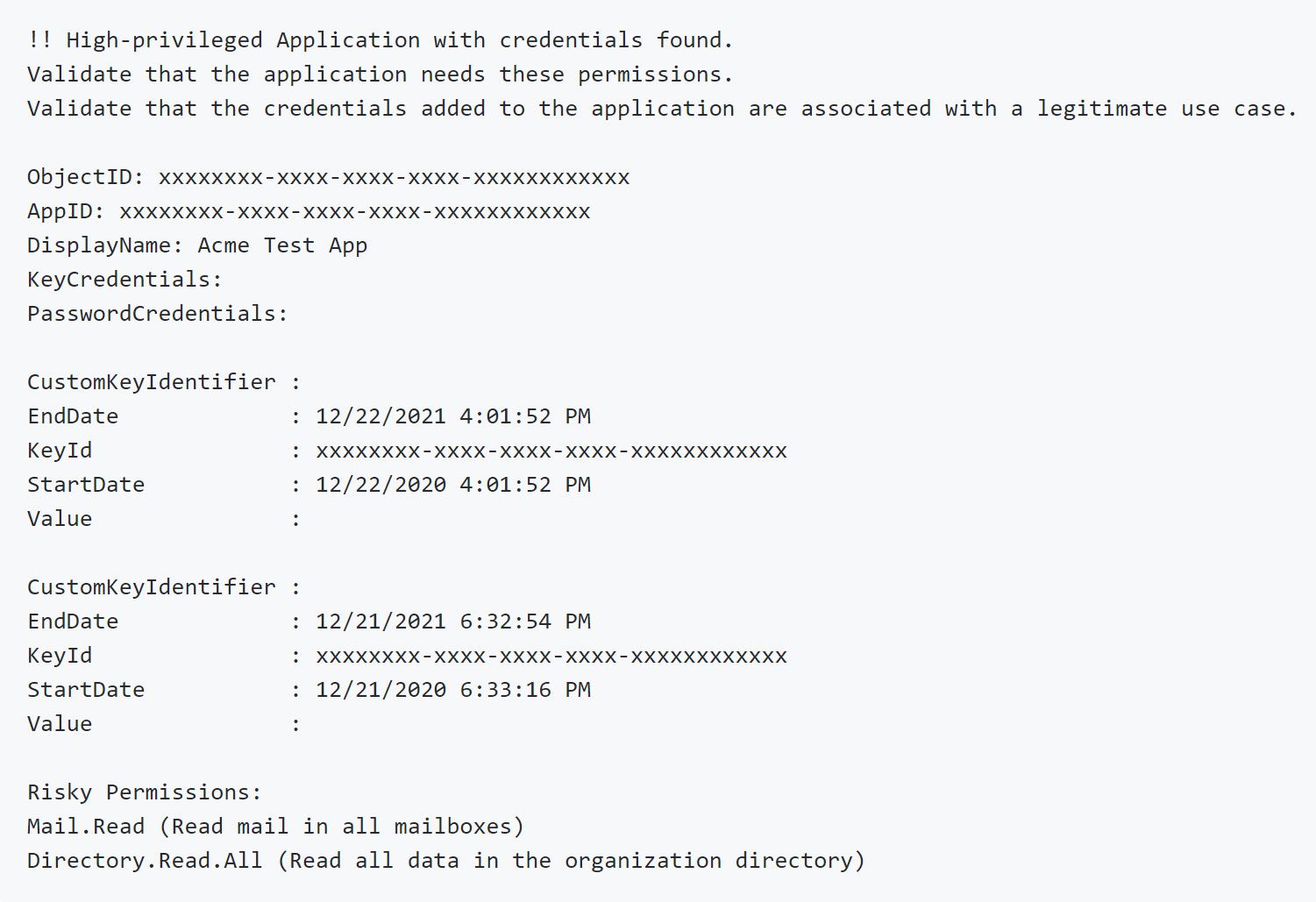
- Service Principals with high-level privileges and added credentials – Identifies Service Principals that have high-risk API permissions assigned and added credentials. While the Service Principal and added permissions are likely legitimate, the added credentials may not be. Verify that the Service Principal credentials are part of a legitimate use case. Verify that the Service Principal needs the listed permissions.
