metabadger v0.1.11 releases: Prevent SSRF attacks on AWS EC2
Metabadger
Prevent SSRF attacks on AWS EC2 via automated upgrades to the more secure Instance Metadata Service v2 (IMDSv2).

Metabadger
Purpose and functionality
- Diagnose and evaluate your current usage of the AWS Instance Metadata Service along with understanding how the service works
- Prepare you to upgrade to v2 of the Instance Metadata service to safeguard against v1 attack vectors
- Give you the ability to specifically update your instances to only use IMDSv2
- Give you the ability to disable the Instance Metadata service where you do not need it as a way to reduce the attack surface
What is the AWS Instance Metadata Service?
- The AWS metadata service essentially gives you access to all the things within an instance, including the instance role credential & session token
- Known SSRF vulnerabilities that exploit and use this attack as a pivot into your environment
- The famous attacks you have heard about, some of which involved this method of gaining access via a vulnerable web app with access to the instance metadata service
- An attacker could take said credentials from metadata service and use them outside of that particular instance
IMDSv2 and why it should be used
- Ensuring that instances are using V2 of the metadata service at all times by making it a requirement within it’s configuration
- Enabling session tokens with a PUT request with a mandatory request header to the AWS metadata API, IMDSv1 does not check for this making it easier for attackers to exploit the service
- X-Forwarded-For header is not allowed in IMDSv2 ensuring that no proxy-based traffic is allowed to communicate with the metadata service
Problem Statement
Engineering teams may have a vast variety of compute infrastructure in AWS that they need to protect from certain vulnerabilities that leverage the metadata service. The metadata service is required to run on instances if any IAM is used or if there is any user data information the instance might need when it boots. Limiting the attack surface of your instances is crucial in preventing the ability to pivot in your environment by stealing information provided by the service itself. Numerous famous attacks in the past have leveraged this particular service to exploit a role that is attached to the instance or dump sensitive data that is accessible via the metadata service. Metabadger can help to identify where and how you are using the instance metadata service while also giving you the ability to reduce any unwanted attack leverage to lower your overall risk posture while operating in EC2.
Guided Steps for Hardening
Step 1
Initially, we want to discover our overall usage of the metadata service in a particular AWS region. Metabadger will evaluate the current status of your usage in the region where your credentials point to in your /.aws/credentials file or the current role that is assumed. You may also specify the –region flag when running the discover-metadata command if you would like to change to another region than what is currently configured. Once you have a good idea of which version your instances are running and if the service is enabled or disabled, you will be able to make a much more defined action plan for hardening the service. Note that you can find a specific meaning to every metadata option that is set here.
Step 2
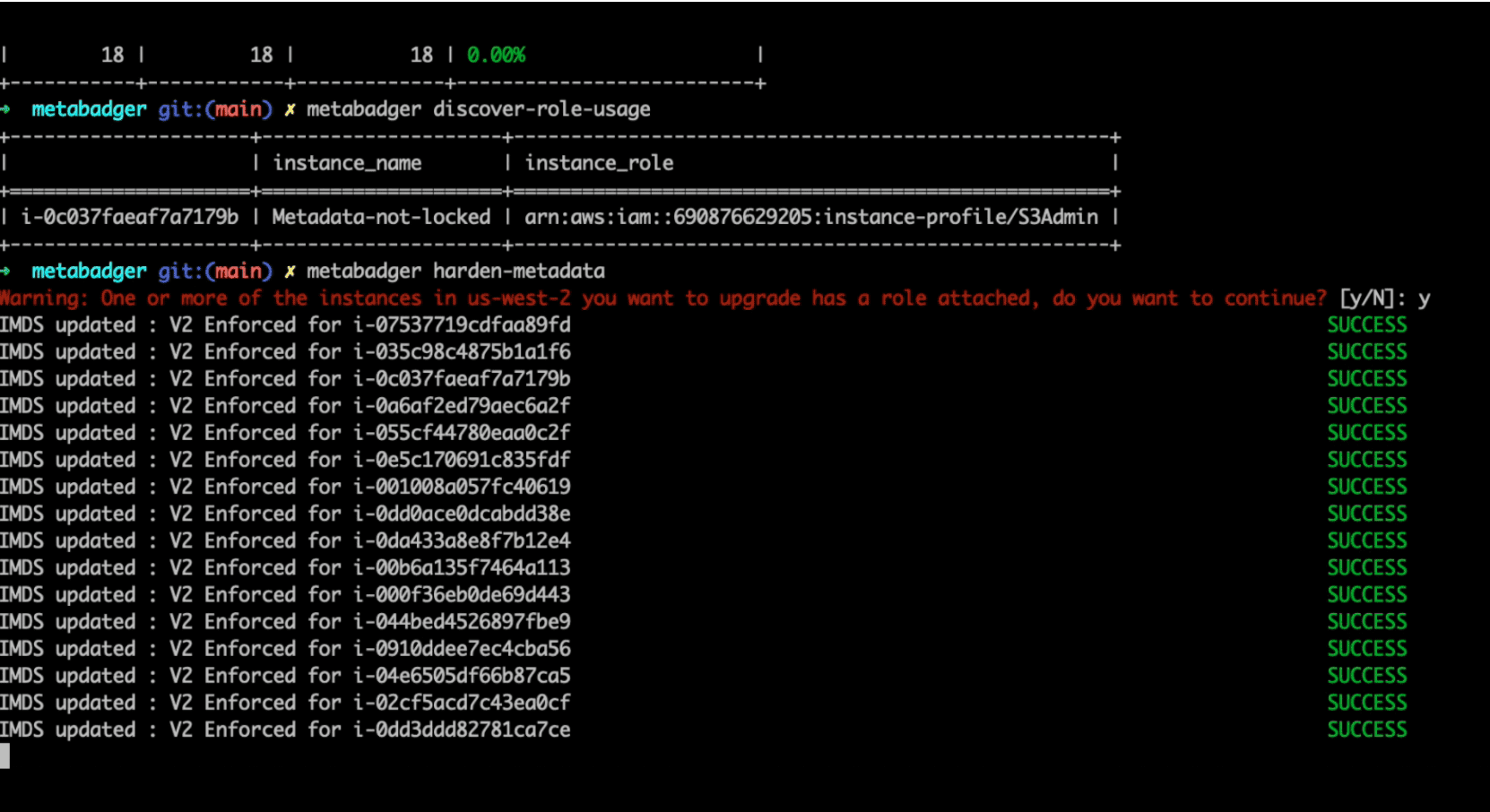
One of the areas that should be evaluated when making the switch to v2 of the service is the use of IAM roles. Metabadger lets you identify instances in a region that may already be using an IAM role. The discover-role-usage command will output a list of instances that have roles attached to them. If you have a lot of instances using roles, you should take precautions when updating the service to v2 to ensure the overall functionality of your workloads does not become impacted.
Step 3
Upon completion of doing your initial discovery and evaluation, you can now create a staged approach to hardening your compute infrastructure to use either v2 of the metadata service or disable it where it may not be used. The harden-metadata command allows you to update all instances in a particular region by default. You can also pass instance tags using the –tags flag or an input file containing a csv of instances that you would like to apply a configuration for. Once you have made the appropriate updates to v2 and disabled the service where it is not used you can re-evaluate using the items in Step 1 to confirm your environment is locked down. If you have certain instances that you don’t want to update you can exclude them via the –exclusion flag by tag or instance id.
Changelog v0.1.11
Changes
- init cloudwatch time update @ashishpatel-git (#27)
Install & Use
Copyright (c) 2021, Salesforce.com, Inc.





