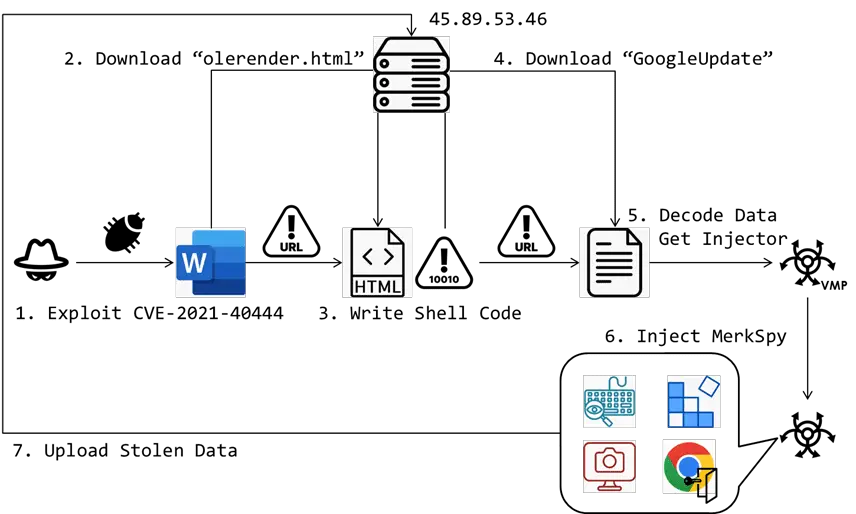
Attack flow
Cybersecurity researchers at FortiGuard Labs have uncovered a sophisticated cyberattack that leverages a known vulnerability in Microsoft Office to deliver a potent spyware payload known as MerkSpy. This insidious malware is designed to infiltrate systems, monitor user activity, and steal sensitive information, posing a significant threat to individuals and organizations alike.

The attack begins with a seemingly innocuous Microsoft Word document, often disguised as a job posting or other enticing content. Upon opening the document, the vulnerability (CVE-2021-40444) is triggered, allowing the attackers to execute malicious code and download additional payloads.
Following the successful exploitation, the malicious document triggers the downloaded payload, “olerender.html,” from a remote server. This HTML file is meticulously crafted, with benign script filling the initial part to disguise its true purpose. The latter part of the file hides the shellcode and injection process, which advances the attack upon execution on the victim’s machine.
The “olerender.html” file first checks the system’s OS version. If it detects an X64 architecture, it extracts the embedded “sc_x64” shellcode. Upon determining the OS version and extracting the appropriate shellcode, “olerender.html” locates and retrieves the Windows APIs “VirtualProtect” and “CreateThread.” These functions are vital for the subsequent steps: “VirtualProtect” modifies memory permissions, allowing the decoded shellcode to be securely written into memory, and “CreateThread” executes the injected shellcode, setting the stage for the next payload download from the attacker’s server.
MerkSpy, the spyware at the heart of this attack, is a formidable tool in the hands of cybercriminals. It can silently record keystrokes, capture screenshots, and even steal login credentials from popular web browsers like Chrome. This stolen information is then transmitted back to the attackers’ servers, potentially compromising personal and financial data.
“This shellcode decodes the downloaded content to execute an injector responsible for loading the MerkSpy spyware into memory and integrating it with active system processes,” said Cara Lin, a senior researcher at FortiGuard Labs. “MerkSpy is capable of sophisticated surveillance activities, including keystroke logging, screenshot capture, and harvesting Chrome browser login data.“
The attack has been observed targeting users in North America and India, highlighting the global reach of this threat. FortiGuard Labs is urging individuals and organizations to remain vigilant and take proactive measures to protect themselves. This includes keeping software up-to-date, exercising caution when opening attachments from unknown sources, and deploying robust security solutions.