Applications (Invoke-MandiantAuditAzureADApplications)
This module uses Azure AD PowerShell to look for and audit Applications in Azure AD.
- Applications with high-level privileges and added credentials – Alerts on Applications that have high-risk API permissions and added credentials. While the Applications and added permissions are likely legitimate, the added credentials may not be. Verify that the Application credentials are part of a legitimate use case. Verify that the Applications need the listed permissions.
Cloud Solution Provider Program (Invoke-MandiantGetCSPInformation)
This module checks to see if the tenant is managed by a CSP or partner and if delegated administration is enabled. Delegated administration allows the CSP to access a customer tenant with the same privileges as a Global Administrator. Although the CSP program enforces strong security controls on the partner’s tenant, a threat actor that compromises the CSP may be able to access customer environments. Organizations should verify if their partner needs delegated admin privileges and remove it if not. If the partner must maintain delegated admin access, consider implementing Conditional Access Policies to restrict their access.
Organizations can check and manage partner relationships by navigating to the Admin Center and navigating to Settings -> Partner Relationships on the left-hand menu bar.
Mailbox Folder Permissions (Get-MandiantMailboxFolderPermissions)
This module audits all the mailboxes in the tenant for the existance of suspicious folder permissions. Specifically, this module will examine the “Top of Information Store” and “Inbox” folders in each mailbox and check the permissions assigned to the “Default” and “Anonymous” users. Any value other than “None” will result in the mailbox being flagged for analysis. In general the Default and Anonymous users should not have permissions on user inboxes as this will allow any user to read their contents. Some organizations may find shared mailboxes with this permission, but it is not recommended practice.
Application Impersonation (Get-MandiantApplicationImpersonationHolders)
This module outputs the list of users and groups that hold the ApplicationImpersonation role. Any user or member of a group in the output of this command can use impersonation to “act as” and access the mailbox of any other user in the tenant. Organizations should audit the output of this command to ensure that only expected users and groups are included, and where possible further restrict the scope.
Unified Audit Log (Get-MandiantUnc2452AuditLogs)
This module is a helper script to search the Unified Audit Log. Searching the Unified Audit Log has many technical caveats that can be easy to overlook. This module can help simplify the search process by implementing best practices for navigating these caveats and handling some common errors.
By default, the module will search for log entries that can record UNC2452 techniques. The log records may also capture legitimate administrator activity, and will need to be verified.
- Update Application – Records actions taken to update App Registrations.
- Set Domain Auth – Records when authentication settings for a domain are changed, including the creation of federation realm objects. These events should occur rarely in an environment and may indicate a threat actor configuring an AAD backdoor.
- Set Federation Settings – Records when the federation realm object for a domain is modified. These events should occur rarely in an environment and may indicate a threat actor preparing to execute a Golden SAML attack.
- Update Application Certificates and Secrets – Records when a secret or certificate is added to an App Registration.
- PowerShell Mailbox Logins – Records Mailbox Login operations where the client application was PowerShell.
- Update Service Principal – Records when updates are made to an existing Service Principal.
- Add Service Principal Credentials – Records when a secret or certificate is added to a Service Principal.
- Add App Role Assignment – Records when an App Role (Application Permission) is added.
- App Role Assignment for User – Records when an App Role is assigned to a user.
- PowerShell Authentication – Records when a user authenticates to Azure AD using a PowerShell client.
- New Management Role Assignments – Records when new management role assignments are created. This can be useful to identify new ApplicationImpersonation grants.
Download & Use
Copyright (C) 2021 mandiant